IIT JAM Chemistry 2022
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
1. The reagent required for the following transformation is

(a) NaBH4
(b) LiAlH4
(c) H3B·THF
(d) Zn(Hg)/HCl
Ans. d
Sol. 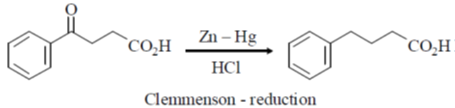

2. The major product formed in the following reaction
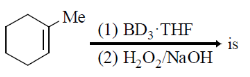
(a) 
(b) 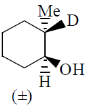
(c) 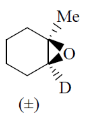
(d) 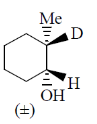
Ans. (b)
Sol. 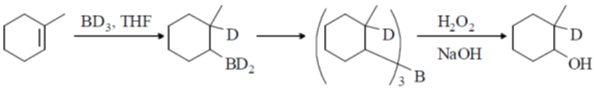
3. The major product formed in the following reaction

(a) 
(b) 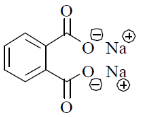
(c) 
(d) 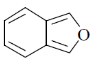
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
4. The major product formed in the following reaction
K+ O2 is
is
(a) K2O
(b) K2O2
(c) KO2
(d) K2O3
Ans. (c)
Sol. K + O2 KO2
KO2
5. Which one of the following options is best suited for effecting the transformation?

(a) MnO2
(b) DMSO, (COCl)2, Et3N
(c) Al(Oi-Pr)3
(d) Ag2O/NH4OH
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
Al(O – iso – Pr)3 and DMSO, (CoCl)2, NH3 will also react with – OH
MnO2 is generally used to oxidiseallylic – OH.
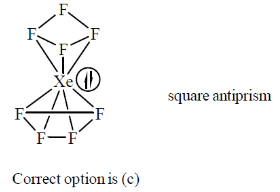
6. The structure of [XeF8]2– is
(a) cubic
(b) hexagonalbipyramid
(c) squareantiprism
(d) octagonal
Ans. (c)
Sol.
7. Among the following, the compound that forms the strongest hydrogen bond is
(a) HF
(b) HCl
(c) HBr
(d) HI
Ans. (a)
Sol. Among the following, the compound that forms the strongest hydrogen bond is for strongtest 'H' bonding more +ive charge 'H'

Correct option is (a)
8. Among the following, the biomolecule with a direct metal-carbon bond is
(a) coenzyme B12
(b) nitrogenase
(c) chlorophyll
(d) hemoglobin
Ans. (a)
Sol. The reaction of adenosine phosphate (ATP) with Vit-B12S field direct cobalt – carbon bond between adenosyl and cobalt the resulting molecule is known as B12 coenzyme.
9. For the reaction
H2PO2– (aq) + OH– (aq)  HPO32– (aq) + H2(g)
HPO32– (aq) + H2(g)
the rate expression is k[H2PO2–][OH–]2. If the concentration of H2PO2– is doubled, the rate is
(a) tripled
(b) halved
(c) doubled
(d) unchanged
Ans. (c)
Sol. Rate1 = K [H2PO2–]1 [OH–]2
When conc. of [H2PO2]– is doubled, new rate
Rate2 = K [2H2PO2–]1 [OH]2
= 2 K[H2PO2–] [OH–]2
= 2 × Rate1
 Rate becomes doubled
Rate becomes doubled
10. The nature of interaction involved at the gas-solid interface in physisorption is
(a) ionic
(b) van der Waals
(c) hydrogen bonding
(d) covalent
Ans. (b)
Sol. Asinphysiosorption weak vanderwaal force of interaction is responsible for adsorption.
11. The major product formed in the following reaction

