GATE Chemistry 2006
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
1. A molecule has a 2-fold axis and a mirror plane perpendicular to that. The point group must have a
(a) C2 axis
(b) Centre of inversion
(c)  plane
plane
(d)  plane
plane
Ans. (b)
Sol. C2 (axis)  reflection
reflection  i (Centre of inversion)
i (Centre of inversion)
Correct option is (b)
2. In the Huckle model for benzene, the  electronic transitions from the occupied to the unoccupied molecular orbitals do NOT occur at
electronic transitions from the occupied to the unoccupied molecular orbitals do NOT occur at
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
Transition from I to IV  Transition from I to III
Transition from I to III 
Transition from II to III  Transition from II to IV
Transition from II to IV 
So,  is not occur in upper transition
is not occur in upper transition
Correct option is (d)
3. The plot that describes a Carnot cycle is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. Plot describing carnot cycle is

Correct option is (a)
4. As the temperature tends to infinity, the partition function for a two-level system is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) infinity
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
———— 0
Correct option is (c)
5. As per the kinetic theory of ideal gases, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
(a) gas particles have mass but no volume
(b) partciles are in a Brownian motion between collisions.
(c) during the ocllision, the system does not lose energy
(d) particles exert same force per unit area on all sides of the container.
Ans. (c)
Sol. According to KMT, during collision system loose energy that result in change in speed which will study by Maxwell Boltzmann Distribution.
Correct option is (c)
6. Which of the following statements in NOT correct regarding fugacity of a Van der Waals gas?
(a) fugacity increases with increase in b
(b) fugacity decreases wit increase in a
(c) fugacity is equal to zero if compressibility is zero
(d) fugacity is equal to one if compressibility is one
Ans. (a)
Sol. Fugacity cannot be zero for gas
Correct option is (a)
7. The homogeneous catalyst that is used in the hydroformylation or hydrocarbonylation is based on
(a) Co
(b) Cr
(c) Ti
(d) V
Ans. (a)
Sol. The Homogeneous catalyst that is used in the hydroformylation or hydrocarbonylation is based on Co, eg. CO2 (CO)8 or HCo (CO)4
Correct option is (a)
8. The pair of ions that most commonly forms complexes with coordination number 2 is
(a) Cd(II) and Hg(II)
(b) Cu(II) and Hg(I)
(c) Cd(II) and Hg(I)
(d) Cu(I) and Hg(II)
Ans. (d)
Sol. Metal ions with d10 configuration show coordination no. 2. These metal ions are Cu+, Ag+, Au+, Hg2+.
Correct option is (d)
9. The experimental magnetic moment of K3[Fe(CN)6] is 2.3 µB and is attributable to the
(a) spin only value of low spin Fe
(b) spin only value of high spin Fe
(c) low spin Fe with orbital contribution
(d) high-spin Fe with orbital contribution
Ans. (c)
Sol. K3[Fe(CN)6]
Fe3+ (Low spin)
(Low spin)  d5 system.
d5 system.
Electronic configuration 

Number of unpaired electron = 1
Calculated 
Experimental magnetic moment is 2.3 µB due to orbital contribution.
Correct option is (c)
10. Iron-sulphur clusters in biological systems are involved in
(a) proton transfer
(b) atom transfer
(c) group transfer
(d) electron transfer
Ans. (d)
Sol. Iron sulphur cluster in biological systems are involved in electron transfer reaction.
Correct option is (d)
11. Mg6Si4O10(OH)8 is commercially known as
(a) asbestos
(b) water-glass
(c) soda-glass
(d) zeolite
Ans. (a)
Sol. Mg6Si4O10(OH)8 is example of sheet silicates and it commercially known asbestos
Correct option is (a)
12. The series with the correct order of decreasing ionic size is
(a) K+ > Ca2+ > S2– > Cl–
(b) S2– > Cl– > K+ > Ca2+
(c) K+ > Cl– > Ca2+ > S2–
(d) Cl– > K+ > S2– > Ca2+
Ans. (b)
Sol. S2–, Cl–, K+, Ca2+ are isoelectronic species.
For isoelectronic species,
ionic radii 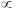 magnitude of negative charge
magnitude of negative charge 
Correct option is (b)
13. The most stable conformation of the following compound is:

(a) 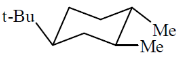
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
14. The correct order of the basicity of the following compound is
I. 
II. 
III. 
IV. 
(a) IV > III > II > I
(b) III > IV > I > II
(c) IV > III > I > II
(d) III > IV > II > I
Ans. (c)
Sol. (I)  Less basic because lone pair of electron is in delocalization with the ring.
Less basic because lone pair of electron is in delocalization with the ring.
(II)  Least basic because lone pair is in delocalization with in the ring system
Least basic because lone pair is in delocalization with in the ring system
(III)  Basic because lone pair is not in delocalization with in the ring and is available for protonation
Basic because lone pair is not in delocalization with in the ring and is available for protonation
(IV)  Most basic saturated heterocyclic compound
Most basic saturated heterocyclic compound
Correct option is (c)
15. Match the following compounds with their respective classes.
I.  II.
II. 
III.  IV.
IV. 
(a) I: Steroid; II: terpenoid; III: alkaloid; IV DNA base
(b) I: terpenoid; II; steroid; III: alkaloid; IV: DNA base
(c) I:terpenoid; II: steroid; III: DNA base; IV: alkaloid.
(d) I:steroid; II: terpenoid; III: DNA base; IV: alkaloid.
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
16. Which of the following absorptions is shown by 1, 3-butadine in its UV absorption spectrum recorded in n-hexane 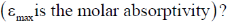
(a) 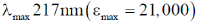
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
1, 3-butadiene in its UV absorption spectrum
Correct option is (a)
17. Which of the following compounds is expected to show a sharp singlet for one of its protons at ppm in 1HNMR spectrum, given that this signal remains unaffected on shaking the solution thoroughly with D2O?
(a) CH3CO2H
(b) CH3CONHC6H5
(c) 
(d) n–C6H13CHO
Ans. (d)
Sol. n – C6H13 CHO protron unaffected D2O
 8 ppm in 1HNMR
8 ppm in 1HNMR
Correct option is (d)
18. The most appropriate starting materials for one step synthesis of the compound (I) are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
19. Which of the statement is CORRECT about the mechanism of the following reaction?

(a) DMSO react with alcohol initially to give  , which reacts with (COCl)2.
, which reacts with (COCl)2.
(b) (COCl)2 reacts with the alcohol initially to give  which reacts with DMSO
which reacts with DMSO
(c) DMSO reacts with (COCl)2 initially to give  , which reacts with the alcohol.
, which reacts with the alcohol.
(d) (COCl)2 react with DMSO initially to give  which reacts with the alcohol.
which reacts with the alcohol.
Ans. (c)
Sol. DMSO reacts with (COCl)2 initally to give 



Correct option is (c)
20. Which of the statement is CORRECT about the mechanism of the following reaction?

(a) DMSO react with alcohol initially to give  , which reacts with (COCl)2.
, which reacts with (COCl)2.
(b) (COCl)2 reacts with the alcohol initially to give  which reacts with DMSO
which reacts with DMSO
(c) DMSO reacts with (COCl)2 initially to give  , which reacts with the alcohol.
, which reacts with the alcohol.
(d) (COCl)2 react with DMSO initially to give  which reacts with the alcohol.
which reacts with the alcohol.
Ans. (c)
Sol. DMSO reacts with (COCl)2 initally to give 




Correct option is (c)
21. To demonstrate the variational principle, a trial function  where C1 and C2 are the variational parameters and
where C1 and C2 are the variational parameters and  and
and  are the 2s, and 3s orbitals of the hydrogen atom, is constructed. The corresponding secular determinant for the hydrogen atom (in eV) is
are the 2s, and 3s orbitals of the hydrogen atom, is constructed. The corresponding secular determinant for the hydrogen atom (in eV) is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 




Correct option is (a)
22. The  transition for a molecule having C3v symmetry is
transition for a molecule having C3v symmetry is
(a) due to dipole pointing in X direction
(b) due to dipole pointing in y direction
(c) due to dipole pointing in z direction
(d) not allowed
Ans. (d)
Sol. In C3v point group character table
A1 A2 A1 = 1 1 1; A2 = 1 1 – 1
A2 A1 = 1 1 1; A2 = 1 1 – 1
A1 × A2 = 1 1 – 1 [Rz]  not allowed
not allowed
Correct option is (d)
23. Which of the following pairs of operators commute?
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 

