IIT JAM Chemistry 2014
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
1. For square matrices M and N, if MN = M and NM = N, then:
(a) M2 = M and N2 = N
(b) 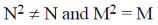
(c) 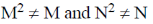
(d) 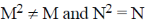
Ans. a
Sol. Given that M and N both are square matrices.
If Mn = M and NM = N
Then both M and N must be diagonal matrix.
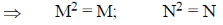
Correct answer is (a)
2. The energy of an electron in a hydrogenic atom with nuclear charge Z varies as:
(a) Z
(b) Z2
(c) 1/Z
(d) 1/Z2
Ans. b
Sol. The energy of H like species is given by 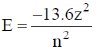
3. The carbonyl stretching frequency 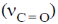 is highest for:
is highest for:
(a) 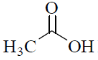
(b) 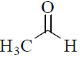
(c) 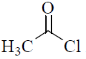
(d) 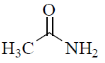
Ans. c
Sol. 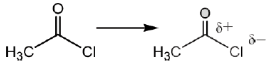
Due to –I effect of chlorine group increases the double bond character. So, option (c) having highest carbonyl stretching frequency.
Correct answer is (c)
4. The homolytic breaking of the Ca – Cb bond is easiest in:
(a) 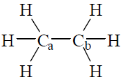
(b) 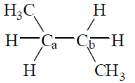
(c) 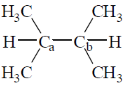
(d) 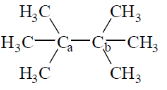
Ans. d
Sol. 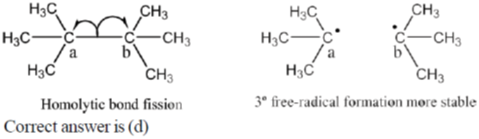
5. Tollen's test will be negative for:
(a) Glucose
(b) Mannose
(c) Sucrose
(d) Galactose
Ans. c
Sol. Tollen's reagent is oxidising agent carbohydrate which have easily oxidisable carbonyl group give positive Tollen's test by reducing it. Since, in given four sachharides sucrose is the only whose both oxidisable group are linked together by 1, 2 linkage [i.e. C-1 of glucosyl unit and C-2 of fructosyl unit]. Since, it contains no anomeric hydroxyl group; thus it is classified as non-reducing sugar. Hence, it give negative Tollen's test.
Correct answer is (c)
6. Which one among the following is a sesquiterpene?
(a) 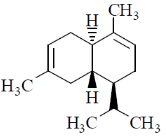
(b) 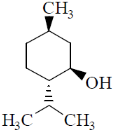
(c) 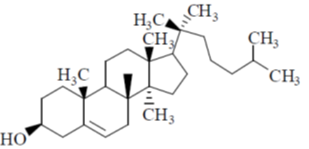
(d) 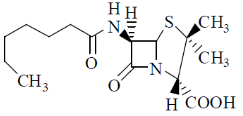
Ans. a
Sol. Terpenes have general formula (C5H8)n; when n = 3, then the terpenes is known as sesquiterpene.
Thus, sesquiterpene has formula C15H24.
In the given structure; structure a has this formula.
Correct answer is (a)
7. The predicted geometry of TeF4 by VSEPR theory is
(a) octahedral
(b) Square planar
(c) Tetrahedral
(d) Trigonal bipyramidal
Ans. d
Sol. In TeF4
Number of bond pairs = 4
Number of lone pairs = 1
Therefore, steric number = 4 + 1 = 5
Hence geometry is trigonal bipyramidal. But shape will be see-saw.
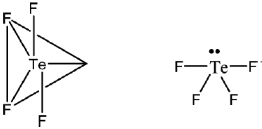
Correct answer is (d)
8. Among the following, the isoelectronic pair is
(a) NO and CO
(b) O2– (superoxide anion) and NO–
(c) NO+ and CO
(d) O2– (superoxide anion) and NO+
Ans. c
Sol. Species having equal number of electrons are known as isoelectronic species. In NO+ total electrons = 7 + 8 – 1 = 14
In CO total electrons = 6 + 8 = 14
Correct answer is (c)
9. The metal ion of an enzyme involved in hydration of CO2 is
(a) Cu(II)
(b) Fe(II)
(c) Mg(II)
(d) Zn(II)
Ans. d
Sol. The metalloenzyme carbonic anhydrase is responsible for hydration of CO2 and the said metalloenzyme have Zn2+ at their active site.