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 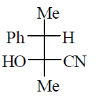
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
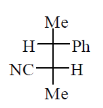
12. An organic compound having molecular formula C9H10O2 exhibits the following spectral characteristics:
1H NMR:  9.72 (t, 1H), 7.1 (d, 2H), 6.7 (d, 2H), 3.8 (s, 3H), 3.6 (d, 2H)
9.72 (t, 1H), 7.1 (d, 2H), 6.7 (d, 2H), 3.8 (s, 3H), 3.6 (d, 2H)
IR:  1720 cm–1
1720 cm–1
The most probable structure of the compound is
(a) 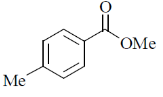
(b) 
(c) 

(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. NMR structure determination
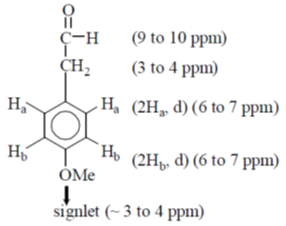
13. The major product formed in the reaction of (2S,3R)-2-chloro-3-phenylbutane with NaOEt in EtOH is
(a) (E)-2-phenyl-but-2-ene
(b) (Z)-2-phenyl-but-2-ene
(c) 3-phenyl-but-1-ene
(d) (2R,3R)-2-ethoxy-3-phenylbutane
Ans. (b)
Sol. 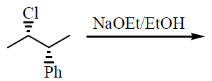

14. The major product formed in the following reaction

(a) 
(b) 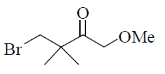
(c) 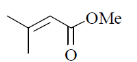
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 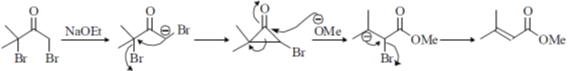
15. The reactivity of the enol derivatives
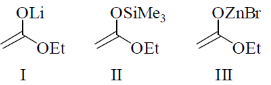
towards benzaldehyde follows the order
(a) I > II > III
(b) III > II > I
(c) II > I > III
(d) I > III > II
Ans. (d)
Sol. More the ionic character of O – M bond more is the –ve charge on oxygen and more isthe reactivity.
Trend of ionic character of O – M bond:
O – Li > O – ZnBr> O – SiMe3
 Same is the trend for reactivity of enol. derivatives.
Same is the trend for reactivity of enol. derivatives.
16. All possible lattice types are observed in the
(a) cubic crystal system
(b) monoclinic crystal system
(c) tetragonal crystal system
(d) orthorhombic crystal system
Ans. (d)
Sol. In orthorhombic crystal system, premittive, body centered, face centered & end centered bravious lattices are present.
17. The structure types of B10H102– and B10H14 , respectively, are
(a) closo and nido
(b) nido and arachno
(c) nido and closo
(d) closo and arachno
Ans. (a)
Sol.

18. The ground state and the maximum number of spin-allowed electronic transitions possible in a Co2+ tetrahedral complex, respectively, are
(a) 4A2 and 3
(b) 4T1 and 2
(c) 4A2 and 2
(d) 4T1 and 3
Ans. (a)
Sol. Co2+(td) 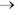 d7
d7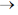 2e– system
2e– system
Ground state 4A2
Number of transition observed = 3
19. The correct statement about the geometries of BH2+ and NH2+ based on valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is
(a) both BH2+ and NH2+ are trigonal planar
(b) BH2+ is linear and NH2+ is trigonal planar
(c) BH2+ is trigonal planar and NH2+ is linear
(d) both BH2+ and NH2+ are linear
Ans. (b)
Sol. Geometry of NH2+ and BH2+
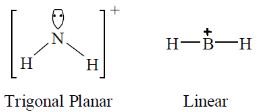
20. The order of increasing CO stretching frequencies in [Co(CO)4]–, [Cu(CO)4]+, [Fe(CO)4]2– and [Ni(CO)4] is
(a) [Cu(CO)4]+< [Ni(CO)4] < [Co(CO)4]–< [Fe(CO)4]2–
(b) [Fe(CO)4]2–< [Co(CO)4]–< [Ni(CO)4] < [Cu(CO)4]+
(c) [Co(CO)4]–< [Fe(CO)4]2–< [Cu(CO)4]+< [Ni(CO)4]
(d) [Ni(CO)4] < [Cu(CO)4]+< [Co(CO)4]–< [Fe(CO)4]2–
Ans. (**)
Sol. 
21. The reaction of 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene with hydrazine produces a yellow orange solid X used for the identification of an organic functional group G. X and G, respectively, are
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) 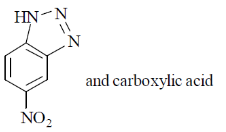
Ans. (b)
Sol.

