IIT JAM Mathematics 2014
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
1. 
(a) f (x + 3)
(b) f (x2 + 3)
(c) 2f (x)
(d) 3f (x)
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
Now




2. Let P(x) be the polynomial of least degree with rational coefficients and 1 +  is a root of
is a root of
(a) x2 – 2x + 4
(b) x2 + 2x + 4
(c) x2 + 2x – 4
(d) x2 – 2x – 4
Ans. (d)
Sol. We know that irrational root comes in pair. So, if one root is  , then another root is
, then another root is  .
.
Now,
Sum of roots = 


3. Let C be the circle passing through the origin with its centre lying on the straight lines 3x – 2y = 0 and y – 5 = 0. Then the equation of C is
(a) x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y = 0
(b) x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y = 0
(c) x2 + y2 – 4x – 6y = 0
(d) x2 + y2 – 4x + 6y = 0
Ans. (c)
Sol. 

and x + y – 5 = 0
 x + y = 5
x + y = 5
 + y = 5 [
+ y = 5 [ from Eq. (i)]
from Eq. (i)]
 2y + 3y = 15
2y + 3y = 15
 5y = 15
5y = 15
 y = 3
y = 3
On putting the value of y = 3 in Eq. (i), we get

 x = × 3
x = × 3
 x = 2
x = 2
According to statement, centre of circle lies on the intersection of two lines given
 Centre of circle = (2, 3)
Centre of circle = (2, 3)
Radius of circle r = 
r = 
r = 

Now, equation of circle with centre (2, 3) and radius  is
is
(x – 2)2 + (y – 3)2 = 
 x2 + 4 – 4x + y2 + 9 – 6y = 13
x2 + 4 – 4x + y2 + 9 – 6y = 13
 x2 + y2 – 4x – 6y + 13 = 13
x2 + y2 – 4x – 6y + 13 = 13
 x2 + y2 – 4x – 6y = 0
x2 + y2 – 4x – 6y = 0
Hence, the required equation of circle is
x2 + y2 – 4x – 6y = 0
4. The range of a random variable X is {0, 1, 2, 3, ...} and the probabilities of X are given by P(X = 0) = , P(X = k) =  , k = 1, 2, 3, ..., where c is a constant. Then P(0 < X < 2) is
, k = 1, 2, 3, ..., where c is a constant. Then P(0 < X < 2) is
(a) 1/e
(b) 4/e
(c) 2/e
(d) 3/e
Ans. (a)
Sol. 









5. Let, x y be real numbers, =  . If
. If  is perpendicular to
is perpendicular to  and
and  = – 4, then which one of the following is TRUE?
= – 4, then which one of the following is TRUE?
(a) x = 2, y = 1
(b) x = –2, y = –1
(c) x = 2, y = –1
(d) x = –2, y = 1
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
Since, c is perpendicular to a
 c.a = 0
c.a = 0

 x + y + 1 = 0
x + y + 1 = 0
 x + y = – 1 ...(ii)
x + y = – 1 ...(ii)
Again, c.b = – 4

 x – y – 1 = – 4
x – y – 1 = – 4
 x – y = – 4 + 1
x – y = – 4 + 1
 x – y = – 3
x – y = – 3
On adding Eqs. (ii) and (iii), we get
 x + y + x – y = – 1 – 3
x + y + x – y = – 1 – 3
 2x = – 4
2x = – 4
 x = – 2
x = – 2
On putting the value of x = – 2 in Eq. (ii), we have
 x + y = – 1
x + y = – 1
 – 2 + y = – 1
– 2 + y = – 1
 y = – 1 + 2 = 1
y = – 1 + 2 = 1
Hence, the required values of x and y be – 2 and 1 respectively.
6. The value of  is
is
(a) –1/12
(b) 1/12
(c) –1/6
(d) 1/6
Ans. (a)
Sol. 





7. A wire of length 50 cm is to cut into two pieces for making a square and a circle. For their combined area to be a minimum, one of the pieces must have a length (in cm) of
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. Let circumference of circle = x cm

and perimeter of square = (50 – x) cm
 4 (Each side) = (50 – x)
4 (Each side) = (50 – x)
 Each side =
Each side =  ...(ii)
...(ii)
 Combined area = Area of circle + Area of square
Combined area = Area of circle + Area of square
A =  + (Each side)2
+ (Each side)2



Now, differentiate w.r.t 'x', we have

For minimum  = 0
= 0




Now, length of one piece = x =  cm
cm
and length of other piece = 50 – x = 50 – 

Hence, the requried value of two pieces be  cm and
cm and  cm respectively.
cm respectively.
8. The solution of the differential equation x – u = 2xInx, x > 0 subject to the condition y(1) = 0 is
– u = 2xInx, x > 0 subject to the condition y(1) = 0 is
(a) 2 In x x
(b) 2 (In) x x
(c) 2 2 (In) x x
(d) In x x
Ans. (b)
Sol. 






General solution of differential equation is





9. A force of magnitude 50N acts in a direction making an angle of 30 with the positive x-axis. Then the components (in N) along the coordinate axes OX and OY are
(a) 25, 25
(b) 25 3, 25
(c) 25, 25/2
(d) 25 3/2, 25/2
Ans. (b)
Sol. We know that, component of force P along, OX = P cos 
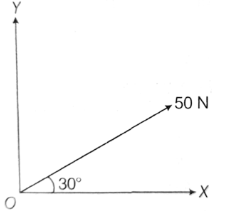
 Component of force 50 N along OX = 50 cos 30°
Component of force 50 N along OX = 50 cos 30°

Now, component of force 50N along OY = 50 sin 30°

= 25 N
10. Let z = x + iy and |z – i| = |z + 1|. Then x and y satisfy the equation
(a) x – y = 1
(b) x + y = 1
(c) x = y = 0
(d) x – y = 0
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
 |z – i| = |z + 1|
|z – i| = |z + 1|
 |x + iy – i| = |x + iy + 1| [∵Given]
|x + iy – i| = |x + iy + 1| [∵Given]
 |x + i(y – 1)| = |(x + 1) + iy|
|x + i(y – 1)| = |(x + 1) + iy|

On squaring both sides, we have
 x2 + y2 + 1 – 2y = x2 + 1 + 2x + y2
x2 + y2 + 1 – 2y = x2 + 1 + 2x + y2
 – 2y = 2x
– 2y = 2x
 – y = x
– y = x
 x + y = 0
x + y = 0
Hence, the required equation is x + y = 0
11. The values of  is
is
(a) 1/4
(b) 1/2
(c) 3/4
(d) 1
Ans. (c)
Sol. 