Correct answer is (d)
10. Among the following, the element having maximum inert pair effect is
[Given: Atomic number of Ge = 30, Pb = 82, Si = 14 and Sn = 50]
(a) Ge
(b) Pb
(c) Si
(d) Sn
Ans. b
Sol. Inert pair effect is reluctance in bonding capacity of ns pair of electron on moving down in the group. Down the group, Inertness of lone pair increases.
 Maximum inert = Pb
Maximum inert = Pb
11. The reactivity of compounds I-IV with maleic anhydride (V) follows the order:
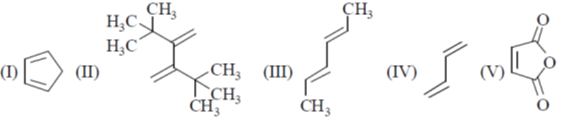
(a) I < II < III < IV
(b) II < IV < III < I
(c) II < I < III < IV
(d) II < I < IV < III
Ans. b
Sol. The reaction of Maleic anhydride with dienes is a well explored example of Diels alder reaction
For a favourable Diels Alder reaction Diene should be cis-oid confirmation.
Trans confirmation around the single bond in the diene is unfavourable for this reaction.
This conversion required very less energy if there is no steric factor involved.
The species which are locked in cis-oid confirmation i.e. in a cyclic ring are best for this reaction as diene as in I.
Thus I will be most suitable.
The Diene which contains electron donating group increases the rate of Diels Alder reaction.
The steric reason also plays here, which increases the energy for the above interconversion.
Thus IV will be least suitable because of its stable trans geometry and higher energy required for its conversion to cis due to steric bulk.
In between III and IV, III will be more suitable because of electron donating CH3 group.
Thus order will be II < IV < III < I
12. Which one among the following molecules is chiral?
(a) 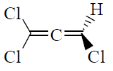
(b) 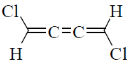
(c) 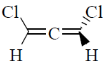
(d) 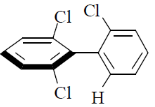
Ans. c
Sol. for allene to be optically active it should fulfill following condition.
(a) The number of double bond should be even.
(b) There should be proper substitution
Condition for proper substitution

Optically inactive (no proper substitution)

For biphenyl the substituent must be bulky to inhibit rotation.
Correct answer is (c)
13. Identify the starting material I in the given reaction
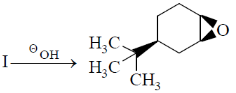
(a) 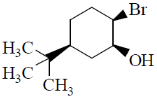
(b) 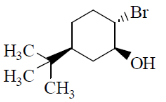
(c) 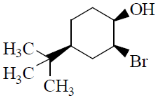
(d) 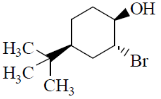
Ans. d
Sol. The epoxide formation is an intramolecular SN2 reaction and as with any SN2 substitution, inter or intramolecular, the incoming nucleophile must still attack into the 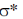 orbital of the leaving group. The only way that is possible, when both the incoming nucleophile and leaving group are trans to each other. Also they must be on axial position. Because when they will trans an thus both present at equatorial, there is no donation or attack of electron, from incoming group into the
orbital of the leaving group. The only way that is possible, when both the incoming nucleophile and leaving group are trans to each other. Also they must be on axial position. Because when they will trans an thus both present at equatorial, there is no donation or attack of electron, from incoming group into the  orbital.
orbital.