Commute each other.
Correct option is (b)
24. The zero-point energy of the vibration of 35Cl2 mimicking a harmonic oscillator with a force constant k = 2293.8 Nm–1 is
(a) 10.5×10–21J
(b) 14.8×10–21J
(c) 20×10–21J
(d) 29.6×10–21J
Ans. (b)
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
25. The molecules active in rotational microwave, infrared absorption as well as rotational Raman spectra is:
(a) CO2
(b) SF6
(c) HCl
(d) H2
Ans. (c)
Sol. CO2 microwave inactive
microwave inactive
SF6 rotational microwave inactive
rotational microwave inactive
H2 rotational infrared inactive
rotational infrared inactive
HCl  rotational microwave active
rotational microwave active
Infrared active, rotational Raman active
Correct option is (c)
26. One mole each of H2CO3, and Na2CO3 are added to water to prepare one litre solution. The pH of the solution is.
(a) 6.37
(b) 8.31
(c) 10.25
(d) 7
Ans. (b)
Sol. One mole each of H2CO3, NaHCO3 and Na2O3 are added to water to prepare one litre solution. The pH of the solution is (Hint:  = 6.4 and
= 6.4 and  = 10.3)
= 10.3)
pH = 
pH =  = 8.31
= 8.31
Correct option is (b)
27. Given the standard potential for the following half-cell reaction at 298K

Calculate the  (kJ) for the reaction,
(kJ) for the reaction, 
(a) –34.740
(b) –65.720
(c) –69.480
(d) –131.40
Ans. (a)
Sol. 


Correct option is (a)
28. One mole each of acetic acid and sodium acetate are dissolved in 1kg of water. Boiling point of the resulting solution is
(a) 100.51°C
(b) 101.02 °C
(c) 101.53 °C
(d) 102.04 °C
Ans. (b)
Sol. Molality = 2m, for water kb = 0.512

Tb = 101.024°C
Correct option is (b)
29.  for the following reaction, at 298 K is:
for the following reaction, at 298 K is:

(a) –197 J K–1
(b) 0 J K–1
(c) –308 J K–1
(d) 111 J K–1
Ans. (d)
Sol. 


Correct option is (d)
30. Consider an exothermic reaction  as the temperature increases
as the temperature increases
(a) k1, k–1 and k1/k–1 increases
(b) k1 increases, k–1 decreases, and k1/k–1 increases.
(c) k1, k–1 increases and k1/k–1 decreases
(d) k1 and k–1 decrease, and k1/k–1 increases.
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
As rate constant increases on increasing the temperature so k1 and k–1 increases on increasing the temeprature.
On increasing the temperature, reaction moves backward.
The magnitude of increase is more for K–1 than K1

Correct option is (c).
31. A radical contains 14N(I=1) with hyperfine constant 1.61 mT and two equivalent protons (I=1/2) with hyperfine constant 0.35 mT. The ESR spectrum will exhibit.
(a) 3 lines
(b) 6 lines
(c) 7 lines
(d) 9 lines
Ans. (d)
Sol. 14N (I = 1)



Number of fine = 9
Correct option is (d)
32. The set of ions expected to show Jahn-Teller distortion in their complexes is
(a) Ti(III), Cu(II), high spin Fe(III)
(b) Cu(I), Ni(II), High spin Fe(III)
(c) Cu(II), Low spin Fe (III), Ti(III)
(d) Low spin Fe (III), Mn(II), Cu(I)
Ans. (c)
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
33. The series with correct order of increasing 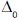 in their complexes is
in their complexes is
(a) I– < PR3 < CH3– < CO
(b) PR3 < CH3– < I– < CO
(c) CH3– < PR3 < I– < CO
(d) I– < CH3– < PR3 < CO
Ans. (a)
Sol.  is not the necessary requirement for high position in spectrochemical series. However ligand which are strong sigma bases will increase the energy of the eg orbitals relative to t2g orbital, therefore CH3– has more splitting in comparison to PR3.
is not the necessary requirement for high position in spectrochemical series. However ligand which are strong sigma bases will increase the energy of the eg orbitals relative to t2g orbital, therefore CH3– has more splitting in comparison to PR3.
Correct option is (a)
34. Coordinated water molecules of a Cd(II) complex can be successively replaced by Br– finally to result in [CdBr4]2–. In this process, the fourth equilibrium constant is observed to be higher than the third one, because
(a) equilibrium constant for the last step is always the highest
(b) three molecules of H2O are released during the fourth step
(c) the aquo-Cd(II) species is a octahedral
(d) an anion (Br–) replaces a neutral (H2O) molecule from the coordination sphere
Ans. (b)
Sol. 