12. In n > 2 and (1 + x)n = a0 + a1x + a2x2 + ... + anxn, then the value of the expression a0 + 2a1 + 3a2 + 4a3 + ... + (n + 1)an equals
(a) 2n – 1 (n + 2)
(b) 2nn
(c) 2n – 1 (n + 1)
(d) 2n – 1 (n + 7)
Ans. (a)
Sol. Given,
(1 + x)n = a0 + a1x + a2x2 + ... + anxn and n > 2 ...(i)
Multiplying x both sides in Eq. (i), we get
x (1 + x)n = a0x + a1x2 + a2x3 + ... + anxn + 1
Now, differentiate above Eq. w.r.t. 'x', we have
 1(1 + x)n + nx(1 + x)n – 1
1(1 + x)n + nx(1 + x)n – 1
= a0 + 2a1x + 3a2x2 + ... + (n + 1)anxn
On putting x = 1 in the above equation, we get
 1(1 + 1)n + n × 1(1 + 1)n – 1
1(1 + 1)n + n × 1(1 + 1)n – 1
 a0 + 2a1 + 3a2 + ... + (n + 1)an
a0 + 2a1 + 3a2 + ... + (n + 1)an
 2n + n2n – 1 = a0 + 2a1 + 3a2 + ... + (n + 1)an
2n + n2n – 1 = a0 + 2a1 + 3a2 + ... + (n + 1)an
 2n – 1(n + 2) = a0 + 2a1 + 3a2 + ... (n + 1)an
2n – 1(n + 2) = a0 + 2a1 + 3a2 + ... (n + 1)an
13. The distance of the point (1, 2, 1) from the plane 3x – 6y + 2z + 7 = 0 is
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) 1/7
(d) 2/7
Ans. (b)
Sol. Given, 3x – 6y + 2z + 7 = 0 and point (1, 2, 1)
We know that, distance of a point (x1, y1, z1) from plane ax + by + cz + d = 0 is 
Now,
Distance of a point (1, 2, 1) from plane
3x – 6y + 2z + 7 = 0

14. The value of the determinant 
(a) (x + y +z) (x + y + z + xyz)
(b) xyz(x + y + z + xyz)
(c) xyz (x + y + z)
(d) xyz(xy + yz + zx)
Ans. (b)
Sol. 



Taking common (x + y + z + xyz) from R1



15. The value of the derivative of y = tan–1  , x
, x  0 at x = 1 is
0 at x = 1 is
(a) 1 4 2 2 –
(b) 1 4 2 2 +
(c) 1/2
(d) 1/4
Ans. (d)
Sol. 




On differentiating the above Eq. w.r.t. x, we get


At x = 1

16. The value of the definite integral  is
is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 


17. A particle is projected at an angle of elevation 45° with a velocity of 1 unit. Then the horizontal distance covered is (g denotes the acceleration due to gravity)
(a) g
(b) 2/g
(c) g/2
(d) 1/g
Ans. (d)
Sol. We know that, R = 
According to statement, U = 1 unit,  = 45°
= 45°


18. The maximum value of 7 10 x y + subject to the constraints x y + > 3 3, x y + < 2 and x > 0, y > 0 is
(a) 20
(b) 10
(c) 14
(d) 15.5
Ans. (a)
Sol. Given, x + 3y > 3 and x + y < 2
Let x + 3y = 3  x = 3 – 3y
x = 3 – 3y

Let x + y = 2  y = 2 – x
y = 2 – x


Let z = 7x + 10y
At A(0, 2)
 z = 7 × 0 + 10 × 2 = 20
z = 7 × 0 + 10 × 2 = 20
At B(0, 1)
 z = 7 × 0 + 10 × 1 = 10
z = 7 × 0 + 10 × 1 = 10
At C(3/2, 1/2)

Hence, the maximum value of 7x + 10y is 20.
19. A simple pendulum of mass m and length l is given a horizontal velocity v when it is at rest in the equilibrium position. Let v2 = gl, where g is the acceleration due to gravity. The angle from the vertical at the turning point is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. Consider the simple pendulum shown below.
Applying conservation of energy between points A and B, we have




20. Figure below shows the variation of stopping potential (V) as a function of frequency (v) of the incident radiation in a phtoelectric experiment. If the intensity of the incident radiation is increased, then in the graph

(a) the slope alone changes
(b) the V-intercept alone changes
(c) both the slope and V-intercept remain the same
(d) both the slope and V-intercept change
Ans. (c)
Sol. Photoelectric equation can be written as below :

where  = threshold frequency
= threshold frequency
V0 = stopped potential
 = frequency of incident radiation
= frequency of incident radiation
 V0 =
V0 =
 Intercept along V-axis
Intercept along V-axis
= – = constant ...(i)
= constant ...(i)
Slope of the curve = = constant ...(ii)
So, from Eqs. (i) and (ii), it can be said that both the slope and V-intercept remains the same.
21. A hydrogen atom in the 3rd excited state can have
(a) 3 Lyman, 2 Balmer and 1 Paschen transitions
(b) 2 Balmer and 1 Paschen transitions
(c) 2 Lyman and 1 Paschen transitions
(d) 2 Lyman, 3 Balmer and 1 Paschen transitions
Ans. (a)
Sol. Number of transitions are N = 

where n = excited state = 3
 N =
N =  = 6
= 6
Maximum number of transition is associated with lowest level (i.e. K).
 We can have
We can have
3 Lyman, 2 Balmer and 1 Paschen as shown in the figure.
22. Four capacitors (each of 1F) are connected as shown in the figure. If the capacitor assembly is charged to V volts by connecting to the points P and R, the total energy stored in the assembly is

(a) 2V2
(b) 
(c) 4V2
(d) V2
Ans. (b)
Sol. Equivalent capacitance between P and R


It the capacitor assembly is charged to V volts by connecting to the points P and R, then the total energy stored in the assembly is given by

23. Figure shows the P-V diagram for an ideal gas. If the system has a temperature T0 at X, the temperature at Y is

(a) T0
(b) 2T0
(c) 3T0
(d) 4T0
Ans. (c)
Sol. Since, xy is an isochoric process.

 According to ideal gas equation, pv = nRT
According to ideal gas equation, pv = nRT
So, being an isochoric process, volume will be constant.


24. The first overtone of an open organ pipe of length I was found to be the same as that of the fundamental frequency of a closed organ pipe when the pipe was immersed in water upto a certain level. Then, the water fills the tube upto a level of
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. First overtone frequency of an open organ pipe

where, v is the speed of the wave and λ is wavelength.
Fundamental frequency of a closed organ pipe

According to the question, f1 = f0


 Levle of water filled
Levle of water filled
Iw = I – I' = I – 
25. For obtaining a REAL image using a bioconvex lens of focal length f, the distance d between the object and the image must satisfy the condition
(a) d =  only
only
(b) 2f < d < 4f
(c) 0 < d < 2f
(d) d > 4f
Ans. (d)
Sol. For obtaining a real image using a biconcave lens of focal length f, we must have
d > 4f

26. An electron having initial velocity v0 and momentum p0 is accelerated in a constant electric field  . Aften a time t, it acquires velocity v and momentum p. The change in the wavelength of the electron is
. Aften a time t, it acquires velocity v and momentum p. The change in the wavelength of the electron is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. Wavelength associated with a moving electron having speed v0 is 
If speed changes, then change in wavelength is


27. If the biasing is changed from forward to reverse across a semiconductor p-n junction, the width of the depletion layer
(a) decreases
(b) does not change
(c) vanishes
(d) increases
Ans. (d)
Sol. If reverse voltage is applied across a semiconductor then, the width of depletion layer increases.
28. A force  is applied to a block of mass M resting on a surface, as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction between M and the surfaces is
is applied to a block of mass M resting on a surface, as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction between M and the surfaces is  . If the mass DOES NOT move, then
. If the mass DOES NOT move, then

(a) F >  Mg
Mg
(b) F <  Mg
Mg
(c) F = Mg
(d) F < Mg
Ans. (b)
Sol. If the mass does not move
F < (fs)max

where, fs is static friction having maximum values

29. When an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically to one-fourth of its original volume, the pressure increases by 8 times. The ratio of the molar heat capacities (CP/CV) of the gas can be
(a) 1.4
(b) 1.67
(c) 1.45
(d) 1.5
Ans. (d)
Sol. For an adiabatic expansion of the gas



