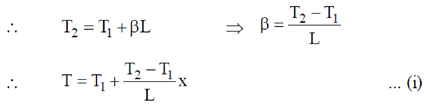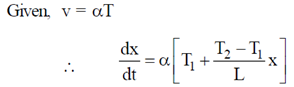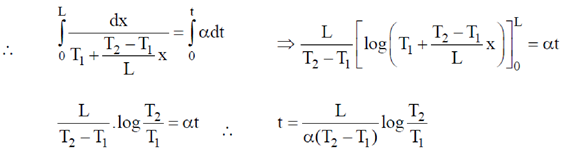IIT JAM PHYSICS 2013
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
1. The inverse of the matrix
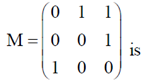
(a) M – I
(b) M2 – I
(c) I – M2
(d) I – M
Where I is the identity matrix.
Ans. (b)
Sol. Let 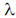 be eigen value of the matrix.
be eigen value of the matrix.
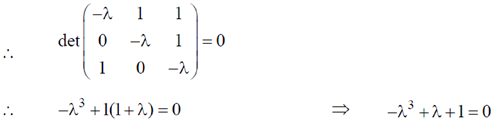
Using caley Hamilton theorem we get, –M3 + M + I = 0
If M–1 be inverse of M. Multiplying above equation by M–1 we get
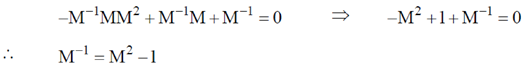
2. 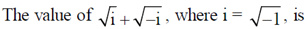
(a) 0
(b) 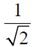
(c) 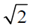
(d) 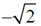
Ans. (c)
Sol. 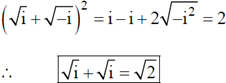
3. A particle is released at x = 1 in a force field 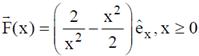 . Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
. Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
(a) 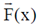 is conservative
is conservative
(b) The angular momentum of the particle about the origin is constant.
(c) The particle moves towards 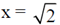
(d) The particle moves towards the origin.
Ans. (d)
Sol. 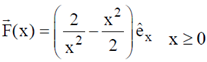
Force is directed along x-axis.
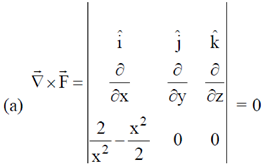
This implies that  is conservative.
is conservative.
(b) 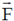 passes through origin, therefore torque due to
passes through origin, therefore torque due to 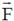 about O is zero. Therefore, angular momentum about origin is conserved.
about O is zero. Therefore, angular momentum about origin is conserved.
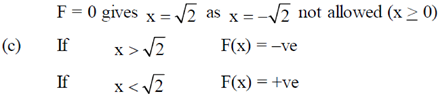
This implies that force is always directed towards 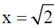 . Therefore particle moves towards
. Therefore particle moves towards 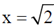 .
.
Therefore, statement of last option that particle moves towards origin is false.
