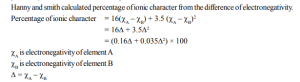What is Electronegativity?
The Electronegativity of an element is defined as the tendency of an atom to attract shared pair of electrons towards itself.
Although, electronegativity was defined by different scientists by different approaches. Some of them are as follows—
1. Pauling’s Scale of Electronegativity
He calculated the electronegativity on the basis of bond dissociation energies. According to Pauling, the dissociation energy of the A – B bond,

The difference between the calculated and theoretical value of dissociation energy value of A – A is because of the difference in electronegativity of A and B.
Here is the complete explanation of electronegativity and its trends in the periodic table- https://youtu.be/m7o4-AsDjgE
2. Mulliken scale
On the basis of an average of ionization energy and electron affinity value, Mulliken calculated the electronegativity of atoms. Mulliken scale is an absolute scale of electronegativity.

3. Allred-Rochow scale
Allred and Rochow determined the electronegativity by the electric field at the surface of an atom.

Factors affecting electronegativity
- Charge on atom: The atom which has acquired a partial or complete positive charge will hold the electrons more strongly than the neutral atom, therefore, would be more electronegative.
- Hybridization: the electronegativity of an atom is directly related with to s-character. The electronegativity of an atom increase with an increase in the s-character of its hybrid orbital.
- Effective nuclear charge: The tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself varies directly with the effective nuclear charge. While going from left to right, Zeff. increases and so do the electronegativity value, whereas on descending down the group, Zeff decreases, and hence electronegativity also decreases.
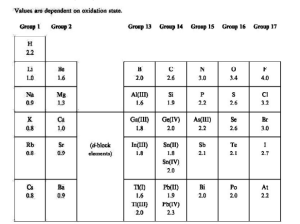
Electronegativity Values
Applications of Electronegativity
1. Nature of Bond
If the difference of electronegativities of the two elements is 1.7 or more, then an ionic bond is formed between them whereas if it is less than 1.7, then a covalent bond is formed. (HF is an exception in which the bond is covalent although the difference of electronegativity is 1.9).
2. Metallic and Nonmetallic Nature
Generally values of electronegativity of metallic elements are low, whereas electronegativity values of nonmetals are high.
3. Partial Ionic Character in Covalent bonds
Partial ionic characters are generated in covalent compounds by the difference in electronegativities.