GATE Chemistry 2013
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
1. The point group symmetry of  is
is
(a) D2h
(b) C2h
(c) C2v
(d) D2d
Ans. (d)
Sol. CH2 = C = CH2
 point group (D2d point group)
point group (D2d point group)
Correct option is (d)
2. Two trial wave function 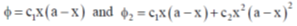 give ground state energies E1 and E2, respectively, for the microscopic particle in a 1 – D box by using the variation method. If the exact ground state energy is E0, the correct relationship between E0, E1 and E2 is:
give ground state energies E1 and E2, respectively, for the microscopic particle in a 1 – D box by using the variation method. If the exact ground state energy is E0, the correct relationship between E0, E1 and E2 is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. A trial wave function that can be expressed as a linear combination of 2 variational parameter leads to variational minimum energy E0 < E2 < E1
Correct option is (c)
3. The ground state energies of H atom and H2 molecule –13.6 eV and –31.7 eV, respectively. The dissociation energy of H2 is ___________ eV.
Ans. (4.5)
Sol. H2 + dissociation energy = 2 h atom
–31.7eV + dissociation energy = 2 × (–13.6)
Dissociation energy = + 31.7 – 27.2 = 4.5

4. A 2 L vessel containing 2g of H2 gas at 27ºC is connected to a 2L vessel containing 176 g of CO2 gas at 27ºC. Assuming ideal behaviour of H2 and CO2, the partial pressure of H2 at equilibrium is _______ bar.
Ans. (6.2325)
Sol. Vtotal = 4L


5. Consider the reaction,  at equilibrium,
at equilibrium,
The equilibrium can be shifted towards the forward direction by
(a) Increasing the amount of carbon in the system
(b) Decreasing the volume of the system
(c) Decreasing the pressure of the system
(d) Increasing the temperature of the system
Ans. (c)
Sol. According to L.C. principles, On decreasing pressure shifts in the direction in which the number of gaseous molecules increases.
Correct option is (c)
6. A sparingly soluble electrolyte M2X ionizes as 
The solubility product (Ksp), molal solubility (S) and molal activity coefficient  are related by
are related by
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
When actually in the form of ion is ksp

7. For the first order consecutive reaction,  under steady state approximation to [Q], the variation of [P], [Q] and [R] with time are best represented by
under steady state approximation to [Q], the variation of [P], [Q] and [R] with time are best represented by
(a) 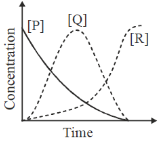
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. The concentration of the component which is present in steady practicaly remains constant except at the very begining and at the very end.
Correct option is (c)
8. At 273 K and 10 bar, the langmuir adsorption of a gas on a solid surface gave the fraction of surface coverage as 0.01. The Langmuir adsorption isotherm constant is ___________ bar–1.
Ans. (0.001)
Sol. 

Correct option is (0.001)
9. Conversion of boron trifluoride to tetrafluoroborate accompanies
(a) Increase in symmetry and bond elongation
(b) Increase in symmetry and bond contraction
(c) Decrease in symmetry and bond contraction
(d) Decrease in symmetry and bond elongation
Ans. (a)
Sol. In BF3, 'B' is sp3 hybridised and there is B–F  back donation, due to which B–F bond order increases and hence bond length decreased. B–F bond length is 130 pm.
back donation, due to which B–F bond order increases and hence bond length decreased. B–F bond length is 130 pm.
Also BF3 is trigonal planar.

In BF4– (tetra fluoro borate) 'B is sp3 hybridised and there is no back donation. Hence B–F bond order is one. [BF4]– perfect Td.

Correct answer is (a)
10. The correct statement with respect to the bonding of the ligands, Me3N and Me3P with the metal ions Be2+ and Pd2+ is,
(a) The ligands bind equally strong with both the metal ions as they are dicationic
(b) The ligands bind equally strong with both the metal ions as both the ligands are pyramidal
(c) The binding is stronger for Me3N with Be2+ and Me3P with Pd2+
(d) The binding is stronger for Me3N with Pd2+ and Me3P with Be2+
Ans. (c)
Sol. According to HSAB concept (Pearson theory)
Hard acid has a tendency to combine with hard base in order to give the stable product. Hence bond is stronger.