Correct answer is (d)
14. The major product for the following reaction is :
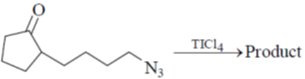
(a) 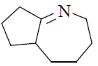
(b) 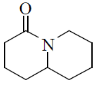
(c) 
(d) 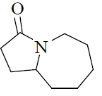
Ans. b
Sol. The chemical reaction involved in above transformation can be illustrated as
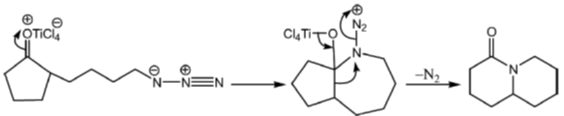
Correct answer is (b)
15. The structure of the major product in the following reaction is:
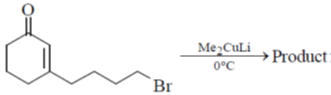
(a) 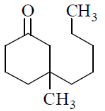
(b) 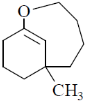
(c) 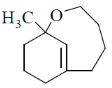
(d) 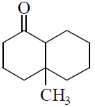
Ans. d
Sol. With Gilman reagent 1, 4 addition is favoured.
The chemical reaction involved in above transformation can be illustrated as
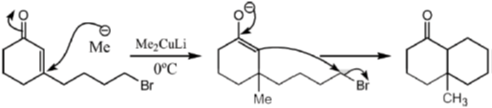
Correct answer is (d)
16. The correct orientation of dipoles in pyrrole and pyridine is
(a) 
(b) 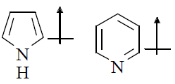
(c) 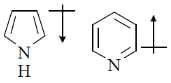
(d) 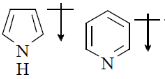
Ans. a
Sol. The direction of dipole moments is shown from positive end to negative end. In pyrrole lone pair is involved in resonance, hence, 'N' gain positive charge density.
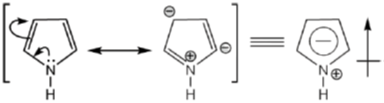
But in pyridine lone pair of nitrogen is not involved in resonance.
Hence, direction of dipole is opposite to pyrrole in case of pyridiene 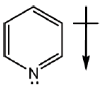
Correct answer is (a)
17. Specific rotations of freshly prepared aqueous solutions of I and II are +112 and +18.7, respectively. On standing the optical rotation of aqueous solution of I slowly decreases to give a final value of +52.7 due to equilibrium with II. Under this state of equilibrium, what is the ratio II : I?
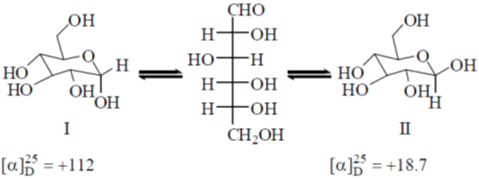
(a) 0.57
(b) 1.00
(c) 1.75
(d) 5.9
Ans. c
Sol. The 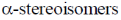 of glucose contain specific rotation +112 and
of glucose contain specific rotation +112 and 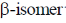 contain specific rotation +18.7.
contain specific rotation +18.7.
Let us suppose I have x fraction and thus II have (1–x) fraction present at equilibrium.
(112.2 × x) + (18.7 × (1 – x)) = 52.7
112.2x + 18.7 – 18.7x = 52.7
93.5x = 34
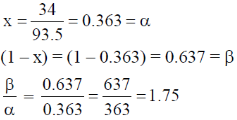
Correct answer is (c)
18. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 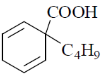
(b) 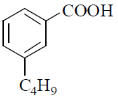
(c) 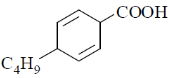
(d) 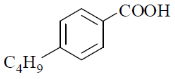
Ans. a
Sol. The chemical reaction involved in above transformation can be illustrated as
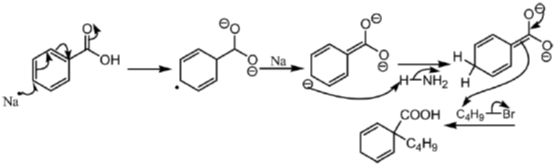
Correct answer is (a).