4. A travelling pulse is given by f(x,t) = A exp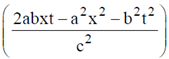 , where A, a, b and c are positive constants of appropriate dimensions. The speed of the pulse is
, where A, a, b and c are positive constants of appropriate dimensions. The speed of the pulse is
(a) 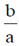
(b) 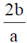
(c) 
(d) 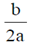
Ans. (a)
Sol. A travelling pulse is given by
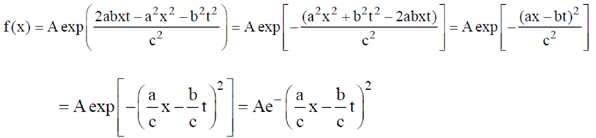
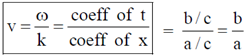
5. If the dimensions of mass, length, time and charge are M, L, T and C respectively, the dimensions of the magnetic induction field 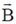 is
is
(a) ML2T–1C–1
(b) MT–1C–1
(c) L2T–1C
(d) L–1T–1C
Ans. (b)
Sol. Using 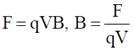
Dimension of F = [M L T–2], Dimension of velocity V = [L T–1]
Dimension of charge q = [C]
Therefore, dimension of magnetic induction field
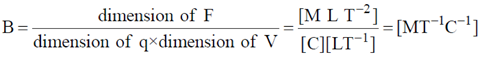
6. A blackbody at temperature T emits radiation at a peak wavelength 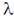 . If the temperature of the blackbody becomes 4T, the new peak wavelength is
. If the temperature of the blackbody becomes 4T, the new peak wavelength is
(a) 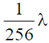
(b) 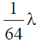
(c) 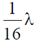
(d) 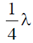
Ans. (d)
Sol. According to Wien's displacement law
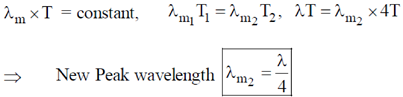
7. Let NMB, NFD denote the number of ways in which two particles can be distributed in two energy states according to Maxwell-Boltzmann, Bose-Einstein and Fermi-Dirac statistics respectively. Then: NMB : NBE : NFD is:
(a) 4 : 3 : 1
(b) 4 : 2 : 3
(c) 4 : 3 : 3
(d) 4 : 3 : 2
Ans. (a)
Sol. MB statistics applies to the system to distinguishable particles, (consider A and B) two particles can be distributed in four ways in two energy states.
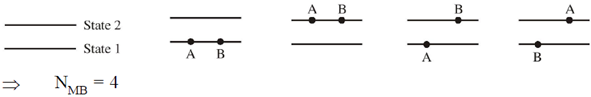
BE statistics applies to system of indistinguishable particles not obeying Pauli's exclusion principal.
Therefore according to this statistics the number of ways NBE in which two particles can be distributed in two energy states is 3. Consider two particle A and A.
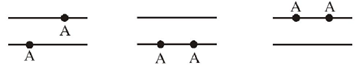
NBE = 3
and FD statistics applies to indistinguishable particles obeying Pauli's exclusion principles.
Therefore, NFD = 1

8. Electric field component of an electromagnetic radiation varies with time as E = a(cos 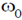 t + sin
t + sin 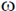 t cos
t cos 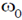 t), where a is a constant and the values of
t), where a is a constant and the values of 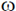 and
and 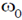 are 1 × 1015 s–1 and 5 × 1015 s–1, respectively. This radiation falls on a metal of work function 2 eV. The maximum kinetic energy in (eV) of photoelectrons is:
are 1 × 1015 s–1 and 5 × 1015 s–1, respectively. This radiation falls on a metal of work function 2 eV. The maximum kinetic energy in (eV) of photoelectrons is:
(a) 0.64
(b) 1.30
(c) 1.70
(d) 1.95
Ans. (d)
Sol. 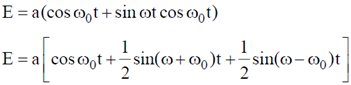
For maximum kinetic energy,
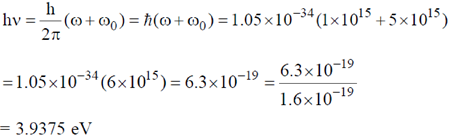
Now according to Einstein, the photoelectric effect in a given metal should obey the equation
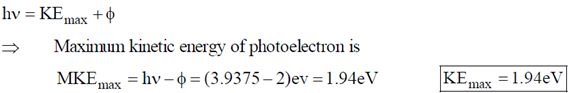
9. The fraction of volume unoccupied in the unit cell of the body centered cubic lattice is
(a) 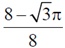
(b) 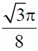