30. Consider two simple harmonic motions represented by x1 A0cos and x2 = A0cos(
and x2 = A0cos( ). At t = 0, x1 = –A0. If these two simple harmonic motions are combined, the amplitude of the resultant motion is
). At t = 0, x1 = –A0. If these two simple harmonic motions are combined, the amplitude of the resultant motion is
(a) zero
(b) 2A0
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. Given that
x1 = A0 cos 
and x2 = A0 cos 
Putting t = 0
x1 = A0 cos  = – A0
= – A0

 Phas difference between the two simple harmonic motions is π
Phas difference between the two simple harmonic motions is π
 Amplitude of the resultant wave
Amplitude of the resultant wave
A = A0 – A0 = 0
31. When the resistance R in an LCR circuit is increased, the resonance frequency of the circuit
(a) increases, but the resonance becomes broader
(b) decreases, but the resonance becomes sharper
(c) remains the same, but the resonance becomes sharper
(d) remains the same, but the resonance becomes broader
Ans. (d)
Sol. Resonant frequency of a series L-C-R circuit

and quality factor Q = 
as resistance increases ω remains same but Q decreases, i.e. resonance curve become together.
32. When the temperature of water is increased from 0°C, its
(a) volume decreases and then increases
(b) volume increases and then decreases
(c) volume increases
(d) volume remains constant PAPER
Ans. (a)
Sol. When the temperature of water increases from 0° to 4°C its volume decreases due to anomalous behaviour of water. If temperature of water further increases, then volume increases.
33. A projectile is launched at an angle  with respect to the horizontal with an initial velocity u. The coordinates of the moving projectile at the highest point are
with respect to the horizontal with an initial velocity u. The coordinates of the moving projectile at the highest point are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. Maximum height attained by the projectile



Coordinate at point P

34. If a conducting sphere of radius R is given a charge Q, which one of the following graphs represents the variation of potential (V) as a function of distance (r) from the centre of the sphere
(a)

(b)
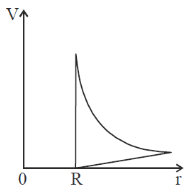
(c)

(d)

Ans. (a)
Sol. Potential of conducting sphere is
V = 
where, r is distance from the centre. R is radius of the sphere.
V = 
These variations are best represented by the graph (a).
35. A particle of mass m tied to a string is made to move in circular path of radius R in a VERTICAL plane. Neglect the air friction and mass of the string. Total work done on the particles when the particle moves from P to Q is

(a) mgR
(b) 
(c) 
(d) Zero
Ans. (b)
Sol. Work done on the particle against the gravity when the particle moves from
P to Q

WPQ = Change in potential energy
= mgR + mgR cos 60°
= mgR (1 + cos 60°)

36. Currents I1 and I2 flow in opposite direction along two long coaxial tubes as shown in the figure. The magnetic field at any point in the annular region depands on

(a) I2 only
(b) I1 only
(c) I1 – I2
(d) I1 + I2
Ans. (b)
Sol. Magnetic in the annular region at any point. P depends only on the current enclosed by an amperian loop passing through P taht is on I1.

37. Which one of the following is considered to be the first biological catalyst when life originated on earth?
(a) RNA
(b) DNA
(c) Protein
(d) Lipid
Ans. (a)
Sol. RNA is considered the first biological catalyst. This is because the complex machinery of the cell proceeds from DNA to protein through an RNA intermediate.
Also, DNA came later during evolution, before that RNA stored both genetic information and catalysed the chemical reactions in primitive cells and during this stage, proteins were not yet engaged in biochemical reactions.
38. "Portuguese man-of-war" belongs to the phylum
(a) Porifera
(b) Cnidaria
(c) Annelida
(d) Arthropoda
Ans. (b)
Sol. The Atlantic Portuguese man-of-war, i.e. Physalia physalis is a marine cnidarian of the family, Physalildae. It has venous tentacles which can deliver a painful sting.
39. If an animal has biradial symmetry, then it has
(a) only one place of symmetry
(b) two axes of rotational symmetry
(c) two planes of symmetry, these two planes have no specific relationship to each other
(d) two planes of symmetry, these two planes are at right angles to each other
Ans. (d)
Sol. Biradial symmetry refers to the arrangement of the body components of an animal, such that similar parts are located to either side of a central axis and each of the four sides of the body is identical to the opposite side but different from the adjacent side. Thus, the two planes are at right angle to each other.
40. A population is isolated by a geographical barrier. The resulting specification known as
(a) parapatric
(b) allopatric
(c) sympatric
(d) pseudopatric
Ans. (b)
Sol. Allopatric speciation occurs when a single species becomes geographically separated and each group evolves new and distinct trait.
41. Consider the following groups :
Group I : Class of compounds
Group II : Typical examples for Group I
Group III : Organism/cell associated with the production of these compounds
Group I
P1. Primary metabolite
P2. Secondary metabolite
P3. Enzyme
P4. Polysaccharide
P5. Recombinant protein
P6. Immunoglobulins
Group II
Q1. Antibiotic
Q2. Amino acid
Q3. Cellulose
Q4. Lignin
Q5. Lipase
Q6. Human insulin
Q7. IgG
Group III
R1. Bacteria
R2. Yeast
R3. Fungus
R4. B Lymphocytes
R5. Plant Cells
Choose the correct match
(a) P1–Q2–R2, P2–Q1–R1, P3–Q5–R3, P4–Q4–R5, P5–Q3–R3, P6–Q7–R4
(b) P1–Q1–R1, P2–Q2–R2, P3–Q3–R3, P4–Q4–R5, P5–Q5–R1, P6–Q6–R4
(c) P1–Q2–R1, P2–Q1–R3, P3–Q6–R4, P4–Q3–R5, P5–Q7–R5, P6–Q1–R4
(d) P1–Q2–R1, P2–Q1–R3, P3–Q5–R2, P4–Q3–R5, P5–Q6–R1, P6–Q7–R4
Ans. (d)
Sol. The correct match for the following are :

42. Which one of the following modifications targets the proteins selectively to lysosomes?
(a) Addition of N-acetygalactosamine to a serine residue of the protein
(b) Addition of a precise number of mannose residues to the protein
(c) Phosphorylation of a specific mannose residue to mannose-6-phosphate
(d) Addition of a peptide signal sequence to the N-terminus of the protein
Ans. (c)
Sol. Proteins destined for incorporation into lysosomes are specifically recognised and modified by the addition of phosphate groups to the 6th position of mannose residues. In the first step of the reaction, N-acetylglucosamine phosphates are transferred to mannose residues from UDP-N-acetylglucosamine. The N-acetylglucosamine groups are then removed, leaving 6-phosphates.
43. Consider the following three groups :
Group I : Viruses
Group II : Associated diseases
Group III : Nature of genetic material-single standard (ss) or double stranded (ds) DNA/RNA
Group I Group II
P1. HIV Q1. Common cold
P2. Herpes virus Q2. Cancer
P3. Rhinovirus Q3. Diarrhea
P4. Rotavirus Q4. AIDS
P5. Human papilloma virus Q5. Chickenpox
Group III
R1. ssRNA
R2. ssDNA
R3. dsRNA
R4. dsDNA
Choose the correct match
(a) P1–Q2–R1, P2–Q3–R2, P3–Q1–R3, P4–Q5–R4, P5–Q4–R4
(b) P1–Q4–R1, P2–Q5–R4, P3–Q1–R1, P4–Q3–R3, P5–Q2–R4
(c) P1–Q4–R1, P2–Q5–R2, P3–Q1–R3, P4–Q3–R4, P5–Q2–R2
(d) P1–Q2–R3, P2–Q3–R1, P3–Q4–R2, P4–Q1–R1, P5–Q5–R4
Ans. (b)
Sol. The correct match for the following are

