GATE Chemistry 2016
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
1. [CpMoCl2]2 obeys the 18 electron rule. The correct structure of this compound is (atomic number of Mo = 42)
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. According to 18 electron count of neutral atom method ;
Unit Contribution of electron
M–M bond (Mo–Mo) 2
Bridging halogen (Mo–Cl–Mo) 3
Mo 6
Cp 5
Hence, 2Mo atom
 2 × 6 = 12 e–
2 × 6 = 12 e–
4μ2–Cl  4 × 3 = 12 e–
4 × 3 = 12 e–
2Cp  2 × 5 = 10 e–
2 × 5 = 10 e–
One (Mo–Mo) bond  1 × 2 = 2 e–
1 × 2 = 2 e–
36 e–
Hence, Per Mo  18 electron
18 electron
Correct option is (c)
2. During oxygen transport by hemerythrin, oxygen is bound as
(a) O2– to one Fe(III) only
(b) HO2– to one Fe(III) only
(c) O22– to one Fe(II) and one Fe(III)
(d) O22– to two Fe(II)
Ans. (b)
Sol. During oxygen transport by hemerythrin, oxygen is bound as HO2– to one Fe(III) only
Correct option is (b)
3. Among the following, the most stable isotope to radioactive decay is
(a) 
(b) 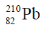
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. Lead (Pb) has four stable isotopes :
204Pb, 206Pb, 207Pb, 208Pb, 204Pb is entering a primordial nuclide and is not a radiogenic nucldie
Correct option is (a)
4. At pH 7.2 and 10 Torr oxygen partial pressure, the extent of O2 binding is
(a) high for both haemoglobin and myoglobin
(b) high for haemoglobin and low for myoglobin
(c) high for myoglobin and low for haemoglobin
(d) low for both haemoglobin and myoglobin
Ans. (c)
Sol. At low pH and low pressure Hb has less oxygen binding tendency. While for Mb is more oxygen binding tendency.
Correct option is (c)
5. In the first row high-spin transition metal complexes [M(H2O)6]Cl2 with d5 and d7 metal ions, the d-d transitions are
(a) spin-forbidden for both
(b) spin-allowed for both
(c) spin-forbidden for d5 and spin-allowed for d7
(d) spin-allowed for d5 and spin-forbidden for d7
Ans. (c)
Sol.  , high spin complex with d5 configuration
, high spin complex with d5 configuration


[M(H2O)6]Cl2 with d7 configuration is spin allowed and with d5 spin forbidden.
Correct option is (c)
6. Among the given boranes and heteroboranes, the example which belongs to 'closo' type is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) GeC2B9H11
(d) B6H10
Ans. (c)
Sol. Hetero atom Replace with
C, Si, Ge, Sn BH
N, P, As BH2
S, Se BH3
(a) B5H8– is derived from B5H54–, a nido speices
(b) [C2B9H11]2– is equivalent to B11H13–2, derived from B11H11–4, a nido speices
(c) GeC2B9H11 is equivalent to B12H14 is derived from B12H122–, a closo speices
(d) B6H10 is derived from B6H64–, a nido speices
Correct option is (c)
7. The reaction of P2O5 with HNO3 and HClO4, respectively, gives
(a) NO2 and ClO2
(b) N2O5 and Cl2O6
(c) N2O3 and Cl2O7
(d) N2O5 and Cl2O7
Ans. (d)
Sol. 

8. When crystals of sodium chloride are heated in the presence of sodium vapor, they turn yellow. This is due to the formation of
(a) Schottky defects
(b) Frenkel defects
(c) F-centres
(d) H-centres
Ans. (c)
Sol. When crystals of sodium chloride are heated in the presence of sodium vapour they turn yellow due to the formation of F-centres.
Correct option is (c)
9. One mole of an ideal gas is comlpressed from 5L to 2L at constant temperature. The change in entropy, in JK–1, of the gas is ____________. (R = 8.314 JK–1 mol–1)
Ans. (–7.61)
Sol. 

Correct answer is (–7.61)
10. The linear momentum of a particle described by the wavefunction e–ikx is
(a) kh
(b) –kh
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. Linear momentum = 


Correct option is (d)
11. For an elementary bimolecular gas phase reaction, activation energy is 5.5 kJ mol–1. Enthalpy of activation, in kJ mol–1, at 300K is ________. (R = 8.314 JK–1 mol–1)
Ans. (0.5116 kJ/mole)
Sol. Enthalpy of activation,

12. The titration of a strong acid with a strong base is represented by the plot
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. For strong acid vs strong base E = E0 + 0.0591 pH.
Plot of E vs volume of base will have same shape as  volume
volume
Similarly, for other plots too.