Step 4 is entropically driven due to decrease in coordination number from 6 to 4 which increases number of product molecules and consequently k4 > k3 (which does not enjoy such entropy benefits).
Correct option is (b)
35. The Correct statement regarding the thermodynamic stability and kinetic reactivity of metal ion complexes is that
(a) more stable complexes are less reactive
(b) there exists a dependence on the bulkiness of the ligand
(c) there exists no direct relation between these two phenomenon
(d) there exists a dependence on the size of the metal ion
Ans. (c)
Sol. Thermodynamic stability is a measure of the extent to which the complex will form. It depends upon the metal-ligand bond energies, stability constants etc.
Kinetic reactivity, on the other hand, refers to the speed with which transformations leading to the attainment of equilibrium will occur. It depends upon the activation energy.
Thus, these two, i.e., thermodynamic stability and kinetic reactivity, have no direct relation. (A stable complex may be inert or labile or an inert complex may be stable or unstable).
Correct answer is (c)
36. The correct order of the rate of exchange of water molecules between the coordination sphere and the bulk is
(a) Cr3+ < Al3+ < Cr2+ < Ni2+
(b) Cr3+ < Al3+ < Ni2+ < Cr2+
(c) Cr3+ < Ni2+ < Cr2+ < Al3+
(d) Cr3+ < Cr2+ < Al3+ < Ni2+
Ans. (b)
Sol. Metal ions are classified in four categories based on rate of exchange of coordinated water

Correct order of water exchange rates
Cr2+ > Ni2+ > Al3+ > Cr3+
Correct option is (b)
37. The amino acid side chain high affinity for Ca2+ and Cu2+ in metallo-proteins is:
(a) carboxylate in both the cases.
(b) imidazole in both the cases.
(c) caboxylate for Ca2+ and imidazole for Cu2+.
(d) imidazole for Ca2+ and carboxylate for Cu2+
Ans. (c)
Sol. Carboxylate for Ca2+ and imidazole for Cu2+.
Correct option is (c)
38. The correct order of the soft character (as per HSAB Principle) of the central metal ion is
(a) [CrO4]2– < [CrCl4]– < [Cr(bipy)3] < [Cr(CO)5]2–
(b) [CrCl4]– < [Cr(bipy)3] < [CrO4]2– < [Cr(CO)5]2–
(c) [CrO4]2– < [Cr(bipy)3] < [Cr(CO)5]2– < [CrCl4]–
(d) [CrCl4]– < [CrO4]2– < [Cr(CO)5]2– < [Cr(bipy)3]
Ans. (a)
Sol. Softness of any species depends upon polarizability of central metal which depends on its oxidation state, therefore