22. The stability of adducts H3B·PF3, H3B·NMe3, H3B·CO, H3B·OMe2 follows the order
(a) H3B·OMe2< H3B·CO < H3B·PF3< H3B·NMe3
(b) H3B·PF3< H3B·CO < H3B·NMe3< H3B·OMe2
(c) H3B·CO < H3B·PF3< H3B·NMe3 . H3B·OMe2
(d) H3B·PF3< H3B·CO < H3B·OMe2 . H3B·NMe3
Ans. (d)
Sol. When good lewis acid binds with good lewisbase then stable adduct formation will occurs.
(d) H3B·PF3< H3B·CO < H3B·OMe2 . H3B·NMe3
Correct option is (d)
in option (c) < H3B · NMe3< H3B · OMe2
23. The spacing between successive rotational energy levels of a diatomic molecule XY and its heavier isotopic analogue X'Y' varies with the rotational quantum number, J, as
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. EJ+1 – EJ = 2B (J+1)

slope = 2B, intercept = 2B
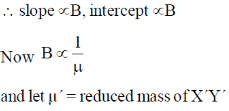
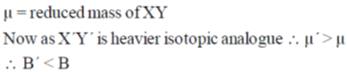

24. The ratio of the 2p  1s transition energy in He+ to that in the H atom is closest to
1s transition energy in He+ to that in the H atom is closest to
(a) 1(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 8
Ans. (c)
Sol. H Z = 1
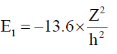


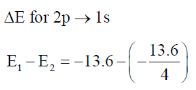

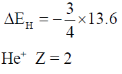
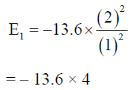
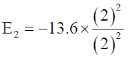

E1 – E2 = – 13.6 × 4 – (–13.6)
= – 13.6 × 4 + 13.6
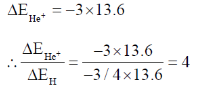
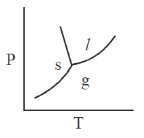
25. The phase diagram of water is best represented by
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 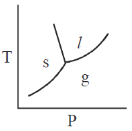
(d) 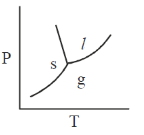
Ans. (d)
Sol. The phase diagram of water is best represented by a diagram that shows the relationship between temperature, pressure and the different phaes of water: Solid (ice), liquid (water) and gas (vapour)
For water, 
Hence, required phae diagram of water is:
26. Capillary W contains water and capillary M contains mercury. The contact angles between the capillary wall and the edge of the meniscus at the air-liquid interface in W and M are W  and M
and M  , respectively.
, respectively.
The contact angles satisfy the conditions
(a) 
(b) 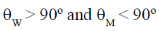
(c) 
(d) 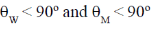
Ans. (d)
Sol. Water < 90º

27. The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution 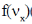 of one-dimensional velocities
of one-dimensional velocities 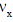 at temperature T is
at temperature T is
[Given: A is a normalization constant such that  and kB is the Boltzmann constant]
and kB is the Boltzmann constant]
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 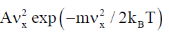
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. Number of particle in velocity range 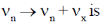
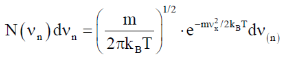