Correct answer is (c)
11. A crystal has the lattice parameters  The crystal system is
The crystal system is
(a) Tetragonal
(b) Monoclinic
(c) Cubic
(d) Orthorhombic
Ans. (d)
Sol. A crystal has the lattice parameters  The crystal system is orthorhombic.
The crystal system is orthorhombic.
Correct option is (d)
12. The by – product formed in the characteristic reaction  is
is
(a) CO
(b) MeOH
(c) MeCHO
(d) MeCONH2
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
Fischer carbene, Carbene carbon is electrophilic in nature
Correct option is (b)
13. The catalyst and co – catalyst used in Wacker process, respectively, are
(a) PdCl2 and Cu
(b) CuCl2 and [PdCl4]2–
(c) Pd and CuCl
(d) [PdCl4]2– and CuCl2
Ans. (d)
Sol. The [PdCl4]2– (cat) can be removed by reaction with CuCl2 (Co Catalyst)

Correct answer is (d)
14. Oxymyoglobin Mb(O2) and oxhyhemoglobin Hb(O2)4, respectively, are
(a) Paramagnetic and paramagnetic
(b) Diamagnetic and diamagnetic
(c) Paramagnetic and diamagnetic
(d) Diamagnetic and paramagnetic
Ans. (b)
Sol. Oxymyglobin Mb(O2)


Due to antiferromagnetic coupling it is diamagnetic in nature.
Correct option is (b)
15. Hapticity of cycloheptatriene in is __________
Ans. 6
Sol. Mo(C7H8) (CO)3
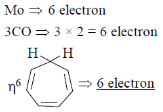
18electron
To follow stable 18 electron rule the heptacity of C7H8 
Correct option is (6)
16. The number of oxygen molecule (s) that a molecule of hemerythrin can transport is ________
Ans. 1
Sol. 
Thus, number of dioxygen molecule transported by one hemerythrin is one
Correct answer is (1)
17. The maximum number of stereoisomers possible for the compound given below is __________

Ans. 4
Sol. 
Correct answer is 4
18. The correct sequence of the amino acids present in the tripeptide given below is

(a) Val – Ser – Thr
(b) Val – Thr – Ser
(c) Leu – Ser – Thr
(d) Leu – Thr – Ser
Ans. (a)
Sol. 


So, the correct sequence of the tripeptide is val–ser–thr
Correct option is (a)
19. Among the compounds given in the options (a) – (b), the one that can be used as a formyl anion equivalent (in the presence of a strong base) is:
(a) ethylene
(b) nitroethane
(c) 1, 3 – dithiane
(d) 1, 4 – dithiane
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
Correct answer is (c)
20. The major product formed in the reaction given below is:

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. 

Correct answer is (d)
21. The major product formed in the reaction given below is:

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
Correct answer is (a)
22. The pericyclic reaction given below is an example of

(a) [1, 3] – sigmatropic shift
(b) [1, 5] – sigmatropic shift
(c) [3, 5] – sigmatropic shift
(d) [3, 3] – sigmatropic shift
Ans. (d)
Sol. It is an example of 3, 3-sigmatropic shift.

Correct option is (d)
23. The major product formed in the reaction of quinoline with potassium amide (KNH2) in liquid ammonia is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. It is an example of chichibabin reaction

Correct answer is (b)
24. The number of signals that appear in the proton decoupled 13C NMR spectrum of benzonitrile (C7H5N) is _________.
Ans. (5 to 5)
Sol. 
So, the pronton decopled 13C NMR is 5.

Correct answer is (5 to 5)
25. Among the compound given in the option (a) to (d), the one that exhibits a sharp band at around 3300 cm–1 in the IR spectrum is:
(a) 1, 2 – butadiene
(b) 1, 3 – butadiene
(c) 1 – butyne
(d) 2 – butyne
Ans. (c)
Sol. 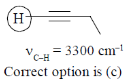
26. In the metathesis reaction given below, 4.32 g of the compound X was treated with 822 mg of the catalyst Y to yield 2.63 g of the product Z. The mol% of the catalyst Y used in this reaction is ___________ [Atomic weights of Ru = 101; P = 31; Cl = 35.5]
Ans. (5)
Sol. 4.32 of compound (X) 

The mol% of the catalyst Yused in this reaction 
= 0.05 × 100% = 5%
0.02 >> 10–3, it can be neglected.
Correct option is (5)
27. An organic compound Q exhibited the following spectral data:
IR: 1760 cm–1

Compound Q is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
Correct answer is (a)
28. The major product formed in the Beckmann rearrangement of the compound given below is:

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
Correct answer is (d)
29. The major product formed in the reaction given below is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
(Example of Pinacole-Pinacole rearrangement)

30. The major product formed in the reaction given below is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
Correct answer is (d)
31. The major product (s) formed in the reaction sequence given below is/are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 

Correct answer is (a)
32. Match the compound in the Column – I with photochemical reactions that they can undergo given in the Column – II:


(a) (i) – (q); (ii) – (s); (iii) – (p)
(b) (i) – (r); (ii) – (p); (iii) – (s)
(c) (i) – (p); (ii) – (r); (iii) – (q)
(d) (i) – (r); (ii) – (q); (iii) – s)
Ans. (b)
Sol. 