19. In boron neutron capture therapy, the initial boron isotope used and the particle generated after neutron capture respectively are:
(a) 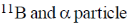
(b) 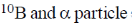
(c) 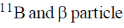
(d) 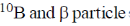
Ans. b
Sol. 10B has high absorption cross-section for thermal neutron, even for high energy neutron (104–106 eV) it is more effective than any other nuclide. The accompanying 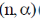 reaction produces Li and He which are non-radioactive and harmless.
reaction produces Li and He which are non-radioactive and harmless.
This fact recently has used in B-10 neutron capture therapy of brain tumours.
Correct answer is (b)
20. The number of  particle(s), generated in the following radioactive decay process, are:
particle(s), generated in the following radioactive decay process, are:
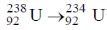
(a) 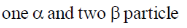
(b) 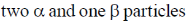
(c) 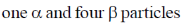
(d) 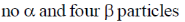
Ans. a
Sol. 
Change in A = 238 – 234 = 4.
Hence, only one 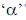 is emitted. Now increases in z = 92 – 2 + 2 = 92
is emitted. Now increases in z = 92 – 2 + 2 = 92
Hence, two 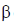 particle will be emitted
particle will be emitted
Correct answer is (a)
21. In the measurement of hardness of water by complexometric titration, identify P and Q in the following equation.
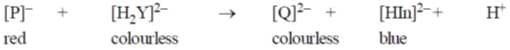
(a) P = MgY, Q = MgIn
(b) P = MgY2, Q = MgIn2
(c) P = MgIn2, Q = MgY2
(d) P = MgIn, Q = MgY
Ans. c
Sol. Hardness is determined by titration by using eriochrome-T indicator.
Uncomplexed indicator is of blue coloured and with M++ (Ca++, Mg++) complex it forms real-pink colour.
Correct answer is (c)
22. An aqueous solution of haemoglobin has a molar absorptivity value of 18,600 L mol–1 cm–1 for an absorbance value of 0.1 at 540 nm (Guiven: cell thickness = 1 cm). The concentration 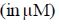 of the haemoglobin solution is
of the haemoglobin solution is
(a) 0.537
(b) 5.37
(c) 53.7
(d) 537.0
Ans. b
Sol. 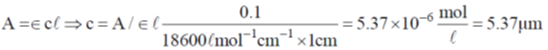
Correct answer is (b).
23. The electronic transitions responsible for the colour of K2Cr2O7 and porphine in their solid state respectively are:
(a) 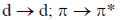
(b) 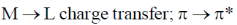
(c) 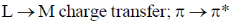
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. In K2Cr2O7 the Cr is in +6 oxidation state and it have vaccant d-orbital. Therefore, there is transfer of electron from 2p filled orbital of oxygen to vacant orbital leading to L-M-charge transfer.
Porphyrin is highly conjugated system hence the most probable transition is the transfer 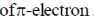 to
to 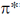 molecular orbital, which falls in the visible region of spectrum responsible for the colour of porphyrin.
molecular orbital, which falls in the visible region of spectrum responsible for the colour of porphyrin.
Correct answer is (c)
24. The correct order of M–C(M = Ti, V, Cr and Mn) bond stretching frequency is:
(Given: Atomic number of Ti = 22, V = 23, Cr = 24 and Mn = 25)
(a) [V(CO)6]– < Cr(CO)6 < [Mn(CO)6]+ < [Ti(CO)6]2–
(b) [Ti(CO)6]2– < [V(CO)6]– < Cr(CO)6 < [Mn(CO)6]+
(c) [Mn(CO)6]+ < Cr(CO)6 < [V(CO)6]– < [Ti(CO)6]2–
(d) [Mn(CO)6]+ < [V(CO)6]– < Cr(CO)6 < [Ti(CO)6]2–
Ans. c
Sol. In metal carbonyl as electron density on metal increases back donation from metal to 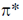 orbital of CO increases and M-C bond strength increases while C-O bond strength decreases.
orbital of CO increases and M-C bond strength increases while C-O bond strength decreases.