Correct option is (c)
13. Of the following inequalities, the criteria for spontaneity of a chemical reaction is/are

(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Ans. (d)
Sol. Correct criterion, is 

Correct option is (d)
14. A protein sample consists of an equimolar mixture of ribonuclease (molar mass = 13.7 kg mol–1), hemoglobin (molar mass = 15.5 kg mol–1), and myoglobin (molar mass = 17.2 kg mol–1). The statement that is true about the weight-average molar mass  , the number-average molar mass
, the number-average molar mass  , and the polydispersity index (PDI) for this sample is
, and the polydispersity index (PDI) for this sample is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. M1 = 13.7
M2 = 15.5 
M3 = 17.2
N1 = N2 = N2 = N

P.D.I. = 
Correct option is (a)
15. The band structure given below represent a

(a) n-type semiconductor formed by doping Si with B
(b) n-type semiconductor formed by doping Si with P
(c) p-type semiconductor formed by doping Si with P
(d) p-type semiconductor formed by doping Si with B
Ans. (d)
Sol. p-type semiconductor formed by doping Si with B
Correct option is (d)
16. The experimental ionization energies of hydrogen and helium atoms in their ground states are, respectively, 13.6 eV and 24.6 eV. The ground state energy of helium atom, in eV, is
(a) 
(b) –4(13.6) – 24.6
(c) 
(d) –2(13.6) – 24.6
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
I.p. hydrogen = 13.6 V
I.p. Hecting = 24.6 eV
Ground state for He = –4(13.6) – 24.6
Correct option is (b)
17. Ring flipping of the compound in the following conformation leads to

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
On ring flipping axial bond convert into equatorial and quatorial convert into axial bond.
Correct option is (b)
18. The total number of lines expected (due to spin-spin coupling of proton with fluorine and deuterium nuclei) in the 1H NMR spectrum of the following compound is ___________.

Ans. (6)
Sol. 
multiplicity [2NIF + 1] [2NID + 1]

Correct answer is (6)
19. The compound in 'R' configuration is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
20. The most suitable reagent for performing the following transformation, is

(a) LiAlH4
(b) H2, Pd/C
(c) PPh3, H2O
(d) Li, Liq. NH3
Ans. (c)
Sol.

Staudinger reaction, it does not affect the other functional groups.
Correct option is (c)
21. The major product obtained in the following reaction, is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol.

22. The Favourable transition state leading to the formation of the product in the following reaction, is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol.

Correct option is (d)
23. The major product of the following reaction is,

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans.
Sol.

Correct option is (d)
24. The major product obtained in the following reaction, is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol.
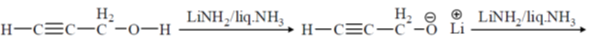


Correct option is (a)
25. The major product formed in the following reaction, is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
26. The Larmor frequency of 1H at 1 Tesla (T) is 42.57 MHz. If the magnetogyric ratios for 1H and 13C are 26.75 × 107 rad T–1 s–1 and 6.72 × 107 rad T–1 s–1, respectively, the Larmor frequency of 13C, in MHz, at 1 Tesla will be ___________
Ans. (10.6)
Sol. 

Correct answer is (10.6)
27. At 1 bar and 298K, for the process  , the
, the  is 200 J mol–1 and
is 200 J mol–1 and  is –2×10–6 m3 mol–1. The minimum pressure, in bar, at which the process becomes spontaneous at 298K is _______. (1 bar = 105 Pa).
is –2×10–6 m3 mol–1. The minimum pressure, in bar, at which the process becomes spontaneous at 298K is _______. (1 bar = 105 Pa).
Ans. (1001)
Sol. 

For reaction to be spontaneous  < 0
< 0
or to find minimum pressure at which reaction become spontaneous, we can put  = 0
= 0
 = Vm (P2 – P1)
= Vm (P2 – P1)
 0 – 200 = – 2 × 10–6 (P2 – 105)
0 – 200 = – 2 × 10–6 (P2 – 105)
 108 = P2 – 105
108 = P2 – 105
 P2 = 105 + 108
P2 = 105 + 108
 P2 = 105 (1 + 1000) Pa
P2 = 105 (1 + 1000) Pa
 P2 = 1001 × 105 Pa = 1001 bar
P2 = 1001 × 105 Pa = 1001 bar
Correct answer is (1001)
28. The reaction,  , is first order in both the directions. The forward and reverse rate constants are and 1.04×10–3s–1, respectively. The relaxation time for this reaction, in seconds, in a temperature jump experiement is ___________
, is first order in both the directions. The forward and reverse rate constants are and 1.04×10–3s–1, respectively. The relaxation time for this reaction, in seconds, in a temperature jump experiement is ___________
Ans. (684.93)
Sol. 
K1 = 4.2 × 10–4 s–1 ; K2 = 1.04 × 10–3s–1