(c) 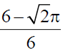
(d) 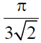
Ans. (a)
Sol. In the unit cell of the body centred cubic lattice
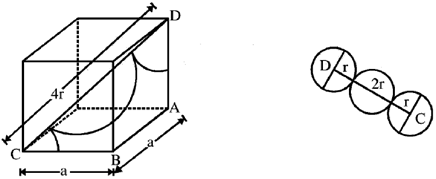
a is the lattice constant. Coordination number 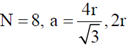 is the nearest neighbour distance number of atoms per unit cell
is the nearest neighbour distance number of atoms per unit cell
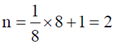
Volume of all the atoms in a unit cell 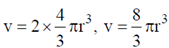
and volume of the unit cell 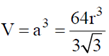
Therefore, unoccupied volume = 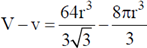
and the fraction of volume unoccupied unit cell of body centred cubic lattice
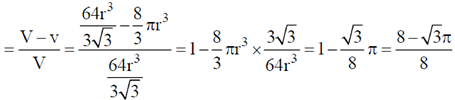
10. For an ideal op-amp circuit given below, the dc gain and the cut off frequency, respectively are
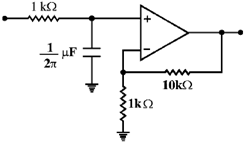
(a) 1 and 1 kHz
(b) 1 and 100 Hz
(c) 11 and 1 kHz
(d) 11 and 100 Hz
Ans. (c)
Sol. 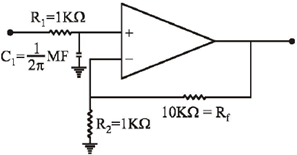
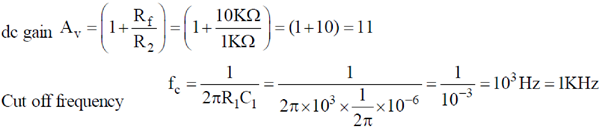
11. The solution of the differential equation dz(x, y) + xz(x, y) dx + yz (x, y)dy = 0 is _________
Sol. dz(x, y) = –z(x, y) [xdx + ydy]
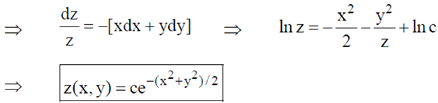
12. Given that f(1) = 1, f ´(1) = 1 and f ´´(1) = 1, the value of f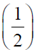 is ________
is ________
Sol. Given f(1) = 1, f´(1) = 1, f´´(1) = 1
Using Taylor Series
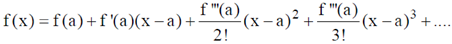
Taking a = 1 and 3 terms of it
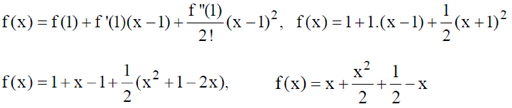
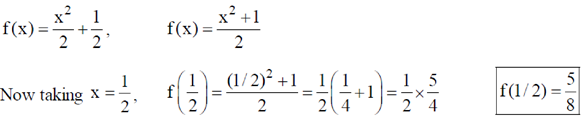
13. Two tubes A and B are connected through another tube C. A mercury manometer is connected between B and C (see figure). The diameter of B and C are 0.04 m and 0.01 m, respectively. An incompressible fluid of density 1.0 × 103 k gm–3 enters A, and leaves B with a constant speed 0.2 ms–1. If the density of mercury is 13.6 × 103 k gm–3, the height 'h' of the mercury column in the manometer is _______
(Take acceleration due to gravity g = 10 ms–2)
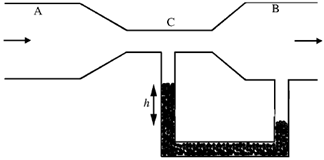
Sol. Given arrangement is actually a venturi meter
Given speed of the fluid in tube B, VB = 0.2 m/s
Diameter of Tube B = 0.04 m, It's radius rB = 0.02 m, Diameter of Tube C = 0.01m
It's radius rC = 0.005 m
According to the continuity equation for incompressible fluid
AV = constant, A = Area, V = velocity
ACVC = ABVB
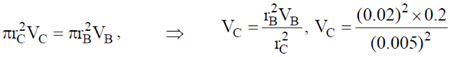
VC = 3.2 m/s
Pressure drop, indicated by the manometer
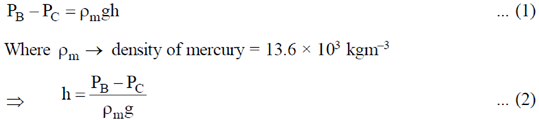
To find P1 – P2, we can use Bernoulli's principle
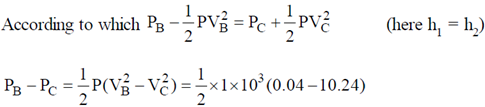
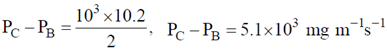
Now substituting this value in equation (2)
Magnitude of height h of the mercury column in the manometer is given by
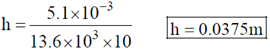
14. The path of a particle of mass 'm', moving under the influence of a central force, in plane polar coordinates is given by r = 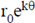 , where r0 and k are positive constants of appropriate dimensions. The angular momentum of the particle is L and its total energy is zero. The potential energy function V(r), in terms of m, L and k is __________
, where r0 and k are positive constants of appropriate dimensions. The angular momentum of the particle is L and its total energy is zero. The potential energy function V(r), in terms of m, L and k is __________
Sol. Angular momentum in central force motion (planar motion) is given as
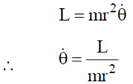
Kinetic energy of particle is given as
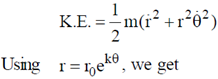
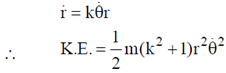