As oxidation state decreases, softness increases.
Correct option is (a)
39. The crystal structure of Pb3O4 contains
(a) octahedral and tetrahedra units
(b) only octahedral units
(c) octahedral and pyramidal units
(d) octahedral and square-planar units
Ans. (c)
Sol. The crystal structure of Pb3O4 contains octahedral and pyramidal units.
Correct option is (c)
40. The symmetry elements that are present in BF3 are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
41. [Co(CO)4] is isolobal with
(a) CH4
(b) CH3
(c) CH2
(d) CH
Ans. (b)
Sol. Co(CO)4 Valence electron of fragment = 17 electron
Valence electron of fragment = 17 electron
CH3 Valence electron
Valence electron  7
7
Correct option is (b)
42. The CORRECT order of the CO stretching vibrational frequency is
(a) [Ti(CO)6]2– > [V(CO)6]– > CO > [Cr(CO)6]
(b) [Cr(CO)6] > > [V(CO)6]– > [Ti(CO)6]2–
(c) CO > [V(CO)6]– > [Ti(CO)6]2– > [Cr(CO)6]
(d) CO > [Cr(CO)6] > [V(CO)6]– > [Ti(CO)6]2–
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
As the electron density on metal increases back bonding increase. Hence, metal to carbon strength increases and C–O bond strength in carbonyl decreases.
CO > [Cr(CO)6] > [V(CO)6]– > [Ti (CO)6]–2
Correct option is (d)
43. When a reduced cytochrome transfers an electron from its Fe(II) to the bound O2,
(a) The bond order of O2 is reduced by one and  decreases.
decreases.
(b) A metal bound superoxide is formed and  decreases.
decreases.
(c) A metal bound superoxide is formed and  increases.
increases.
(d) The bond order of O2 is reduced by one and  increases.
increases.
Ans. (b)
Sol. When a reduced cytochrome transfers an electron from its Fe(II) to the bound O2, a metal bound superoxide is formed and  decreases. Because bond order of O2 is 2 and O2– is 1.5.
decreases. Because bond order of O2 is 2 and O2– is 1.5.
Correct option is (b)
44. The atomic radius (in cm) of an element with a body centered cubic unit cell of volume 75.8 cm3 mol–1, molecular weight 137.3 and density 3.62 g cm–3 is
(a) 1.5×10–8
(b) 1.6×10–8
(c) 2.0×10–8
(d) 2.2×10–8
Ans. (d)
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
45. If the dipole moment of HCl is 1.08 D and the bond distance is 1.27Å, then partial charge on hydrogen and chlorine, respectively, are
(a) + 1.0 and –1.0
(b) + 0.85 and –0.85
(c) +0.356 and – 0.356
(d) +0.178 and – 0.178
Ans. (b)
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
46. One gram of 90Sr gets converted to 0.953 g after 2 years. The half life of 90Sr, and the amount of 90Sr remaining after 5 years are
(a) 1.44 years and 0.916g
(b) 57.6 years and 0.75g
(c) 28.8 years and 0.887g
(d) 100 ears and 0.982 g
Ans. (c)
Sol. [90Sr]0 = 1g
[90Sr] = 0.953 g, t = 2 year

t1/2 = 28.75 year
After 5 years amount of 90Sr.

Correct option is (c)
47. The metal ion that is expected to shift the C1– methylene group in heptanol from 2 to 10 ppm in 1H NMR is
(a) Eu(III)
(b) T l (III)
(c) Al (III)
(d) Sc (III)
Ans. (a)
Sol. 