Electron density on metal 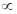 M-C bond order
M-C bond order 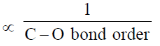
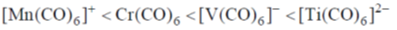
On moving left to right
Electron density increases
M-C bond order increases.
Correct answer is (c)
25. For the following reactions, the metal complexes X and Y are

(a) 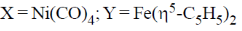
(b) 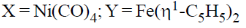
(c) 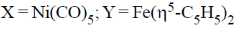
(d) 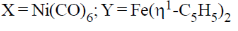
Ans. a
Sol. 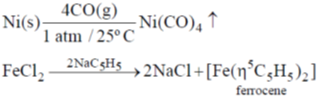
Correct answer is (a)
26. The correct order of crystal field strength is (Given: en = ethylenediamine)
(a) 
(b) 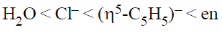
(c) 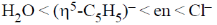
(d) 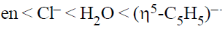
Ans. a
Sol. 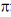 ligands are usually stronger than
ligands are usually stronger than 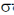 ligands.
ligands.

A pattern of increasing 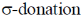 is followed halide donar < O-donar < N-donar < C-donar.
is followed halide donar < O-donar < N-donar < C-donar.
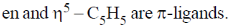
Hence, according to spectrochemical series the field strength is
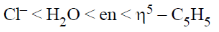
Correct answer is (a)
27. The carbon-oxygen bond in an organic compound absorbs electromagnetic radiation of frequency 6 × 1013 Hz. This frequency corresponds to the region:
(a) Infrared
(b) Microwave
(c) Ultraviolet
(d) Visible
Ans. a
Sol. The regions of the electromagnetic spectrum can be represented as
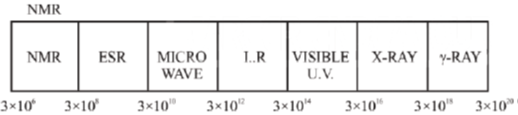
C-O bond in an organic compound absorbs electromagnetic radiation of frequency 6 × 1013 Hz. This range absorb in IR (3 × 1012 – 3 × 1014 Hz)
Correct answer is (a)
28. According to the equipartition principle of energy, the molar heat capacity at constant volume for CO2(g), SO2(g) and H2O(g) follows the trend:
(a) CO2 = SO2 = H2O
(b) CO2 > SO2 = H2O
(c) H2O > SO2 = CO2
(d) CO2 = SO2 > H2O
Ans. a
Sol. CO2 is a linear molecule
U = translational contribution + rotational contribution + vibrational contribution
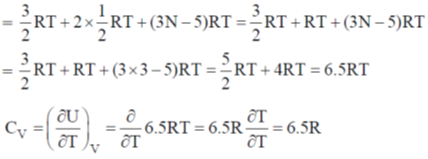
For non-linear molecule (SO2 or H2O)
U = translational contribution + vibrational contribution + rotational contribution
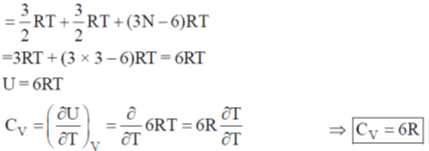
CV of linear molecule is greater than CV of non linear.
CO2 > H2O = SO2.
Hence, correct answer is (a)
29. 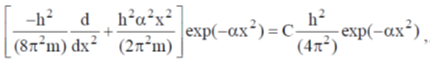 where
where 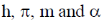 are constants.
are constants.