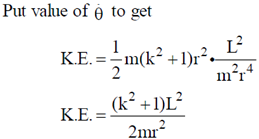
Given, T.E. = 0
P.E. + K.E. = 0
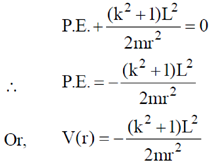
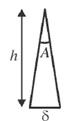
15. The dimensions of a thin convex lens of refractive index n are shown in the figure. The radius of curvature of the lens in terms of n, h and  (where,
(where, 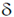 << h) is _______________
<< h) is _______________
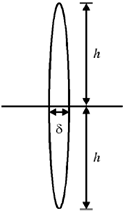
Sol. Consider a parallel beam of light incident on the lens. Let it undergoes a deviation of
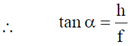
If 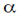 is small (which true for thin lenses)
is small (which true for thin lenses)

Upper half of the lens can be approximately considered as a prism of vertex angle
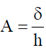
We know that a light ray passing through a prism undergoes a deviation of A(n – 1)
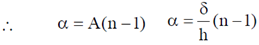
Comparing with (i), we get

For a thin biconvex lens using lens-maker formula we get,
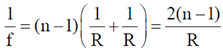
Using equation (ii), we get

16. A charged particle of mass m, charge q and constant velocity 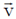 enters a uniform magnetic field
enters a uniform magnetic field 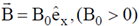 , at an angle
, at an angle 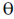 to the direction of magnetic field. Find the angle
to the direction of magnetic field. Find the angle 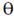 , if in one revolution of the helical motion, the particle advances along the direction of the magnetic field a distance equal to the radius of the helical path. _____________
, if in one revolution of the helical motion, the particle advances along the direction of the magnetic field a distance equal to the radius of the helical path. _____________
Sol. If a charge particle of mass m, charge q and constant velocity v enters a uniform magnetic field 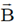 , at an angle
, at an angle 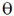 to the direction of magnetic field, its motion is along a helical path with axis of helix being the field direction. The radius of this path is given by
to the direction of magnetic field, its motion is along a helical path with axis of helix being the field direction. The radius of this path is given by 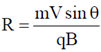 and pitch of the helix, which is actually the distance covered by e– along the field direction in one revolution.
and pitch of the helix, which is actually the distance covered by e– along the field direction in one revolution.
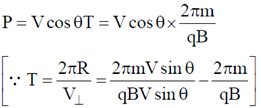
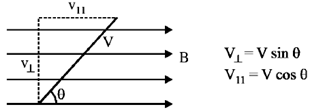
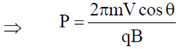
Given, Pitch of the helix = Radius of helical path
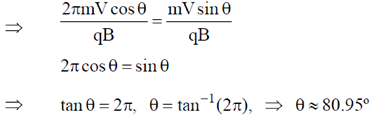
17. Two thermally isolated identical systems have heat capacities which vary as CV = 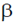 T3 (where
T3 (where 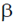 > 0). Initially one system is at 300 K and the other at 400 K. The systems are then brought into thermal contact and the combined system is allowed to reach thermal equilibrium. The final temperature of the combined system is _________
> 0). Initially one system is at 300 K and the other at 400 K. The systems are then brought into thermal contact and the combined system is allowed to reach thermal equilibrium. The final temperature of the combined system is _________
Sol. Let T = temperature of combined system. Therefore using principle of calorimetry we get,
heat lost = heat gained.