33.  is an eigen function on the operator
is an eigen function on the operator  The corresponding eigen value is
The corresponding eigen value is
(a) +4
(b) –4
(c) +2
(d) –2
Ans. (b)
Sol. Eigen function 

For eigen value function operate by operator

Eigenvalue = –4
Correct option is (b)
34. The infrared spectrum of HCl gas shows an absorption band centered at 2885 cm–1. The zero point energy of HCl molecule under hamonic oscillator approximation is:
(a) 2.866 × 10–22 J
(b) 2.8665 × 10–20 J
(c) 5.7330 × 10–22 J
(d) 5.7330 × 10–20 J
Ans. (b)
Sol. For harmonic oscillator every band gap is 


35. For the reaction  given the values,
given the values,  = 84 J K–1,
= 84 J K–1, 
(a) –11.08 kJ
(b) + 11.08 kJ
(c) – 13.55 kJ
(d) + 13.55 kJ
Ans. (a)
Sol. 


 = 13.955 kJ – 298 × 0.84 = 13.955 kJ – 25.032 kJ = –11.08 kJ
= 13.955 kJ – 298 × 0.84 = 13.955 kJ – 25.032 kJ = –11.08 kJ
Correct option is (a)
36. The change in enthalpy when 3 mol of liquid benzene transforms to the vapour state at its boiling temperature (80ºC) and at 1 bar pressure is ____________ kJ.
Ans. (92.13)
Sol. 
For 3 mole = 92.1 3 kJ
Correct option is (92.13)
37. The moment of iertia of a homonuclear diatomic molecular is 7.5 × 10–45 kg m2. Its rotational partition function at 500 K is___________.
Ans. (4649.5)
Sol. I = 7.5 × 10–45 kgm–2




38. For a reaction of the type  the correct rate expression is ([X]0 and [X] corresponds to the concentration of X at time t = 0 and t = t, respectively)
the correct rate expression is ([X]0 and [X] corresponds to the concentration of X at time t = 0 and t = t, respectively)
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 


Correct option is (b)
39. The temperature dependence of partition are as follows:


According to the Conventional Transition State Theory (CTST), the temperature dependence of the Arrhenius pre – exponential factor for a reaction of the type given below is
linear molecule + linear molecule  non – liner linear transition state
non – liner linear transition state 
(a) T–1
(b) T0
(c) T1
(d) T2
Ans. (a)
Sol. 

Arrhenius pre-exponential factor


Correct answer is (a)
40. Decarbonylation reaction of [cis – (CH3CO) Mn (13CO)(CO)4] yields X, Y and Z, where X = [(CH3) Mn (CO)5]; Y = [cis – (CH3) Mn (13CO) CO4]; [Z = trans – (CH3) Mn (13CO) (CO)4]
The molar ratio of the products (X : Y : Z) in this reaction is
(a) 1 : 1 : 1
(b) 1 : 2 : 1
(c) 1 : 1 : 2
(d) 2 : 1 : 1
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
Correct answer is (b)
41. According to polyhedral electron count rule, the structure of Rh6(CO)16 is:
(a) closo
(b) nido
(c) arachno
(d) hypo
Ans. (a)
Sol. Rh6 (CO)16

Polyhedral electron cont (PEC) = 86 – 6 × 12 = 14

42. The increasing order of melting points of the halides NaCl, CuCl and NaF is:
(a) CuCl < NaCl < NaF
(b) NaF < NaCl < CuCl
(c) NaF < CuCl < NaCl
(d) CuCl < NaF < NaCl
Ans. (a)
Sol. In NaCl CuCl

In NaF and NaCl, 'Cl–' is of bigger size than F– hence Cl– will be easily polarisable than F–. Due to this NaCl will have more polarisation, more co-valent character (Fajan rule) and lower melting point.
Therefore, overall order of melting point will be
CuCl < NaCl < NaF
Correct option is (a)
43. The correct electronic configuration and spin only magnetic moment of Gd3+ (atomic number 64) are
(a) [Xe]4f7 and 7.9 BM
(b) [Xe]4f7 and 8.9 BM
(c) [Xe]4f65d1 and 7.9 BM
(d) [Rn]5f7 and 7.9 BM
Ans. (a)
Sol. Electronic configuration of Gd3+ = [Xe]4f 7