Correct option is (a)
28. The potential for a particle in a one-dimensional box is given as:
V(x) = 0 for 0 < x < L, and V(x) =  elsewhere.
elsewhere.
The locations of the internal nodes of the eigenfunctions 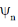 (x) , n > 2, are
(x) , n > 2, are
[Given: m is an integer such that 0 < m < n]
(a) 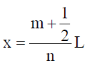
(b) 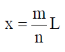
(c) 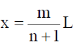
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. For 1 – D box position of internal nodes is for n > 2
Where m = interger 

For every integer of m and every value of n > 2
We get our positions
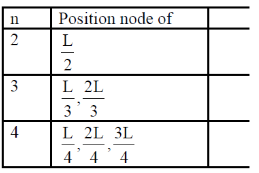
29. The number of CO stretching bands in the infrared spectrum of Fe(CO)5 is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans. (b)
Sol.
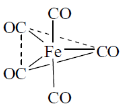
One band equational CO and one band for axial CO.
30. The standard Gibbs free energy change for the reaction

at 2500 K is +118 kJ mol–1.
The equilibrium constant for the reaction is
[Given: R = 8.314 J K–1mol–1]
(a) 0.994
(b) 1.006
(c) 3.42 × 10–3
(d) 292.12
Ans. (c)
Sol. 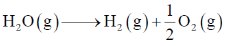
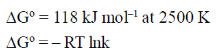
= 118 × 103 J mol–1 = – 8.314 JK–1mol–1 × 2500 K ln k
K = 3.42 × 10–3
31. Among the following, the reaction(s) that favor(s) the formation of the products at 25 ºC is/are
(a) 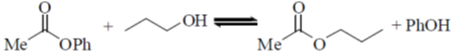
(b) 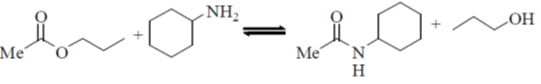
(c) 
(d) 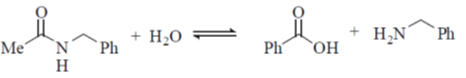
Ans. (a, b)
Sol.
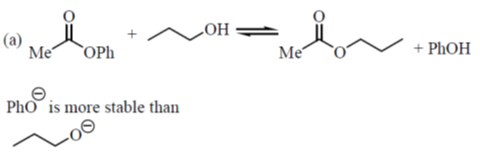

32. Among the following, the correct statement(s) is/are:
(a) The first pKa of malonic acid is lower than the pKa of acetic acid while its second pKa is higher than the pKa of acetic acid.
(b) The first pKa of malonic acid is higher than the pKa of acetic acid while its second pKa is lower than the pKa of acetic acid.
(c) Both the first and the second pKas of malonic acid are lower than the pKa of acetic acid.
(d) Both the first and the second pKas of malonic acid are higher than the pKa of acetic acid.
Ans. (a)
Sol.

First is lower, second is higher
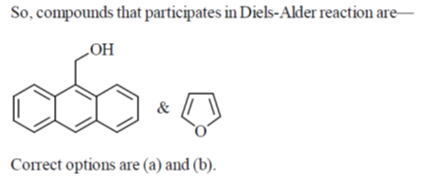
33. The compound(s) that participate(s) in Diels-Alder reaction with maleic anhydride is/are
(a) 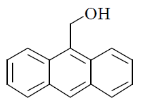
(b) 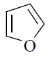
(c) 
(d) 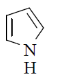
Ans. (a, b)
Sol.

34. Among the following, the suitable route(s) for the conversion of benzaldehyde to acetophenone is/are
(a) CH3COCl, anhydrous AlCl3
(b) (i) HS(CH2)3SH, F3B·OEt2; (ii) n-BuLi; (iii) MeI; (iv) HgCl2, CdCO3, H2O
(c) NaNH2, MeI
(d) (i) MeMgBr; (ii) aq. acid; (iii) pyridiniumchlorochromate (PCC)
Ans. (c, d)
Sol. 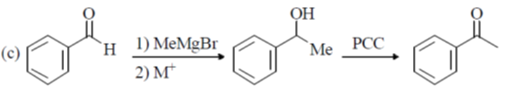

35. The reaction
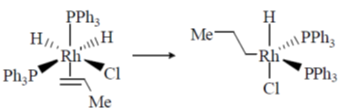
involve(s)
(a) migratory insertion
(b) change in electron count of Rh from 18 to 16
(c) oxidative addition
(d) change in electron count of Rh from 16 to 18
Ans. (a,b)
Sol.