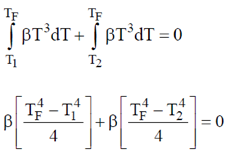
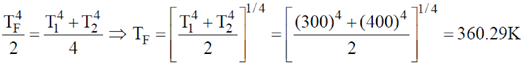
18. A beam of X-rays of wavelength 0.2 nm is incident on a free electron and gets scattered in a direction with respect to the direction of the incident radiation resulting in maximum wavelength shift. The percentage energy loss of the incident radiation is __________
Sol. Loss in energy of incident radiation
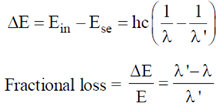
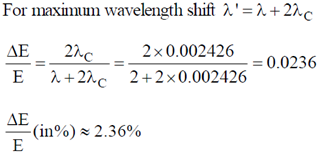
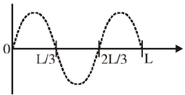
19. A free particle of mass 'm' is confined to a region of length L. The de-Broglie wave associated with the particle is sinusoidal in nature as given in the figure. The energy of the particle is _________
Sol. 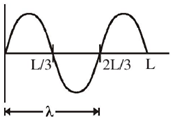
This is 2nd excited state (n = 3) of the particle because it has 2 nodes.
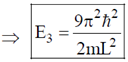
20. A variable power supply (5V-20V) is connected to a Zener diode specified by a breakdown voltage of 10V (see figure). The ratio of the maximum power to the minimum power dissipated across the load resistor is ______
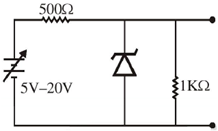
Sol. 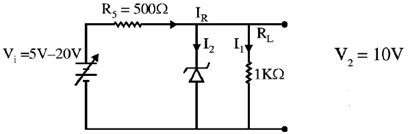
To check the status of zener diode (ON or OFF)
For V = 20 V
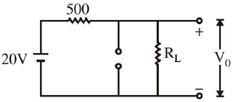
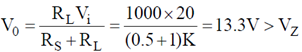
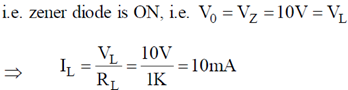
than maximum power dissipation across load resistor is
Pmax = V2L2 = 10 × 10 × 10–3 = 100 mW
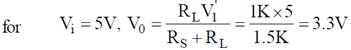
here V0 < V2
The zener diode is OFF
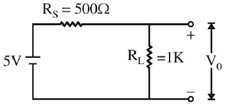
Min power dissipation across load resistor Pmin = I2 × RL = 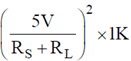
21. Apply Gauss divergence theorem to the gravitational field due to spherical object of mass M and uniform density  located at the origin. Obtain Gauss's law for gravitation (analogous to the Gauss law in electrostatics) in integral and differential forms.
located at the origin. Obtain Gauss's law for gravitation (analogous to the Gauss law in electrostatics) in integral and differential forms.
Sol. 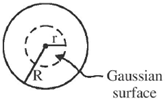
Consider an insider point at a distance r < R from centre.