The most frequently used shift reagent are the Eu(III). Europium reagents generally induce downfield shifts in resonance spectroscopy. Eu(III) shifted larger downfield shift for the methylene signals.
Correct option is (a)
48. When Al4C3 and Mg2C3 reacts with H2O, then major products formed respectively, are
(a) ethyne and ethane
(b) methane and propyne
(c) propane and propene
(d) methane and propene
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
49. The arrangement of sulphur in zinc blende and wurtzite structures, respectively, are
(a) hexagonal close packing and cubic close packing
(b) cubic close packing and hexagonal close packing
(c) simple cubic packing in both the structures
(d) hexagonal close packing in both the structures
Ans. (b)
Sol. The arrangement of sulphur in zinc blende and wurtzite structures, are cubic close packing and hexagonal close packing respectively
(Correct option is (b)
50. The reaction between Pr6O11 and dilute HCl leads to the formation of
(a) a coloured solution
(b) only a black precipitate PrO2
(c) a black precipitate of PrO2 & soluble PrCl3
(d) only soluble PrCl3
Ans. (a)
Sol. Reaction between Pr6O11 and dil HCl leads to formation of Pr(III) O2 and Cl2 gas. Solution Pr(III) is coloured.
Correct option is (a)
51. [XeO6]4– is octahedral whereas XeF6 is a disordered one, because
(a) fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen
(b) Xe has a lone-pair in XeF6
(c) XeF is neutrla whereas [XeO6]4– is anionic.
(d) Xe-F bond has more ionic character
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
52. In biological system, the metal ion involved in the dioxgyen transport besides Fe is
(a) Co
(b) Zn
(c) Mg
(d) Cu
Ans. (d)
Sol. In biological systems, the Cu involved in the dioxygen transport besides Fe
Correct option is (d)
53.  , when it absorbs at 452 nm, is a very good oxidizing as well as reducing agent due to the formation of
, when it absorbs at 452 nm, is a very good oxidizing as well as reducing agent due to the formation of
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. Upon visible light excitation of [Ru (bpy)3] 2+, the resulting metal to ligand charge transfer (MLCT) excited state species
[Ru''' (2, 2' – bipyrdyl)2 (2, 2' – bipyridyl)]2+
can be reductively or oxidatively quenched with the appropriate single electron donar or acceptor.
Correct option is (d)
54. In the prooton decoupled 13C and 31P NMR spectra of (CH3)3 P = 0, the number of lines observed, respectively, are
(a) two and one
(b) one and two
(c) three and one
(d) two and two.
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
In 13C NMR number of line due to 31P = (2NI + 1) =  = 2 line
= 2 line
In 13P NMR  One line singlet (No splitting with 13C)
One line singlet (No splitting with 13C)
Correct option is (a)
55. Among, RO–, AsMe3, ROR', CN–, RCO2–, SCN–, the set of ligands with good  -acceptor nature are
-acceptor nature are
(a) RO–, RCO2–, SCN–
(b) RO–, RCO2–, AsMe3
(c) AsMe3, CN–, SCN–
(d) RO–, ROR', RCO2–
Ans. (c)
Sol. RO– is  donor ligand. AsMe3, CN– and SCN– are good
donor ligand. AsMe3, CN– and SCN– are good  acceptor.
acceptor.
Correct option is (c)
56. Identify the correct stereochemical relationship amongst the hydrogen atoms Ha, Hb and Hc in the following molecule:

(a) Ha and Hb : enantiotopic
(b) Ha and Hb : diastereotopic
(c) Ha and Hc : enantiotopic
(d) Hb and Hc : diastereotopic
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
A and B are diastereomers, because the environment of Ha and Hb are different.
Hence, Ha and Hb are diastereotopic.
Correct option is (b)
57. The configurations of the reactant and the product in the following reaction, respectively, are

(a) R, R
(b) R, S
(c) S, R
(d) S, S
Ans. (d)
Sol. Above product formed through SN2 mechanism in which (CN–) group attack from back side. (inversion mechanism) given priority according to CIP rule.

Correct option is (d)
58. Match the reactions of some p-substituted benzene derivatives (a)–(d) given in List I with the Hammett's p-values (i) - (iv) in List II and identify the correct mathc.

(a) a-i, b-iv, c-iii, d-ii
(b) a-iv, b-i, c-ii, d-iii
(c) a-i, b-ii, c-iv, d-iii
(d) a-iv, b-iii, c-i, d-ii
Ans. (d)
Sol. A positive  value means more electron in the transition state in starting material. A negative
value means more electron in the transition state in starting material. A negative  value means fewer electrons in the transition state than in starting material.
value means fewer electrons in the transition state than in starting material.
Correct option is (d)
59. On heating with dilute sulfuric acid, napththalene-1 sulfonic acid gives predominantly
(a) natphthalene
(b) napththalene-2-sulfonic acid
(c) 1-naphthol
(d) 2-naphthol
Ans. (a)
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
60. Predict the major product P in the following reaction

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
61. Select the correct classification in the following reaction from option I to IV gives below.

(I) Conrotatory electrocyclic reaction
(II) Disrotatory electrocyclic reaction
(III) Valence isomerization
(IV)  cycloaddition reaction
cycloaddition reaction
(a) I and III
(b) II and IV
(c) II and III
(d) I and IV
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
Movement of electron only without the moment of atoms is called valence isomerization
Correct option is (c)
62. Identify the major product P in the following reaction.

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
63. Identify the major product P and Q in the following reactions from the list of compounds I to IV.