Then C is
(a) 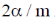
(b) 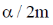
(c) 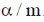
(d) 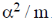
Ans. c
Sol. 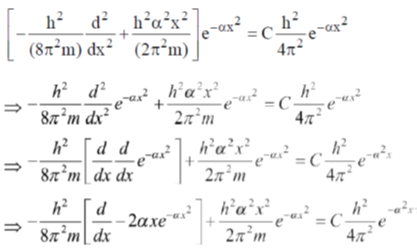

Correct option is (c)
30. Among Ar, NH4Cl, HF and HCl, the strength of interatomic / intermolecular forces follows the order:
(a) NH4Cl > HF > HCl > Ar
(b) HF > HCl > Ar > NH4Cl
(c) HCl > Ar > NH4Cl > HF
(d) Ar > NH4Cl > HF > HCl
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
31. The number of degrees of freedom in the homogeneous liquid region of a two component system with a eutectic point, at one atmosphere pressure, is:
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Ans. c
Sol. Two component with a eutectic point
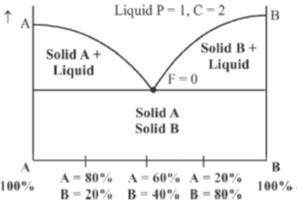
In the liquid region,
F + P = C + 1 (For two component)
F + 1 = 2 + 1
F = 3 – 1
F = 2
Correct answer is (c)
32. The ionic strength of 0.1 M aqueous solution of Fe2(SO4)3 is
(a) 0.1 M
(b) 0.65 M
(c) 1.3 M
(d) 1.5 M
Ans. d
Sol. 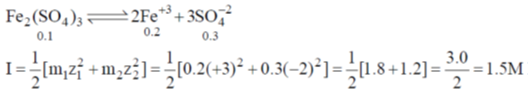
Correct option is (d)
33. If the transport number of Na+ is 0.463 (dilute solution of NaCl in methanol), the transport number of H+ (dilute solution of HCl in methanol) is:
(Given, 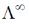 NaCl in methanol) = 96.9 ohm–1 cm2 mol–1 and
NaCl in methanol) = 96.9 ohm–1 cm2 mol–1 and 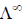 (HCl in methanol) = 192 ohm–1 cm2 mol–1)
(HCl in methanol) = 192 ohm–1 cm2 mol–1)
(a) 0.27
(b) 0.46
(c) 0.54
(d) 0.73
Ans. d
Sol. t+ of Na+ = 0.463 (dilute solution of NaCl in CH3OH)
t+ of H+ (dilute solution of NaCl in CH3OH) = ?
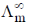 (NaCl in CH3OH) = 96.9 ohm–1 cm–1 mol–1
(NaCl in CH3OH) = 96.9 ohm–1 cm–1 mol–1
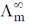 (HCl in CH3OH) = 192 ohm–1 cm–1
(HCl in CH3OH) = 192 ohm–1 cm–1
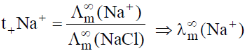 = 0.463 × 96.9 ohm–1 cm–1 mol–1
= 0.463 × 96.9 ohm–1 cm–1 mol–1
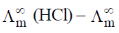 (NaCl) = (192 – 96.9) ohm–1 cm–1 mol–1 = 95.1 ohm–1 cm–1 mol–1
(NaCl) = (192 – 96.9) ohm–1 cm–1 mol–1 = 95.1 ohm–1 cm–1 mol–1
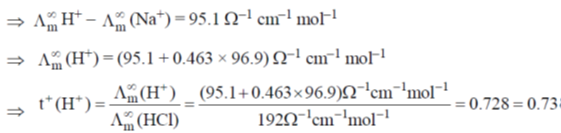
Correct answer is (d)
34. Charcoal (1 gram) of surface are 100 m2 per gram, absorbs 60 mg of acetic acid from an aqueous solution at 25ºC and 1 atmosphere pressure. The number of moles of acetic acid adsorbed per cm2 of charcoal surface is
(a) 10–2
(b) 10–6
(c) 10–5
(d) 10–9
Ans. d
Sol. 100 m2 adsorbs 60 mg, i.e. amount of acetic acid adsorbed 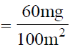
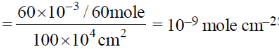
35. The change in entropy for the following transformations is respectively: (+ indicates increase, – indicates decrease and 0 indicates no change)
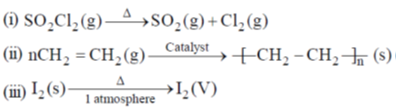
(iv) Adiabatic reversible expansion of an ideal gas
(a) +, –, 0, +
(b) +, –, 0, 0
(c) –, +, +, 0
(d) +, –, +, 0
Ans. d
Sol. 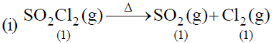
Entropy positive; one gaseous molecule form two gaseous molecule (2–1) = +ve
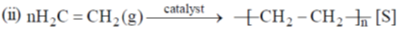
Gas to solid random ness decreases.