Gravitational field at this point is, 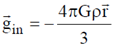
Therefore, flux of 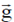 through a sphere of radius 'r' is
through a sphere of radius 'r' is
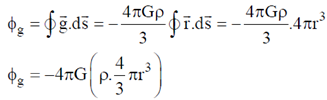
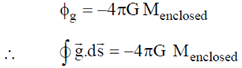
For outside point: Gravitational field at a distance r > R from centre of a sphere is given as
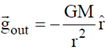
Therefore, flux through a surface of radius 'r' is
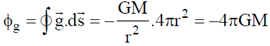
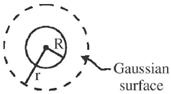
In this case sphere is completely enclosed enclosed by the Gaussian surface
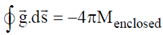
Therefore, in general for any point we can write for gravitational field
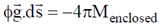
Using Gauss's div theorem we get, 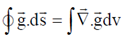 and
and 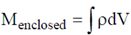
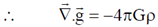
22. A thin annular disc of inner and outer radii a and b (a < b) respectively has uniform mass density ss and is placed in the soy-plane such that its axis lies along the z-axis. Determine the gravitational force due to the disc on a particle of mass 'm' located on the z-axis at a distance z from the origin. If the particle is released at z, such that z << a, b, describe the nature of motion of the particle.
Sol. Consider an elementary part of the disc: Take it to be a thin ring of radius 'r' and thickness 'dr' as shown in the figure.

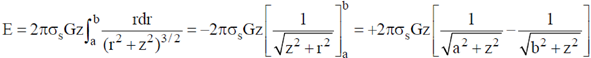
Therefore, gravitational force,
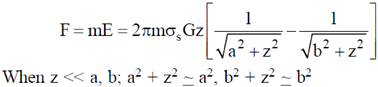
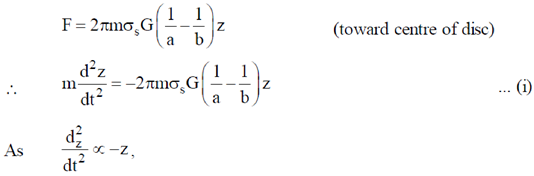
Therefore, particle will undergo S.H.M. and frequency of oscillation is obtained by comparing equation (i) to standard equation of S.H.M.
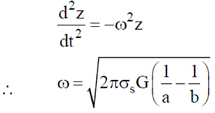
23. A concentric spherical volume of inner radius 'a' and outer radius 'a' and outer radius 'b' is filled with a material of finite conductivity specified by 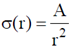
where A is a positive constant of appropriate dimensions. The outer surface is grounded and the inner surface is maintained at a potential V0. Calculate the resistasnce of this configuration.
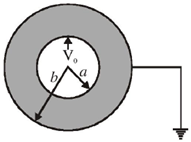
Sol. We know that resistance of a conductor is given as
Where l = length or spacing between cross section through which current flows.
A = area of cross section. In the present problem area of cross section is not constant.
Therefore, we first calculate resistance of elementary part and then integrate it to get total resistance. The flow of current is shown by dotted arrow.
Therefore, for elementary part (which is a shell of radius 'r' and thickness 'dr'). Resistance is given as
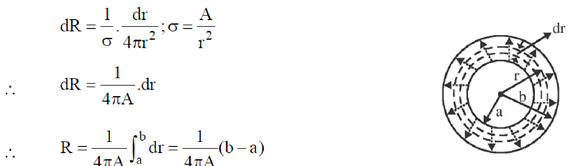
24. A conducting solid sphere of radius a, carrying a charge q is kept in a dielectric of dielectric constant k, such that half the sphere is surrounded by the dielectric as shown in figure. Find the surface charge densities in the upper and lower hemispherical surfaces.
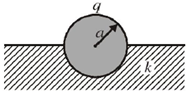
Sol. Let us assume that charge on upper half is q1 and that on lower half is q2.

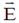 and
and 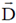 field lines are shown in the figure.
field lines are shown in the figure.
We know that parallel components of E vector at the boundary of two media is same. Therefore,
E1 = E2 ... (ii)
To get E1 = E2 we first calculate D1 and D2. We draw Gaussian surface as shown in the figure dotted line. Inside metal D = 0.