1. Complex goes from 18 e– to 16 e–.
2. Migratory insertion is taking place.
36. The reason(s) for the lower stability of Si2H6 compared to C2H6 is/are
(a) silicon is more electronegative than hydrogen
(b) Si – Si bond is weaker than C – C bond
(c) Si – H bond is weaker than C – H bond
(d) the presence of low-lying d-orbitals in silicon
Ans. (b, c)
Sol. in Si – Si, then is bond formation via overlapping of 3p – 3p orbital which is weaker in compersion to C – C bond in which overlapping occur via 2p – 2p orbital overlapping & Si – H bond is polar in nature which make its less stable than C – H which is non polar& stable in nature.
37. For an N-atom nonlinear polyatomic gas, the constant volume molar heat capacity Cv,m has the expected value of 3(N – 1) R, based on the principle of equipartition of energy. The correct statement(s) about the measured value of Cv,m is/are
(a) The measured Cv,m is independent of temperature.
(b) The measured Cv,m is dependent on temperature.
(c) The measured Cv,m is typically lower than the expected value.
(d) The measured Cv,m is typically higher than the expected value.
Ans. (b, c)
Sol. According to the principle of equipartition of energy states that each degree of freedom in a molecule contributes (1/2) R to the molar heat capacity at constant volume (Cv,m) where R is ideal gas constant.
For a monlinear polyatomic gas with N atoms:
No. of degree of freedom = 3N – 6
Hence, Cv,m = 3 (N – 1) R
However, in reality, the measured value of Cv,m for polyatomic gases often deviates from the expected value due to various factor such as:
(i) Intermolecular interaction
(ii) Vibrational rotational coupling
(iii) Quantum effects
These deviations are more profround at low temperature.
Hence the correct statements are that the increased Cv,m is dependent on temperature and typically lower than expected value.
38. Zinc containing enzyme(s) is/are
(a) carboxypeptidase
(b) hydrogenase
(c) carbonic anhydrase
(d) urease
Ans. (a, c)
Sol.

(b) inhydrogenase Fe and Ni metal present
(d) in urease Ni metal present
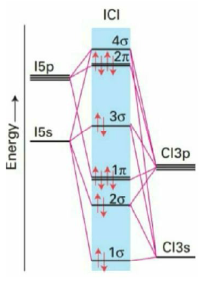
39. The conversion of ICl to ICl+ involve(s)
(a) the removal of an electron from a* molecular orbital of ICl
(b) an increase in the bond order from 1 in ICl to 1.5 in ICl+
(c) the formation of a paramagnetic species
(d) the removal of an electron from a molecular orbital localized predominantly on Cl
Ans. (a, b, c)
Sol.
40. The common point defect(s) in a solid is/are
(a) Wadsley defect
(b) Schottky defect
(c) Suzuki defect
(d) Frenkel defect
Ans. (b, d)
Sol. Point defects are the defects which exist at some lattice positions.
Schottky and Frenkel defect are point defects.
41. Among the following

the number of aromatic compounds is _______.
Ans. 5
Sol. 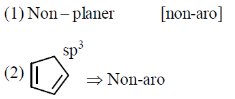


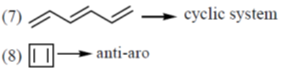
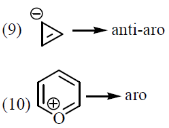