Correct option is (a)
44. Among the following octahedral complexes, the one that has the highest enthalpy of hydration is
(a) [Ca(H2O)6]2+
(b) [Mn(H2O)6]2+
(c) [V(H2O)6]2+
(d) [Cr(H2O)6]2+
Ans. (c)
Sol. [V(H2O6)]2+ has V2+ metal having 3d3 electronic configuration due to which it has maximum negative value of CFSE out of all. Hence posses maximum enthalpy of hydration.


Greater the negative value of CFSE greater will be its hydration energy.
Correct option is (c)
45. A metal crystallizes in the face – centered cubic lattice parameter of 4.20Å. The shortest atom to atom contact distance in the lattice is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
46. Polarographic method of analysis to obtain individual amounts of Cu2+ and Cd2+ in a given mixture of the two ions (Cu2+ and Cd2+) is achieved by measuring their
(a) half – wave potentials
(b) migration currents
(c) decomposition potentials
(d) diffusion currents
Ans. (d)
Sol. Polarography method of analysis to obtain individual amounts of Cu+2 and Cd–2 in a given mixture of the two ions (Cu2+ and Cd+2) is achioeved by measuring their diffusion currents.
Ilkovic equation = id = 708 n D1/2 m2/3 t1/6 C
Correct option is (d)
47. The ground state term of [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 


Orgel diagram of d8 – Oh compound
Correct option is (c)
Common Data for Q. 48 and Q.49:
N, N – Dimethylformamide (DMF) gives different patterns of signals for the methyl protons whenits 1H NMR spectrum is recorded at different temperatures.
48. Match the patterns of the NMR signals givenin the Column – I with temperatures given in the Column – II.

Column – I Column – II
(i) Two singlets, for three protons each, at  2.87 and 2.97 ppm (x) 25ºC
2.87 and 2.97 ppm (x) 25ºC
(ii) One sharp singlet for six protons at  2.97 ppm (y) 120ºC
2.97 ppm (y) 120ºC
(iii) One broad signal for protons (z) 150ºC
(a) (i) – (x); (ii) – (y); (iii) – (z)
(b) (i) – (x); (ii) – (z); (iii) – (y)
(c) (i) – (z) ; (ii) – (x)– (iii) – (y)
(d) (i) – (z); (ii) – (y); (iii) – (x)
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
at normal 25°C two singlet for three proton
at 120°C one broad signal for six proton
at 150°C one sharp singlet for six proton
Correct option is (b)
49. Based on the above data, the calculated difference in the frequencies of the two methyl singlets, if the spectrum is recorded on a 300 MHz spectrometer, is ___________ Hz.
Ans. (30)
Sol. 

Common Data for Q. 50 and Q. 51:
Heating a mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium tetrahydridoborate gives one liquid product (X), along with other products under ambient conditions.
50. Compound X is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. By the reaction of NaBH4 and NH4Cl, Borazine is formed.

51. Compound X is an example of
(a) Ionic liquid
(b) saturated heterocycle
(c) molecular cage
(d) unsaturated heterocycle
Ans. (d)
Sol. Compound (X) has different atom in rings hence it is unsaturated heterocyclic compound.
Linked Answer Q. 52 and Q. 53:
52. The major product X formed in the reaction given below is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. cis-diol undergoes protection faster than that of trans–diol.

53. Oxidation of the product X, obtained in the above reaction, with active manganse dioxide, followed by acidic hydrolysis gives
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. Since MnO2 oxidised preferentially allylic alcohol. So,

Correct option is (c)
Statement for Linked Answer Q. 54 and Q. 55:
The standard half – cell reduction potential of Fe3+ (aq)| Fe is – 0.036 V and that of OH– (aq)| Fe (OH)3(s) | Fe is – 0.786 V
54. For the determination of solubility product (KSP) of Fe (OH)3, the appropriate cell representation and its emfare, respectively.
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 



= 0.786 – 0.036 = – 0.750 volt
Correct option is (b)
55. The value of loge (KSP) for Fe(OH)3 at 298 K is
(a) –38.2
(b) + 87.6
(c) – 96.0
(d) –87.6
Ans. (d)
Sol. 

In Ksp = 2.303 × log10 Ksp = 2.303 × (–38.2) = –87.97
Correct option is (d)