44. A class of spermicides (used for contraception) inhibits the flagger motion of the sperm thereby preventing it from swimming towards the egg. This is achieved by
(a) inhibiting the motor protein dyneine
(b) inhibiting the motor protein kinesin
(c) disrupting the microfilaments
(d) depolymerizing microtubles
Ans. (a)
Sol. The motor protein dynein converts the chemical energy contained in the ATP into the mechanical energy of movement. Axonemal dynein causes sliding of microtubules in the axonemes of cilia and flagella and is found in cells like sperm cells. Thus, spermicides works by inhibiting the motor protein dynein.
45. Which one of the following signaling pathways is CORRECT?
(a) Signal  GPCR
GPCR  G-Protein
G-Protein  Adenyl cyclase
Adenyl cyclase  cAMP
cAMP  Protein kinapse
Protein kinapse  Cellular response
Cellular response
(b) Singal  G-Protein
G-Protein  GPCR
GPCR  Phospholipase C
Phospholipase C  Inositol triphosphate (IP3)
Inositol triphosphate (IP3)  IP3-gated calcium channel
IP3-gated calcium channel  Release of Ca2+ ions
Release of Ca2+ ions
(c) Hormone diffusion  Hormone receptor (HR) complex
Hormone receptor (HR) complex  Nuclear transport of HR complex
Nuclear transport of HR complex  G-protein modification of HR complex (Transcription Factor)
G-protein modification of HR complex (Transcription Factor)  Binding of Transcription Factor to DNA
Binding of Transcription Factor to DNA  Transcription of a gene
Transcription of a gene
(d) Signal  GPCR
GPCR  G-Protein
G-Protein  Tyrosine kinase
Tyrosine kinase  Protein phosphorylation
Protein phosphorylation  cAMP
cAMP  Cellular response
Cellular response
Ans. (a)
Sol. The correct signaling pathway is
Signal  GPCR
GPCR  G-Protein
G-Protein  Adenyl cyclase
Adenyl cyclase
Cellular response  Protein kinase A
Protein kinase A  cAMP
cAMP 
This takes as the binding of adrenaline to an adrenergic receptor like b-adrenergic G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) initiates a cascade of reaction inside the cell. The signal transduction cascade begins when adenylyl cyclase, a membrane bound enzyme is activated by G-protein molecules associated with GPCR. Adenylyl cyclase creates multiple cyclic AMP molecules, which fan out and activate protein kinases (PKA in this example).
Protein kinases can enter the nucleus and affect transcription which is cellular response.
46. Which one of the followin can be used to transfect DNA into mammalian cells?
P. Liposomes
Q. Cholesterol
R. CaCl2 + HEPES buffer (calcium phosphate)
S. Magnesium chloride
(a) Only P
(b) P and Q
(c) P and R
(d) P and S
Ans. (c)
Sol. Calcium phosphate transfection, electroporation and liposome mediated transfection are three methods which can be used to efficiently produce cell lines containing stably integrated DNA.
47. Choose the correct set of matches between Group I and Group II
Group I
P. One extra copy of chromosome 13 Q. XO
R. XXY S. One extra copy of chromosome 21
Group II
1. Edwards syndrome
2. Klinefelter syndrome
3. Patau syndrome
4. Down syndrome
5. Turner syndrome
(a) P–1, Q–5, R–3, S–2
(b) P–3, Q–5, R–2, S–4
(c) P–2, Q–1, R–3, S–4
(d) P–1, Q–1, R–2, S–5
Ans. (b)
Sol. The correct match are as follows :
(i) Patau's syndrome is caused by a chromosomal abnormality in which some or all of the cells of the body contain extra genetic material at chromosome 13.
(ii) Turner's syndrome is a condition in which a female have partly or completely missing an X-chromosome. Thus, have 45 or XO conditions.
(iii) Klinefelter's syndrome is characterised by the presence of an extra X-chromosome in the pair of sex chromosome making it 47 or XXY condition.
(iv) Down's syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality arising due to trisomy at chromosome 21 caused due to non-disjunction of chromosomes during cell division.
48. Which one of the following events DOES NOT take place in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell?
(a) Translation of mRNA to the corresponding polypeptide chain
(b) Folding of the polypeptide chain
(c) Post-translational modifications of the polypeptide chain
(d) Phospholipid synthesis
Ans. (a)
Sol. Following functions are performed by endoplasmic reticulum (ER), which is divided into smooth ER and Rough ER.
-
The SER is the site of lipid biosynthesis, detoxification and calcium regulation.
(ii) The RER lumen is the site for formation of disulphide bonds, proper folding, addition and processing of carbohydrates, specific proteolytic cleavages and assembly into multimeric proteins.
49. Rowland and Molina were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the year 1995 for their model which states that
(a) chlorine monoxide, monoatomic chlorine and monoatomic oxygen produced from chlorofluorocarbons react with atomspheric ozone to cause destruction of ozone layer
(b) ocean's capacity to absorb additional carbon dioxide is limited, resulting in global warming
(c) acid rains are the major problems to countries which burn more coal and gasoline in the process of industrilization
(d) UV light damages DNA
Ans. (a)
Sol. The Nobel Prize in chemistry, 1995 was awarded jointly to Paul J. Crutzen, Mario J. Mollina and F. Sherwood Rowland 'for their work in atomspheric chemistry, particularly concerning the formation and decomposition of ozone'. Most importantly, they explained how sensitive the ozone layer is to the influence of anthropogenic emissions of certain compounds.
By giving the chemical mechanisms that affect the thickness of the ozone layer, the three researchers have contributed to our salvation from a global environmental problem that could have catastrophic consequences.
50. In some goats, the presence of horns is produced by an autosomal allele that is dominant in males and recessive in females. A horned female is crossed with a hornless male. One of the resulting F1 females is crossed with a hornless male. Then,
(a) all male progeny and nono of the female progeny will be horned
(b) all female progeny and none of the male progeny will be horned
(c) 50% of the male progeny and none of the female progeny will be formed
(d) 50% of the female progeny and none of the male progeny will be horned
Ans. (b)
Sol. The presence of horns is produced by an autosomal allele in goats were
(i) Alleles dominant in males (AHAH) – Horned
(ii) Alleles recessive in females (AhAh) – Horned
F1-generation
 (All females horned but since, the condition is autosomal dominant in males. Thus, no male will be horned as no dominant allele is present)
(All females horned but since, the condition is autosomal dominant in males. Thus, no male will be horned as no dominant allele is present)
F2-generation

(Same as F1-generation will be formed with all females horned and all male hornless).
51. An enzymatic reaction following Michaelis-Menten kinetics (Km = 50 ) converts 10% of the substrate (initial concentration S0 = 1mM) to the product in 5 minutes. The maximum reaction velocity (in
) converts 10% of the substrate (initial concentration S0 = 1mM) to the product in 5 minutes. The maximum reaction velocity (in  /minute) of the enzyme is approximately
/minute) of the enzyme is approximately
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 50
(d) 180
Ans. (b)
Sol. Km = 50 × 10–6 M, S0 = 1 × 10–3 M