Number of aromatic compounds = 5
42. The number of stereoisomers possible for the major product formed in the reaction

is ________.
Ans. 2
Sol. 
43. The number of signals observed in the 1H NMR spectrum of the compound

is _______.
Ans. (3)
Sol. Number of signal
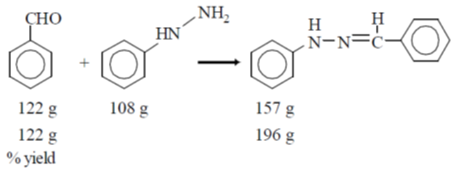
44. The reaction of 122 g of benzaldehyde with 108 g of phenylhydrazine gave 157 g of the product

The yield of the product is _______ %. (round off to the nearest integer)
Ans. (80)
Sol.

45. The B – B bond order in B2 is _______.
Ans. (1)
Sol. 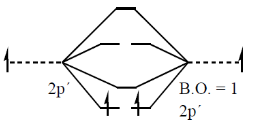
46. The number of unpaired electrons in [Co(H2O)6]2+ is _______.
Ans. 3
Sol. [Co(H2O)6]2+
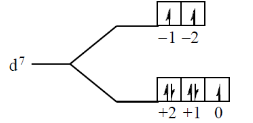
The number of unpaired electrons in [Co(H2O)6]2+ is 3.
47. The number of significant figures in 5.0820 × 102 is _______.
Ans. 5
Sol. 5.0820 × 102
Number of significant figures = 5
48. The d spacing for the first-order X-ray ( = 1.54 Å) diffraction event of metallic iron (fcc) at
= 1.54 Å) diffraction event of metallic iron (fcc) at  = 20.2º is ________ Å. (round off to three decimal places)
= 20.2º is ________ Å. (round off to three decimal places)
Ans. (4.391)
Sol. 
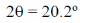
= 1 × 1.54 Å = 2 × d × sin (10.1)
d = 4.391 Å
49. The volume fraction for an element in an fcc lattice is _____. (round off to two decimal places)
Ans. 0.74
Sol.
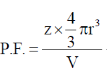
Z for FCC = 4
V = a3 (where a is edge length of cube)
also in FCC, 
After putting the values, the volume fraction for an element in an fcc lattice is 0.74.
50. A steady current of 1.25 A is passed through an electrochemical cell for 1.5 h using a 12 V battery. The total charge, Q, drawn during this process is ______ Coulombs. (round off to the nearest integer).
Ans. (6750 C)
Sol. i = 1.25 A
t = 1.5 hr
Q = i × t = 1.25 × 1.5 × 3600
= 6750 C
51. The specific rotation of optically pure (R)-1-phenylethylamine is +40 (neat, 20 °C). A synthetic sample of the same compound is shown to contain 4:1 mixture of (S)- and (R)-enantiomers. The specific rotation of the neat sample at 20 °C is _________. (round off to the nearest integer)
Ans. -24º
Sol. (R) 1-phenylethylamine = + 40º
sample 4 : 1
S : R
Specific rotation of sample = ?
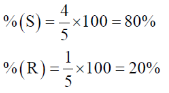
ee = 60% in (S)

= – 24º
52. The number of  particles emitted in the nuclear reaction
particles emitted in the nuclear reaction  is _____.
is _____.
Ans. (6)
Sol. 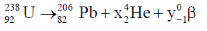
92 = 82 + 2x – y
92 – 82 = 2x – y
10 = 2x – y ... (1)
238 = 206 + 4x + 0
32 = 4x