29. Adsorption of CO on charcoal at 273K follows Langmuir isotherm. A plot of P(kPa)/V(cm3) versus P (kPa) is linear with a slope of 0.01 y-intercept of 0.5. The equilibrium constant, K (kPa–1), for the adsorption is __________.
Ans. (0.02)
Sol. 

or K = 0.02
Correct answer is (0.02)
30. For the following reaction,

if steady state approximation can be applied on [I], the observed rate constant of product formation, in L mol–1 s–1, will be __________
Ans. (100)
Sol. 



So, rate constant of product formation is 

Correct answer is (100)
31. The correct set of infra-red spectral bands (in cm–1) for the  stretching mode of the given carbonyl complex is
stretching mode of the given carbonyl complex is

(a) 1827, 1783, 1766
(b) 1973. 1827, 1794
(c) 1833, 1775, 1650
(d) 1960, 1918
Ans. (a)
Sol. All carbonyl are µ2-bridging and range of bridging 1720 – 1850 cm–1
Correct option is (a)
32. The 19F NMR spectrum of ClF3 when measured at –60ºC will be observed as a
(a) singlet
(b) doublet
(c) doublet and triplet
(d) doublet of doublet and a doublet of triplet
Ans. (c)
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
33. Among the given platinum(II) complexes, the one that is thermally the most unstable is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. In contrast to s, p block metal, transition metal possess vaccant d-orbital which involve kinetically facile reaction such as  -H elimination, alkene insertion, etc. which leads to transformation of alkyl ligand into other group.
-H elimination, alkene insertion, etc. which leads to transformation of alkyl ligand into other group.
Hence, compound which have  -hydrogen w.r.t. metal are unstable.
-hydrogen w.r.t. metal are unstable.
Correct option is (c)
34. The shapes of XeF5+ and XeF5–, respectively, are
(a) pentagonal planar and square pyramidal
(b) pentagonal planar and trigonal bipyramidal
(c) square pyramidal and pentagonal bipyramidal
(d) square pyramidal and pentagonal planar
Ans. (d)
Sol.

Correct option is (d)
35. Sodium salt of pseudohalogens, X, Y and Z form colorless solutions in water. Solution of X decolorizes I3– solution with brisk effervescence. Solution of Y gives an intense red colour on reaction with Fe3+ solution. Solution of Z gives an intese blue color on reaction with a solution containing Fe3+ and Fe2+ ions. The pseudohalogens X, Y and Z respectively are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
36. On reacting 1.55g of a diol with an excess of methylmagnesium iodide, 1.12L (corrected to STP) of methane gas is liberated. The molecular mass (g mol–) of the diol is _________
Ans. (62)
Sol. di – ol + excess MeMgBr  2CH4
2CH4
Mg(molecular weight) = 2 × 22.4L CH4

Correct answer is (62)
37. The structure of the compound having the following characteristics spectral data, is IR : 1690 cm–1.
1H-NMR : 1.30 (3H, t, J = 7.2 Hz); 2.41 (2H, q, J = 7.2 Hz); 2.32 (3H, s); 7.44 (1H, t, J = 7.0 Hz); 7.57 (1H, dt, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz); 7.77 (1H, t, J = 3.0 Hz); 7.90 (1H, dt, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz); EI mass : m/z 119 (100%); 57 (80%)
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol.

Correct option is (a)
38. The major products X and Y formed in the following formed in the following synthetic scheme, are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol.


Correct option is (b)
39. The major product S and T formed in the following synthetic schemem, are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol.



Correct option is (a)
40. Among the following, the transformation(s) that can be accomplished using umpolung concept is(are)


(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (i) and (ii)
Ans. (d)
Sol. "Umpolung concept" polarity inversion in organic chemistry is the chemical modification of a functional group with the aim of the reversal of polarity of that group.
Correct option is (d)
41. A disaccharide does NOT give a positive test for Tollen's reagent. Upon acidic hydrolysis, it gives an equimolar mixture of two different monosaccharides, both of which can be oxidized by bromine water. This disaccharide is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. Disaccharide (a), (c) and (d) have glycose linkages at both the anomeric carbons, hence they give negative Tollen's test. While as disaccharide (b) gives positive Tollen's test. Upon hydrolysis disaccharide (a) is hydrolysed into D-glucose and D-fractose. While as disaccharide (c) is converted into 2-moles of D-glucose. Disaccharided upon hydrolysis is converted in D-glucose and D-galactose both of which gives Br2/H2O test.
Correct option is (d)
42. The major products M and N in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol.