52. Four mutant strains of E.coli having the following characteristics were isolated.
Mutant strain 1 : Iac-represor is not able to bind to operator because of a mutation in the operator region of the Iac operon.
Mutant strain 2 : Allolactose is not able to bind to repressor because of a mutation in the reperssor encoding gene.
Mutant strain 3 : Catabolite activator protein (CAP) is not able to bind to the promoter because of a mutation in the promoter region.
Mutant strain 4 : cAMP is not able to bind to CAP because of a mutation in the CAP-encoding gene Iac Genes are expressed in strain (s)
(a) 1 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1 and 2 only, but in the presence of IPTG
Ans. (a)
Sol. A mutation in the lac repressor gen that causes it to lose its ability to recognise the operator would also cause the operon to turn on, even in the absence of lactose. This is because the repressor would be incapable of recognising and repressor would be incapable of recognising and binding to the operator. A mutation in a repressor that prohibits the lactose from binding turns the synthesis off even if there is lacotse in the medium.
If there was a mutation in both lac repressor gene and the operator region they might compensate for each other and a lactose control could be restored. Thus, in the question lac gene are expressed only by mutant strain 1.
53. 8M urea solution became cold when it was prepared by disolving an appropriate amount of urea in water at room temperature. This is because the dissolution of urea is
(a) exothermic and exergonic
(b) exothermic and endergonic
(c) endothermic and exergonic
(d) endothermic and endergonic
Ans. (d)
Sol. The dissolution of urea in water is endothermic and endergonic reaction as the temperature goes down because the reaction absorbs energy from the solution.
54. In the pentose phosphate pathway, glucose is first converted to ribulose-5-phosphate by oxidation decarboxylation. Then, ribolose-5-phosphate undergoes
(a) further oxidation
(b) reduction
(c) further decarboxylation
(d) only rearrangement of carbon skeleton
Ans. (d)
Sol. After the conversion of glucose to ribulose-5-phosphate by oxidative decarboxylation during pentose phosphate pathway, the ribulose-5-phosphate only undergoes rearrangements of carbon skeleton into ribose-5-phosphate or xylulose 5-phosphate by enzyme ribulose-5-phosphate isomerase and ribulose-5-phosphate 3-Epimerase, respectively.
55. Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
(a) All microarrays are DNA microarrays
(b) Complete genome sequence should be known to make a microarray
(c) All the microarrays use radioisotopes
(d) Microarrays can be used to measure mRNA levels
Ans. (d)
Sol. Only statement d is true. As a DNA microarray is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a soild surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to genotype multiple regions of a genome. Each DNA spot contains picomoles (10–12 moles) of a specific DNA sequence, known as probes. These can be a short section of a gene or other DNA element that are used to hybridise a cDNA or cRNA (also called anti-sense RNA) sample under high-stringency conditions.
In an mRNA or gene expression profiling experiment the expression levels of thousands of genes are simultaneously monitored to study the effects of certain treatments, diseases and developmental stages on gene expression by these.
56. The metabolit that is NOT used by brain as a source of energy under condition of prolonged low blood-glucose levels is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. Structure 'a' is of acetic aci. In brain Imidazole-4-acetic acid (IMA), a naturally occurring metabolite of histamine is present which acts to stimulate post-synaptic GABA receptors directly but is not used by brain under prolonged low blood glucose levels.
57. Which one of the following protects membrane lipids against damage by reactive oxygen species produced in the chloroplast?
(a) Carotenoids
(b) Chlorophyll a
(c) Chlorophyll b
(d) Phycocyanin
Ans. (a)
Sol. Carotenoids are organic pigments that are found in the chloroplasts and chromoplasts of plants and some other phostosynthetic organisms. Including some bacteria and some fungi. Carotenoids serve two key roles in plants and algae, they absorb light energy for use in photosynthesis and they protect chlorophyll from photodamage.
58. A DNA sequencing reaction was performed with the fragment 5'-XXXXGCGATCGYYYY-3' as the template, dideoxy GTP, all the four dNTPs, and the require primers and enzyme. XXXXX and YYYY in the given DNA fragment represent primer binding sites. The set of fragments obtained during the reaction will be (the primers are not shown in the amplified fragments)
(a) 5'-CGATCGC-3' only
(b) 5'-CG-3', 5'-CGCTAG-3', 5'-CGCTAGC-3'
(c) 5'CG-3', 5'CGATCG-3', 5'CGATCGC-3'
(d) 5'G-3'M 5'-GCG-3', 5'GCGATCG-3'
Ans. (c)
Sol. The DNA sequencing performed on fragment 5'-XXXXGCGATCGYYYY-3' as the template would produce fragment 5'-CG-3', 5'-CGATCG-3', 5'-CGATCGC-3' respectively.
59. According to the Linnean system of biological classification, the term "Hominidae" indicates
(a) class
(b) order
(c) family
(d) genus
Ans. (c)
Sol. According to linnean system of biological classification the term Hominidae indicates family. As
Kingdom – Animalia
Phylum – Chordata
Class – Mammalia
Order – Primates
Super family – Hominoidea
Family – Hominidae
60. The endosperm in an angiosperm plant is
(a) haploid
(b) diploid
(c) triploid
(d) tetraploid
Ans. (c)
Sol. One of the distinguishing feature of angiosperm and gymnosperms is that angiosperms have triploid endosperm produced during triple fusion but gymnosperms have haploid endosperm as it is produced before fertilisation.
61. The technique appropriate for sterilizing animal tissue culture media is
(a) filtering through a 0.45  filter
filter
(b) autoclaving at 120°
(c) boiling at atmospheric pressure
(d) using chemical agents
Ans. (a)
Sol. During sterilising animal tissue culture the serum or supermatent are filtered through a 0.45  filter and is maintained at –20°C.
filter and is maintained at –20°C.
Sterilisation refers any process that eliminates or kills all forms of life and other biological agents such as prions, viruses, etc. Sterilisation can be achieved by one or more of the following, i.e. heat, chemicals, irradation, high pressure and filtration. During heat sterilisation autoclave is used.
These steam heat is 121°-134°C under pressure. Chemical sterilisation may damage heat sensitive materials like biological materials, thus not used for them. Filtration is done using microfilters or nanofilters.
62. Which two of the following statements are TRUE in relation to human pregnancy?
P: The blastocyst consists of trophoblast, an inner cell mass and a central cavity
Q: The morula becomes embedded in the endometrium during implantation
R: The placenta acts as an exchange mechanism between the mother and the fetus
S: Maternal and fetal blood are mixed while passing through the placenta
(a) P and Q
(b) R and S
(c) Q and S
(d) P and R
Ans. (d)
Sol. The statements true in relation to human pregnancy are that, the blastocyst is a structure formed in the early development of mammals which possesses an inner cell mass which subsequently forms the embryo. The outer layer of the blastocyst consist of cells collectively called the trophoblast. This layer surrounds the inner cell mass and a fluid filled cavity known as the blastocoele.
Also, the placenta connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply, fight against internal infection and produce hormones to support pregnancy.
63. In Drosophila melanogaster, cherub wings (ch) black body (b) and cinnabar eyes (cn) are recessive to their corresponding alleles (representred as ch+, b+ and cn+, respectively) and are all located on chromosome 2. Homozygous wild type flies were mated with cherub, black and cinnabar flies and the resulting F1 females were test crossed with cherub, black and cinnabar males. The following progeny were produced from the test cross
ch b+ cn 110
ch + b cn 780
ch+ b cn 70
ch+ b+ cn 6
ch b cn 769
ch b+ cn+ 60
ch+ b cn+ 111
ch b cn+ 9
Total 1915
Of these three genes, which one is in the middle?
(a) The locus that determines cherub wings
(b) The locus that determines cinnabar eyes
(c) The locus that determines black body
(d) Cannot be determined from the given data
Ans. (b)
Sol. We know that the genotypes found most frequently are the parental genotypes and from the table in the question that are ch+ b+ cn+ and ch b cn. Also, the double crossover gametes are always in the lowest frequency and from the table the ch+b+cn and ch b cn+ are with the lowest frequency, i.e. 6 and 9 individuals.
Thus, during the test cross if we have cn, i.e. cinnabar eye allele in the middle of ch and b allele then only the double crossover will produce the given results.