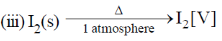
Solid to vapour randomness increases 
Correct answer is (d)
36. Using crystal field theory (CFT), for the [Co(NH3)6]3+ ion
(a) Draw the d-orbital splitting including their orbital labels (designations) and show their electron occupancy.
(b) Calculate the crystal field stabilization energy (ignore pairing energy) and spin-only magnetic moment values. (Given: atomic number of Co = 27).
Sol. In [Co(NH3)6]3+ cobalt is in +3 oxidation state i.e. Co3+ = [Ar]3d64s0
The complex is octahedral in which splitting takes place as
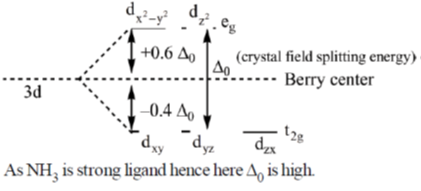
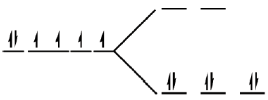
Each electron entering in t2g looses 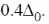 Hence, crystal field stabilisation energy will be CFSE = –(6 ×0.4)
Hence, crystal field stabilisation energy will be CFSE = –(6 ×0.4) 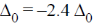
As number of unpaired electrons and zero hence spin only magnetic moment is given by
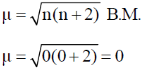
37. (a) Write the correct order of lattice energy for LiX, X = F, Cl, Br and I.
(b) A first order reflection from (111) plane is observed for LiX with 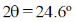 (X-ray of wavelength 1.54 Å). Assuming LiX to be a cubic crystal system, calculate the length of the side of the unit cell in Å.
(X-ray of wavelength 1.54 Å). Assuming LiX to be a cubic crystal system, calculate the length of the side of the unit cell in Å.
Sol. (a) Lattice energy depends upon effective binding small sized Li+ ion has strongest binding interaction with smaller F–. Thus lattice energy will be greatest in LiF.

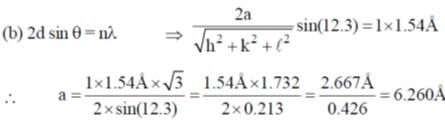
38. For the reaction:

(i) Write the expression for the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentrations of NO and H2O.
(ii) Given the following data for the above reaction, find the order of the reaction with respect to (a) NO and (b) H2 and the rate constant of the reaction along with the proper unit,
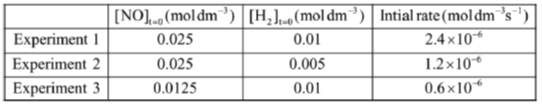
Sol. 
(i) Expression for rate of reaction in terms of change in concentration of NO and H2O is
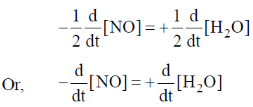
And complete rate law expression is
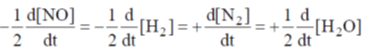
(ii) From experiment (1) and experiment (2), we observe that
On doubling the concentration of H2, rate becomes double
Therefore, order of reaction w.r.t. H2 = 1
And from experiment (1) and experiment (3), we observe that
On doubling the concentration of NO, rate becomes 4 times
Therefore, order of reaction w.r.t. NO = 2
Therefore, rate law is r = k[NO]2[H2]
From experiment (1),
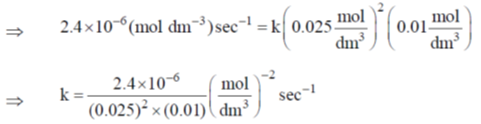
= 0.3840 mol–2 dm–6 sec–1
39. The vapour pressure of benzene is 5333 Pa at 7.6ºC and 53330 Pa at 60.6ºC. Calculate the heat of vapourization of benzene and the normal boiling point of benzene.