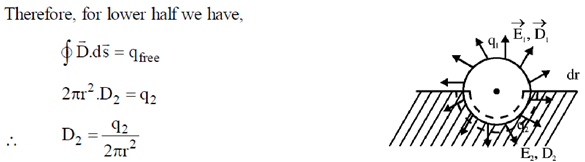
Similarly, for upper half we get,
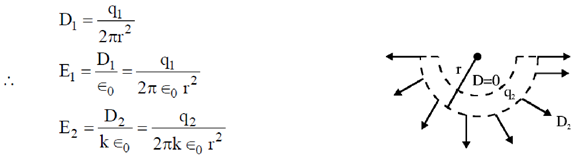
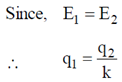
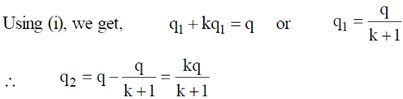
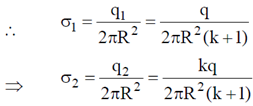
25. A particle of mass 'm' is subjected to a potential V(x) = ax2, – < x <
< x < 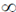 , where 'a' is a potive constant of appropriate dimensions. Using the relation
, where 'a' is a potive constant of appropriate dimensions. Using the relation 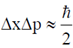 , estimate the minimum energy of the particle.
, estimate the minimum energy of the particle.
Sol. Let x = displacement from mean position
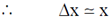
Using Heisenberg uncertainty relation we get, 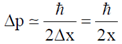
Therefore, minimum energy is
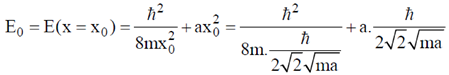
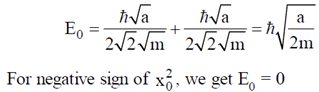
26. A hollow cylinder (closed at both ends) with adiabatic walls is divided into 'n' equal cells (C1, C2, ....... Cn) using discs D1, D2, ........ Dn–1 (see figure). The discs can slide freely without friction. The first disc (D1) is adiabatic and the remaining discs are diathermal (thermally conducting). Each cell contains one mole of ideal monoatomic gas. Let the initial pressure, volume and temperature of each cell be P0, V0 and T0 respectively. The gas in cell C1 (first cell) is heated slowly until the temperature of the gas in cell Cn (last cell) reaches final equilibrium temperature 4T0. Find the volume of the first cell in terms of the number of cells (n) and the initial volume (V0).
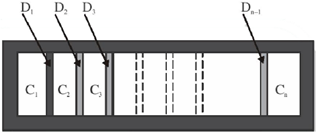
Sol. Process is slow, and discs D2, D3....Dn-1 are conducting. Therefore, when temperature of cn reaches 4T0
Temperature of chambers c2, c3, ..... cn–1 also becomes 4T0. Therefore, chambers c2, c3, .... cn can be considered as a single chamber of initial volume (n –1) V0.
We have following situation,
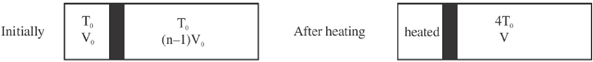
When gas on the left is heated gas on the right undergoes adiabatic process.
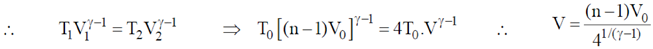
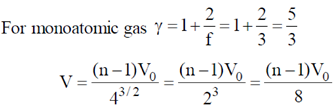
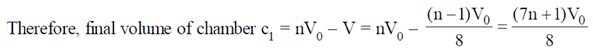
27. A spaceship S1 leaves the Earth along the positive x-direction. Another spaceship S2 also leaves the earth along the direction which makes an angle 60º with x-axis. The speeds of S1 and S2 are measured by 0.6c and 0.9c respectively by an observer on the Earth. Find the speed of S2 as measured by an observer in S1.