64. The enzyme that is used to make the first strand cDNA from mRNa is
(a) Reverse transcriptase
(b) Restriction endonuclease
(c) DNA polymerase
(d) T4 DNA ligase
Ans. (a)
Sol. Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme used to make the first strand cDNA from mRNA. This process is called reverse transcription. It is mainly associated with retro virus.
65. Which one of the followin compounds, on transmination, DOES NOT result in one of the genetically coded 20 amino acids?
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. Amino acid biosynthesis pathways involves transamination reactions in which the alpha amino group from one amino acid is transferred to an alpha-keto acid to produce a new amino acid. This reaction is catalysed by enzyme amino transferses. in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of eukaryotes cells these enzyme possess two types of specificity.
(i) The type of  -amino acid that donates the
-amino acid that donates the  -amino group.
-amino group.
(ii) The  -keto acid that accepts the
-keto acid that accepts the  -amino group.
-amino group.

Thus, cannot be formed after transcription.
66. Choose the correct set of words denoted by (P), (Q), (R), (S) and (T) to fill in the blanks. (P) use (Q) for antigen presentation. These antigen-displaying MHC molecules are recognized by (R), which express a unique co-receptor on their cell surface called as (S). On interaction with the antigen presenting cells, T cells respond by producing cytokines such as (T).
(a) P. All nucleate cells, Q. MHC I, R.l Cytotoxi T Cells, S. CD4, T.  -Interferon
-Interferon
(b) P.Macrophages, Q. MHC II, R. Cytotoxic T Cells, S. CD4, T.  -Interferon
-Interferon
(c) P. B Lymphocytes, Q. MHC Ii, R. Helper T Cells (TH2), S. CD4, T. Interleukin-4
(d) P.Dendritic Cells, Q. MHC I, R. Helper T Cells (TH1), S. CD8, T. GMCSF PAPER : IIT JAM 2007 11
Ans. (c)
Sol. The correctly placed words in the paragraph are as follows :
B-lymphocytes use MHC-II for antigen presentation. These antigen displaying MCH molecules are recognised by helper T-cells (TH2), which express a unique coreceptor on their cell surface called as CD4. On interaction with the antigen presenting cells, T cells respond by producing cytokines such as interleukin-4.
67. Group I lists relationships that can exist between two organism. Their descriptions are given in Group II. Find the correct set of matches between Group I and II.
Group I
P. Ammensalism
Q. Commensalims
R. Symbiosis
S. Parasitism
Group II
1. One popular is benefited and the other is harmed
2. Two diasimilar species living together in close association
3. Heterotrophic organisms that ingest other organisms
4. One population is inhibited but the othe is to affected
5. One population is benefited but the other is not affected
(a) P–4, Q–2, R–3, S–5
(b) P–4, Q–1, R–2, S–5
(c) P–3, Q–4, R–2, S–1
(d) P–2, Q–1, R–3, S–4
Ans. (d)
Sol. The correct matching are as follows :
(i) Ammensalism is a relationship between organisms in which one population is inhibited but the other is unaffected.
(ii) Commensalism is a relationship between organisms in which one population is benefitted but the other is not affected.
(iii) Symbiosis is close and often long term interaction between two biologically different species.
(iv) Parasitism is a relationship when one population is benefitted and the other is harmed.
68. Choose the correct set of matches between Group I and II.
Group I
P. Embryoid
Q. Callus
R. Meristem
S. Scutellum
Group II
1. An unorganized growth of plant cells in a culture medium
2. A localized group of actively dividing cells from which permanent tissue systems such as root, shoot, leaf, and flower and derived
3. A process whereby specialized, non-diving cells begin to proliferate by mitotic division, presumed to involve regression to an undifferentiated state
4. Mass of cells which has an external morphology resembling a prrombryo
5. The embroyonic cotyledon of monocot plants
(a) P–4, Q–2, R–3, S–5
(b) P–4, Q–1, R–2, S–5
(c) P–3, Q–4, R–2, S–1
(d) P–2, Q–1, R–3, S–4
Ans. (b)
Sol. The correct match for the following are :
(i) Embryoid is mass of cells which has an external morphology resembling a proembryo.
(ii) Callus is an unorganised growth of plant cells in a culture medium.
(iii) Meristem is a localised group of actively dividing celsl from which permanent tissue systems such as root, shoot, leaf and flower are derived.
(iv) Scutellum is the embryonic cotyledon of monocot plants.
69. Match the hormones (Group I) to the glands producing them (Group II).
Group I Group II
P1. Oxytocin R1. Ovary
P2. Insulin R2. Pituitary
P3. Calcitonin R3. Testis
P4. Estrogen R4. Pancreas
P5. Epinephrine R5. Throid
P6. Testosterone R6. Pineal
R7. Adrenal
(a) P1–R5, P2–R4, P3–R2, P4–R1, P5–R6, P6–R3
(b) P1–R4, P2–R6, P3–R5, P4–R3, P5–R7, P6–R1
(c) P1–R2, P2–R4, P3–R5, P4–R1, P5–R7, P6–R3
(d) P1–R1, P2–R4, P3–R7, P4–R1, P5–R6, P6–R5
Ans. (c)
Sol. The correct match as follows :

70. The G0 phase of the animal cell cycle can occur
(a) just before the G1 phase
(b) just before the mitotic (M) phase
(c) during the G2 phase
(d) late in the G1 phase
Ans. (a)
Sol. G0 phase of the animal cell cycle can occur just before the G1 phase.

Diagrammatic view of a cell cycle indicating formation of two cells
71. Which one of following options correctly describes the import of Pi and ADP into the mitochondria?
(a) By ADP – H+ antiport and Pi – H+ antiport
(b) By ADP – ATP antiport and Pi – OH– antiport
(c) By ADP – OH– antiport and Pi – OH– antiport
(d) By ADP – ATP antiport and Pi – H+ antiport
Ans. (b)
Sol. The import of Pi and ADP into the mitochondria is by ADP–ATP antiport and Pi-OH+ antiport. This takes place as transport of ATP out of the mitochondria is accomplished by an adenine nucleotide translocase which moves one ADP into the mitochondria for each ATP exported into the cytosol. Since, the net charge of ATP is – 4, whereas ADP has a charge of –3, the exchange is accompanied by the import of one proton per ATP into the mitochondria and is driven by the pH gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Export of ATP from the mitochondria in exchange of ADP also results in a net export of phosphate. Sustained ATP export thus requires a phosphate transporter, which imports cytosolic phosphate (Pi) in exchange for a hydroxyl ion. The exchange of Pi for a hydroxyl ion also result in a net import of one proton into the mitochondrion.
72. If the genotypes Aa Bb Cc dd Ee and Aa bb Cc Dd Ee are crossed, what will be the proportion of AABBCCDDEE genotype among the progeny?
(a) 1/32
(b) 1/64
(c) 1/256
(d) Zero
Ans. (d)
Sol. If the genotype Aa Bb Cc dd Ee is crossed with genotype Aa bb Cc Dd Ee then no progeny can be formed with genotype AA BB CC DD EE as in allelic pair DD cannot be formed.
This is due to the fact that only one 'D' is present in one of the parent. Thus, its paired condition cannot be formed in the progeny.
73. An enzymatic reaction following Michaelis-Menton kinetics  converts 10% of the substrate (initial concentration s0 = 1mM) to the product in 5 minute. If the enzyme concentration is doubled and the substrate concentration is brought down to 0.1 mM in the initial reaction mixture, the time (in minutes) taken for 50% conversion will be approximately
converts 10% of the substrate (initial concentration s0 = 1mM) to the product in 5 minute. If the enzyme concentration is doubled and the substrate concentration is brought down to 0.1 mM in the initial reaction mixture, the time (in minutes) taken for 50% conversion will be approximately
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 2.5
(d) 12.5
Ans. (c)
Sol. Case I Km = 50 × 10–6 M
S0 = 1 × 10–3 M