 = 8
= 8
10 = 2x – y
10 = 2 × 8 – y
10 – 16 = – y
1 – 6 = +4
y = 6
 = 6
= 6
53. Iron is extracted from its ore via the reaction
Fe2O3 + 3 CO  2 Fe + 3 CO2
2 Fe + 3 CO2
The volume of CO (at STP) required to produce 1 kg of iron is ______ liters.
(round off to the nearest integer)
[Given: Atomic wt. of Fe = 56; assume STP to be 0 ºC and 1 atm]
Ans. (600)
Sol. Fe2O3 + 3CO  2Fe + 3CO2
2Fe + 3CO2
2 moles of Fe formed by 3 moles of CO
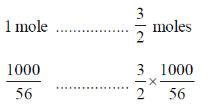
= 26.78 moles of CO
= 26.78 × 22.4 at STP
= 600 l
54. Total degeneracy (number of microstates) for a Ti3+ ion in spherical symmetry is ______.
Ans. 10
Sol. Ti3+ d1
d1
Number of microstate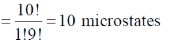
55. A galvanic electrochemical cell made of Zn2+/Zn and Cu2+/Cu half-cells produces 1.10 V at 25 ºC. The ratio of [Zn2+] to [Cu2+] is maintained at 1.0. The  for the reaction when 1.0 mol of Zn gets dissolved is ______ kJ. (round off to the nearest integer)
for the reaction when 1.0 mol of Zn gets dissolved is ______ kJ. (round off to the nearest integer)
[Given: Faraday's constant = 96485 C mol–1]
Ans. (– 212.3)
Sol. Eº = 1.1 V
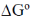 = – nFEº
= – nFEº
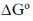 = – 2 × 96500 × 1.1
= – 2 × 96500 × 1.1
 = – 212.3 kJ
= – 212.3 kJ
56. At constant volume, 1.0 kJ of heat is transferred to 2 moles of an ideal gas at 1 atm and 298 K. The final temperature of the ideal gas is ______ K. (round off to one decimal place)
[Given: R = 8.314 J K–1mol–1]
Ans. (358)
Sol. At constant value (qp)V = 
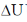 = 1.0 kJ
= 1.0 kJ
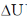 = 1000 J
= 1000 J
We know, DU = nCv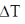
Cv = molar heat capacity at constant volume
For monoatomic gas 
For polyatomic gas  Cv = 5/2 R
Cv = 5/2 R
Since the gas is not specified, we'll assume that it's a monoatomic gas
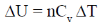
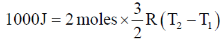 {R = 8.314 JK–1mol–1}
{R = 8.314 JK–1mol–1}
 = 60 K
= 60 K
Final temperature of ideal gas:  = T2 – T1
= T2 – T1
60 = T2 – 298
T2 = 358 K
57. Two close lying bands in a UV spectrum occur at 274 nm and 269 nm. The magnitude of the energy gap between the two bands is _____ cm–1. (round off to the nearest integer)
Ans. (678)
Sol. 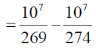
= 37174.72 – 36496.35
= 678.37
= 678.4 = 678 cm–1
58. The pH of an aqueous buffer prepared using CH3COOH and CH3COO–Na+ is 4.80.

(round off to three decimal places)
[Given: pKa of CH3COOH in water is 4.75]
Ans. (0.122)
Sol. 
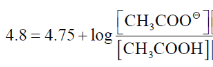
Q = 100.05 = 1.122
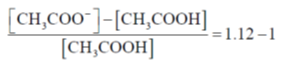
= 0.122
59. At constant temperature, 6.40 g of a substance dissolved in 78 g of benzene decreases the vapor pressure of benzene from 0.125 atm to 0.119 atm.
The molar mass of the substance is _______ g mol–1.
(round off to one decimal place)
[Given: Mol. wt. of benzene = 78 g mol–1]
Ans. (126.9)
Sol. 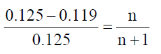
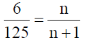
6n + 6 = 125 n
119 n = 6

M = 126.9 g mole–1
60. For a van der Waals gas, the critical temperature is 150 K and the critical pressure is 5 × 106 Pa. The volume occupied by each gas molecule is _______ Å.
(round off to two decimal places)
[Given: R = 8.314 J mol–1 K–1, NA = 6.023 × 1023]
Ans. (12.941)
Sol. 
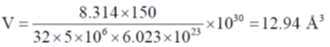
= 12.941