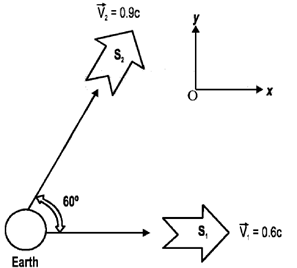
Sol. Speed of S2 as measured in S1 is given as
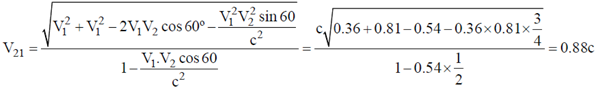
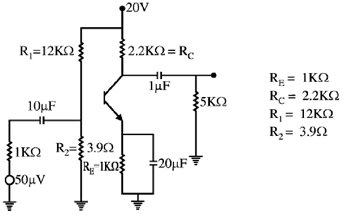
28. For the given circuit, calculate the input impendance, output impedance and voltage gain.
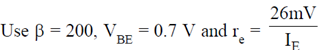
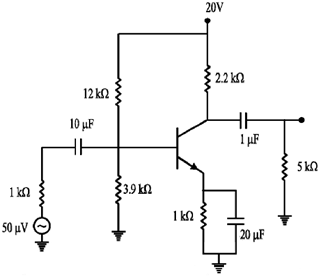
Sol. 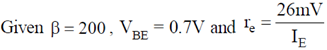
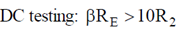
200 × 1K > 10 × 3.9K, 200 K > 39K (Satisfied)
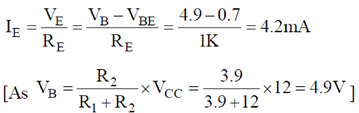
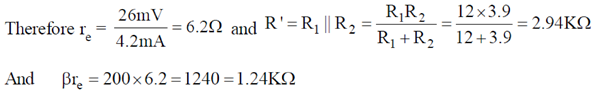
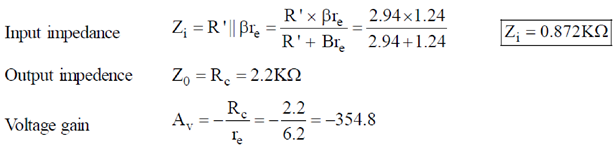
29. The mass density of a disc of mass 'm' and radius R varies as
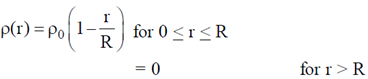
Find the moment of inertia of the disc about the axis perpendicular to the plane of the disc and passing through the centre of the disc in terms of m and R.
Sol. We can determine the moment of inertia of a disc by breaking a disc into many rings.
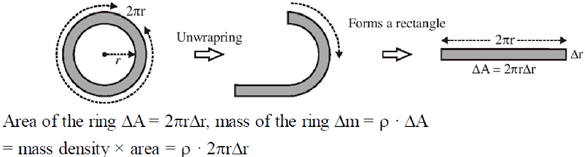
As we allow the number of rings to approach infinity the differential 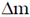 becomes dm,
becomes dm, 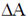 becomes dA while the differential
becomes dA while the differential 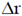 becomes dr.
becomes dr.
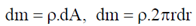
therefore the total mass of the disc
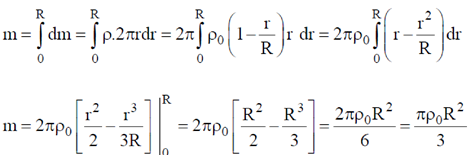
The moment of inertia of the disc.
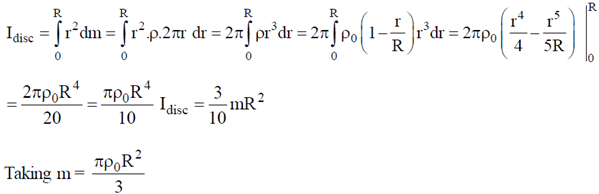
This is the required moment of inertia of the disc about the axis perpendicular to the plane of the disc and passing through the centre of disc in terms of m and R.
30. The speed of sound propagation in air as a function of temperature T is given by v = 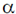 T, where
T, where 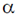 is a constant of appropriate dimensions. Calculate the time taken for a sound wave to travel a distance L between two points A and B, if the air temperature between the points varies linearly from T1 to T2.
is a constant of appropriate dimensions. Calculate the time taken for a sound wave to travel a distance L between two points A and B, if the air temperature between the points varies linearly from T1 to T2.
Sol. It is given that air temperature varies linearly. Therefore, we can assume that at a distance 'x' from A temperature is given as
At A, x = 0, T = T1
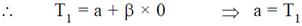
At B, x = L, T = T2