Case II S0 = 0.1 × 10–3 M

t = ?
(0.1 × 10–3 – 0.5 × 0.1 × 10–3) + 50 × 10–6


= 3.09 min = 3 min
74. Which one of the following statements regarding mitochondria is FALSE?
(a) Addition of NADH present in the mitochodrial matrix is coupled to proton transport out of the matrix
(b) Hydrolysis of ATP present in the mitochondrial matrix is coupled to proton transport out of the matrix
(c) Cytochrome c mediates electron transfer from cytochrome bc1 complex to cytochrome as complex
(d) Cytosolic NADH is delivered to the mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase complex by the glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle pathway.
Ans. (d)
Sol. The statement 'd' is incorrect regarding mitochondria. IT can be corrected as electrons from NADH can enter the mitochondrial electron transport chain by being used to reduce dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glycerol 3-phosphate.
Glycerol-3-phosphate is reoxidised by electron transfer to an FAD prosthetic group in a membrane bound glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Subsequent electrons transfer to Q to form QH2 allows these electrons to enter the electron transport chain.

75. The shape of cholesterol is
(a) planar
(b) globular
(c) cylindrical
(d) helical
Ans. (a)
Sol. Molecular formula of cholesterol is C27H46O. It is planar structure which contains steroid rings with a hydroxyl group, two methyl groups and a hydrogen tail.

76. The vitamin, whose derivative is NOT a coenzyme of E.coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is
(a) pyridoxal
(b) thiamine
(c) niacin
(d) riboflavin
Ans. (a)
Sol. Pyridoxal is not a vitamine derivative coenzyme of E.coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. This is because the combined dehydrogenation and decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA involves the sequential action of three different enzymes as well as five different coenzymes or prosthetic groups, i.e. Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP), Flavin Adenine Dinuclotide (FAD), coenzyme A (CoA), Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) and lipoate.
Four different vitamins are vital components of this system thiamine (in TPP), riboflavin (in FAD), niacin (in NAD) and pantothenate (in coenzyme A).
77. For a given unicellular organism, which one of the following needs to be characterized only once?
(a) Genome
(b) Transcriptome
(c) Protocome
(d) Metabolome
Ans. (a)
Sol. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA including all its genes. It is characterised only once for a given unicellular organism since it is singly present in an oragnism. Other like transcriptome (set of all RNA molecules in one cell), metabolome (total number of metabolities present within an organism, cell or tissue) and proteome (entire set of proteins expressed by a genome cell, tissue or organism at a certain time) are characterised more than once.
78. A certain purified DNA sample was cut with two restriction endonucleases E1 and E2. The following results were obtained from agarose gel electrophoresis
Sample cut with E1 alone : two bands of size 35 kb and 15 kb
Sample cut with E2 alone two bands of size 40 kb and 10 kb
Sample cut simultaneously with E1 and E2: three bonds of size 35 kb, 10 kb and 5 kb. From these data, it can be inferred that the DNA has
(a) two sites for E1 and one site for E2
(b) one site for E1 and two sites for E2
(c) one site each for E1 and E2
(d) three sites for E1 and one site for E2
Ans. (c)
Sol. A purified DNA sample when cut with restriction enzymes are as follows :
(i) With E1

(ii) With E2

(iii) With both E1 and E2

This shows that DNA ahs one site for each E1 and E2 restriction enzymes.
79. Which one of the following elements NEED NOT be present in an expression vector?
(a) Selection marker to select for host cells containing the vector
(b) Two different origins of replication
(c) Promoter sequence upstream of the cloned gene
(d) Unique restriction enzyme sites for insertional cloning
Ans. (b)
Sol. Two different origins of replication need not to be present in an expression vector. An expression vector is usually a plasmid or virus designed for protein expression in cells. Elements of expression vector includes an origin of replication, a selectable marker and one or more site for the insertion of a gene, i.e. cloning sites. Also, it has a promotor sequence upstream of the cloned gene.
80.  for the hydrolysis at ATP to ADP and Pi is –32 kJ/mol. This means that when ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and Pi in a cell.
for the hydrolysis at ATP to ADP and Pi is –32 kJ/mol. This means that when ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and Pi in a cell.
(a) –32 kJ/mol of fee energy becomes available to the cell for utilization
(b) free energy available to the cell cannot be more than –32 kJ/mol
(c) at least – 32 kJ/mol of free energy becomes available to the cell for utilization
(d) free energy available to cell cannot be determined solely by the value of 
Ans. (a)
Sol.  = (–)ve i.e. – 32 kJ mol–1
= (–)ve i.e. – 32 kJ mol–1
which means reaction is spontaneous or feasible.
This reaction looks like
ATP  ADP + Pi;
ADP + Pi;  = – 32 kJ mol–1
= – 32 kJ mol–1
Although it also means this – 32 kJ mol–1 of free energy ( ) becomes available to the cell for utilisation.
) becomes available to the cell for utilisation.
81. The product obtained by heating and equimolar mixture of adipic acid and xamethylenediamine is
(a) Nylon 6
(b) Nylon 66
(c) Polyurethane
(d) Terylene
Ans. (b)
Sol. On heating equimolar mixture of adipic acid and hexamethylene diammine a condensation polymer nylon-6, 6 is obtained.

82. A mixture of CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2 and HBr (slight excess) in other DOES NOT show optical activity because
(a) an achiral product is formed
(b) a single chiral product is formed
(c) the product formed is a racemic mixture
(d) CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2 and HBr do not react in ether
Ans. (c)
Sol.

Since, 2°-carbocation is slightly more favourable for SN1 reaction hence its product shows a racemic mixture (50% retention and 50% inversion).
83. The correct match between the items of Group I and Group Ii is
Group I Group II
P. Phosphatidic acid 1. Zwitterionic
Q. Triacylglycerol 2. Hydrophilic
R. Glycogen 3. Hydrophobic
4. Amphiphatic
(a) P–4, Q–2, R–3
(b) P–4, Q–3, R–2
(c) P–1, Q–4, R–2
(d) P–2, Q–3, R–1
Ans. (b)
Sol. Phosphatidic acid : Amphatic in nature

Glycogen contains 30,000 glucose units hydrophilically.
84. The correct match between the items of Group I and Group II is
Group I
P. McLafferty rearrangement
Q. Chemical shift
R. Molar extinction coefficient
S. Revalues
Group II
1. UV-Vis spectroscopy
2. IR spectroscopy
3. NMR spectroscopy
4. Mass spectroscopy
5. Thin layer chromatography
6. Get electophoresis
(a) P–1, Q–3, R–6, S–4
(b) P–3, Q–4, R–2, S–6
(c) P–4, Q–2, R–3, S–5
(d) P–4, Q–3, R–1, S–5
Ans. (d)
Sol. Mc Lafferty rearrangement : Mass spectra
Chemical shift : NMR spectra
Molar extinction coefficient  : UV-vis spectra
: UV-vis spectra
R1 value : Thin layer chromatography.
85. Which one of the following is paramagnetic?
(a) CO
(b) N2
(c) NO
(d) [NO]+
Ans. (c)
Sol. M.O configuration of

Number of unpaired electrons (n) = 0
Hence, diamagnetic
M.O configuration of

n = 0
Hence, diamagnetic
M.O configuration of

n = 1
Hence, paramagentic
M.O configuration of

n = 0
Hence, diamagnetic.
86. Which one of the following molecules has zero dipole moment?
(a) BF3
(b) H2O
(c) CHCl3
(d) HP
Ans. (a)
Sol. Since, H2O, CHCl3 and HF are the polar molecules hence, they have some dipole moment.