Correct option is (a)
43. The major products P and Q in the following reaction sequence, are

(a) 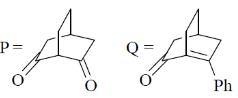
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol.



Correct option is (c)
44. The major product formed in the following reaction, is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol.

45. The following synthetic transformation can be achieved using

Reagents:
(p) (i) NH2OH/H+, (ii) H2SO4
(q) NH3/H+
(r) (i) NH2OH/H+, (ii) NaOH
(a) p only
(b) p and q
(c) q and r
(d) r only
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
(P) = Beckmann rearrangement
(Q) = Schimst reaction
Correct option is (b)
46. Consider a two-state system at thermal equilibrium with equal degeneracy where the excited state is higher in energy than the ground state by 0.1 eV. The ratio of the population of the excited state to that of the ground state, at a temperature for which kBT = 0.05 eV, is __________
Ans. (0.1353)
Sol. 


47. Of the vibrational modes given below, the IR active mode(s) is(are)

(a) (ii) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Ans. (d)
Sol. 

Correct option are (ii) and (iii)
Correct option is (d)
48. A system is described by the following real wave function.

The probability (P) of finding the particle in a region dx around points I, II and III in the figure obeys the trend
(a) P(I) > P(II) > P(III)
(b) P(II) > P(III) > P(I)
(c) P(II) > P(I) > P(III)
(d) P(III) > P(I) > P(II)
Ans. (b)
Sol.

More  region more probability, (P) II > III > I
region more probability, (P) II > III > I
Correct option is (b)
49. The temperature-composition (T-x) phase diagram of the two-component system made of X and Y is given below. At a temperature of 288K and starting at the point P, Y is added until the composition reaches S. Which of the following statements is NOTR TRUE?

(a) At P, the solid and liquid are present in almost equal proportions
(b) At Q, the system is all liquid
(c) At S, the system has more solid than liquid
(d) At R, the liquid is pure X
Ans. (d)
Sol. At R, Y(s) + liquid is present
Correct option is (d)
50. For a system subjected to only P-V work, entropy is given by

(a) I and II
(b) I and IV
(c) I only
(d) II only
Ans. (b)
Sol. dG = – SdT + VdP dA = – SdT – PdV

Correct option is (b)
51. According to Irving-Williams series, the number of d electrons for the first row transition metal (M) ion having the highest overall stability constant (log  ) for [M(EDTA)]2– is ___________
) for [M(EDTA)]2– is ___________
Ans. (9)
Sol. For M2+ ions, the general trend in stability for complexes is,

This trend in stability is known as Irving-Williams series.
Hence, Cu2+ is more stable than other first row transition metals.
Therefore, the number of d-electrons for the first transition metal (M), i.e. Cu2+ ion having the highest overall stability constant (log  ) for [M(EDTA)]2– is 9.
) for [M(EDTA)]2– is 9.
Correct answer is 9.
52. The magnitude of the difference in the crystal field stabilization energies, in  (irnoring pairing energy), of
(irnoring pairing energy), of  and
and  is __________
is __________
Ans. (2.0  )
)
Sol. 







53. The calculated and observed magnetic moments differ considerably for an aqua complex of a Lanthanide (III) ion as a result of low lying states of high J. The ion, among the following, is
(a) Ce3+
(b) Pr3+
(c) Eu3+
(d) yb3+
Ans. (c)
Sol. The calculated magnetic moments for lanthanides have good agreement with observed values. For lanthanoids the value of  is about 1000 cm–1. However, λ value for Eu3+ is about 100 cm–1 which is small value. Therefore, the agreement for Eu3+ is not very good.
is about 1000 cm–1. However, λ value for Eu3+ is about 100 cm–1 which is small value. Therefore, the agreement for Eu3+ is not very good.
Correct option is (c)
54. In the electronic spectra of [CrF6]3–, absorption bands observed at 670, 440 and 290 nm are, respectively, due to the transitions.
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. In the electronic spectra of [CrF6]3– show three transition.


Correct option is (d)
55. Amongst the following, the group that is bound to the metal ion in coenzyme B12 is
(a) methyl
(b) cyanide
(c) adenosyl
(d) hydroxyl
Ans. (c)
Sol. The group that is bound to the metal ion in co-enzyme B12 is adenosyl
Correct option is (c)