Sol. Since Clausius Clapeyron equation,
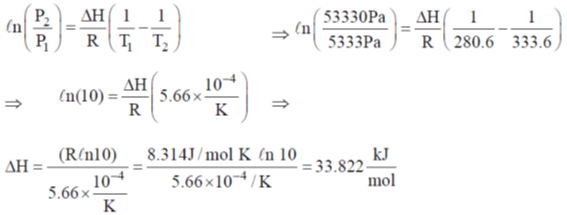


40. The following graph represents the dependence of certain properties I to V (given below) as a function of temperature.
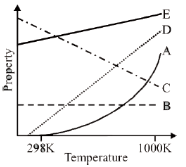
Property
I. The enthalpy change of a gas phase reaction in which the sum of the number of moles of products is greater than the sum of the number of moles of reactants
II. The osmotic pressure of an ideal solution at a given concentration
III. The standard Gibbs free energy of formation of metal oxides
IV. The molar heat capacity at constant volume for a an ideal gas, as predicted by the equipartition of energy
V. The rate constant of a reaction with Ea = 100 kJ mol–1
The lines / curves A, B, C, D and E corresponding to the appropriate property are:
Sol. 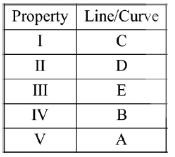
41. Draw the structure A-E for the given transformation:
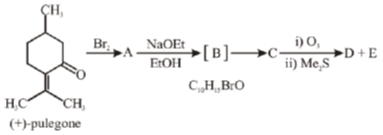
Sol. 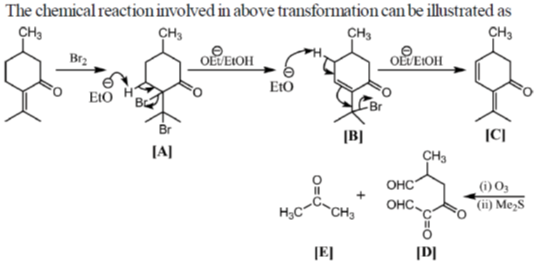
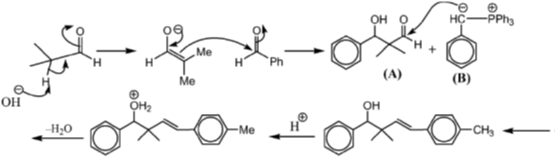
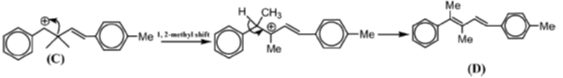
42. In the reaction sequence given below, draw the structure of A, C, D and reagent B.
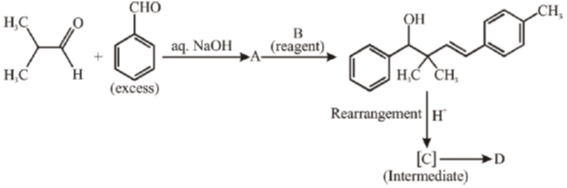
Sol. The chemical reaction involved in above transformation can be illustrated as
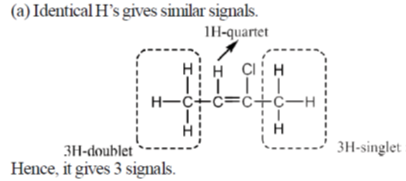
43. (a) How many 1H NMR signals are expected for 2-chlorobut-2-ene? (ignore spin-spin coupling)
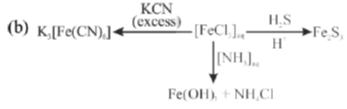
(b) Write down the iron containing chemical species, E, F and G in the following reactions.
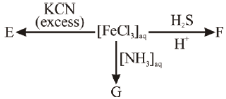
Sol.