But in BF3 because of planar symmetric structure, its magnitude of dipole is cancelled out resulting net dipole moment zero.
87. Which one of the following complex ions has a square planar geometry?
(a) [PiCl4]2–
(b) [NiCl4]2–
(c) [Zn(CN)4]2–
(d) [Cd(CN)4]2–
Ans. (a)
Sol. EC of Pt = [Xe]54 4f145d36s16p0
EC of Pt2+ = [Xe]54 4f145d36s06p0
 Pt2+ ln [PtCl4]2+
Pt2+ ln [PtCl4]2+

Hybridisation; dsp2, geometry : Square planar
While [NiCl4]2– : Tetrahedral
[Zn(CN)4]2– : Tetrahedral
[Cd(CN)4]2– : Tetrahedral
88. The set of qunatum numbers, , = 2, l = 2, m = 0
(a) is forbidden
(b) describes an electron in a 2d orbital
(c) describes an electron in a 2p orbital
(d) describes one of the five orbitals of similar type
Ans. (b)
Sol. Given, n = 2, l = 2, m1 = 0
 Orbital is 2d
Orbital is 2d
It describes an electron in 2d orbital.
89. The rate equation for the reaction 2X + 3Y  Z is rate = k [X][Y]. Consider the following statements
Z is rate = k [X][Y]. Consider the following statements
P: The unit of k is mol L–1s–1
Q: The value of k is independent of the initial concentrations of X and Y
R : By doubling the concentrations of both X and Y, the rate is doubled
Then, which one of the following is CORRECT?
(a) P is true, Q is false, R is false
(b) P is true, Q is true, R is false
(c) P is false, Q is true, R is true
(d) P is false, Q is true, R is false
Ans. (d)
Sol. For the reaction
2X + 3Y  Z
Z
rate = k[X][Y] ...(i)
From Eq. (i), rate depends upon the concentration of X and Y. So, the rate order becomes two
For 2nd order reactions,
Unit of k = (mol)l – n Ln – 1 S–1 = (mol)–1 L s–1
Also, value of k does not depend upon concentration of X and Y.
Rate K[X][Y]
If concentration of both X and Y is doubled, then rate
= K[2x][2y] = 4K[x][y]
i.e. rate of reaction will become 4 times.
90. Consider the equilibrium reaction N2O4 (g)  2NO2 (g). If the total pressure of the equilibrium mixture is p and the degree of dissociation of N2O4 (g) is x at 300 K, the partial pressure of NO2 (g) is
2NO2 (g). If the total pressure of the equilibrium mixture is p and the degree of dissociation of N2O4 (g) is x at 300 K, the partial pressure of NO2 (g) is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 2xp
Ans. (a)
Sol. Given N2O4(g)  2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
Initial concentration 1 0
At equilibrium 1 – x 2x
Total concentration = 1 – x + 2x = 1 + x
We know that at equilibrium

Partial pressure of NO2 = 
91. The correct match between the items of Group I and Group II is
Group I
P. Fehling's solution
Q. Feric chloride solution
R. Schiff's base formation
S. lodoform test
Group II
1. Detection of aldehyde
2. Detection of glucose
3. Detection of phenol
4. Detection of –COCH3
(a) P–2, Q–1, R–3, S–4
(b) P–4, Q–3, R–1, S–2
(c) P–3, Q–2, R–4, S–4
(d) P–2, Q–3, R–4, S–1
Ans. (d)
Sol. Fehling's solution 2 Cu(OH)2 + NaOH : Detection of glucose
Ferric chloride solution (FeCl3) : Detection of phenol
Schiff's base formation : Detection of aldehyde

92. The two compounds given below are

(a) identical
(b) enantiomeric
(c) diastereomeric
(d) meso compounds
Ans. (c)
Sol.

For identical molecule, all stereogenic centre have different configuration.
For enantiomeric, all stereogenic centre have different configuration to each other.
For diastereomeric at least one carbon centre has different configuration.
93. The correct match between the items of Group and Group II is
Group I
P. Preparation of alkanes
Q. C2H6 + C2H5Cl + AlCl3
R. C2H5OH + CHCl3 + NaOH
S. C2H5 Br + KOH (alcoholic)
Group II
1. Reimer-Tiemann
2. Eilmination reaction
3. Friedel-Crafts
4. Wurtz
(a) P–3, Q–2, R–1, S–4
(b) P–4, Q–3, R–1, S–2
(c) P–1, Q–3, R–2, S–4
(d) P–4, Q–2, R–3, S–1
Ans. (b)
Sol. Preparation of alkanes : Wurtz reaction.

94. The acidity of
P: C2H5 COOH
Q: C2H5NH2
R: C2H5OH
S. C2H5SH
follows the order
(a) P > S > R > Q
(b) P > R > S > Q
(c) S > Q > R > P
(d) R > Q > P > S
Ans. (a)
Sol. Acidity of compounds depends upon how easily H' is donated.
So, C2H5COOH is the most acidic among the given while C2H5NH2 is least. Due to lesser electronegativity of S-atom than O-atom donates proton more easily.
So, C2H5SH is more acidic than C2H5OH
Hence, the correct order is

95. The basic oxide amongst the following is
(a) Cl2O
(b) Na2O
(c) P4O50
(d) SO3
Ans. (b)
Sol. Due to maximum availability of Ione pair of electron on O-atom, the oxide becomes more basic. Hence, Na2O is the most basic amongst the given.
Na2O + H2O  2 NaOH
2 NaOH
96. The shape of [BrF4]+ ion is
(a) regular tetrahedron
(b) square planar
(c) trigonal pyramidal
(d) see-saw OR irregular tetrahedron
Ans. (d)
Sol. Fore [BrF4]+, Hybrid orbitals = 4 + 1 = 5
Hybridisation = sp3 d
Geometry = see saw or irregular tetrahedral

97. Assertion [A] : Dilute liquid ammonia solution of alkali metals (M) conduct electricity.
Assertion [B] : The electrical conductivity is due to the formation of solvated electrons and M+ ions. Which one of the following is CORRECT?
(a) [A] is true but [B] is false
(b) Both [A] and [B] are false
(c) Both [A] and [B] are true and [B] is the correct reason for [A]
(d) Both [A] and [B] are true but [B] is not the correct reason for [A]
Ans. (c)
Sol. While dilute solution of liquid ammonia is treated with akali metal (M), produces solvated electrons and M+ ions which conduct electricity.


98. A zero order reaction is 50% complete in 30 minutes. The time (in minutes) from the start of the reaction required for 80% completion is
(a) 42
(b) 48
(c) 52
(d) 60
Ans. (b)
Sol. Given t1/2 for zero order reaction = 30 min



99. The following data are given

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. 





100. From the data given below
A  A2+ + 2e, E° = +0.80eV
A2+ + 2e, E° = +0.80eV
A  A2+ + 3e, E° = 0.99V
A2+ + 3e, E° = 0.99V
the calculated E° for A2+ + e is
(a) +0.19 V
(b) 0.73 V
(c) 1.37 V
(d) 1.79 V
Ans. (c)
Sol. 