(a) P:I and Q:II
(b) P:II and Q:III
(c) P:IV and Q:II
(d) P:IV and Q:III
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
64. Identify the major product P in the following reaction:

(a) 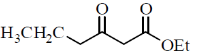
(b)  2
2
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
65. Identify the Correct set of stereochemical relationships amongst the following monosaccharides I-IV

(a) I and II are anomers; III and IV are epimers
(b) I and III are epimers; II and IV are anomers
(c) I and II are epimers; III and IV are anomers
(d) I and III are anomers; I and II are epimers.
Ans. (d)
Sol. Different configuration at only first position known as anomer. Different configuration at any other centre known as epimers.
So, I and III are anomers
Correct option is (d)
66. Select the correct pair of statements:
(I) Complementary strands run antiparallel in a double stranded DNA.
(II) The triplet codons, represented by the genetic code, are expressed by ribonucleic acids.
(III) t-RNA carries the genetic information to the site of DNA replication.
(IV) A nucleoside contains a ribose or deoxyribose and phosphate constituents only.
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) III and IV
(d) I and IV
Ans. (a)
Sol. Statement (I) and (II) are correct.
III. m-RNA carries the genetic information to the site of DNA replication
IV Nucleoside contains a ribose ordeoxyribose and base only.
Correct option is (a)
67. Match the compounds in List-I with the stretching frequencies (cm–1) of the principal functional groups given in List-II

(a) 1-iii, 2-iv, 3-i, 4-v
(b) 1-iii, 2-iv, 3-ii, 4-v
(c) 1-iv, 2-v, 3-ii, 4-i
(d) 1-iv, 2-iii, 3-v, 4-i
Ans. (c)
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
68. Pick the major product P in the following reaction

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
69. Identify the major product P in the following reaction

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 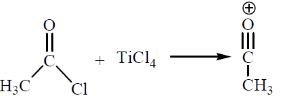

Correct option is (c)
70. Identify the major P in the following two-step reaction:

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
Common Data for Q. 71, Q. 72 and Q. 73:
Methyl ethyl ether (A) and diborane (B) form a compound, which melts congruently at 133 K. The system exhibits two eutectics, one at 25 mole percent B and 123 K and a second at 0 mole percent B and 104 K. The melting points of pure A and b are 131 K and 110 K, respetively.
71. The phases at 55 mole percent B and 108 K are,
(a) solid AB and a solid B phase
(b) solid AB and a liquid phase
(c) solid B and a liquid phase
(d) solid A and a liquid phase
Ans. (b)
Sol. 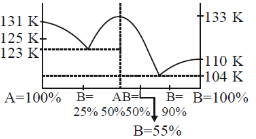
At point a, AB(s) + Melt.
Correct option is (b)
72. What happens if a small amount of solid B is added to the above mixture while keeping the temperature constant?
(a) added B forms compound AB
(b) added B precipitates out
(c) overall liquid phase percentae increases with respect to the overall solid phase
(d) complete solidification takes place
Ans. (b)
Sol. On adding solid B, it will precipitate out.
Correct option is (b)
73. The mixture at 25 mole percent B and at 124 K is cooled slowly to 114 K. The resulting phases are
(a) solid AB and solid A
(b) solid AB and liquid
(c) solid AB and solid B
(d) liquid and solid A
Ans. (a)
Sol. On cooling mixture at 25 mole percent B to 114 K. Solid AB + solid A will exist.
Correct option is (a)
Common Data for Q. 74 to and Q. 75
Consider the following P-V diagrma for an ideal gas that follows the diagonal path from A to B.

74. The work done (in atm-L) on the gas in the process is
(a) 9.5
(b) 99.75
(c) 190
(d) 10 ln (20)
Ans. (d)
Sol. Work done in diagonal process


= 10 ln 20
75. For the above process,
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. Above process is isothermal
Therefore, 
Correct option is (d)
Linked Answer Q. 76 and Q. 77.
76. The first excited state wavefunction for a particle in a box that spans from –a to + a is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 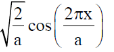
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. For a particle in a box from –a to + a,
Wave function is

For the excited state, n = 2. Then

Correct option is (b)
77. A perturbation V =  (x–a/2) is introduced in the box. The first order energy correction to the first excited state is.
(x–a/2) is introduced in the box. The first order energy correction to the first excited state is.
(a) 0
(b) 2/a
(c) 1/a
(d) 1/2a
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
From dirac-delta property

x lie under limit
So, not need to solve integrity,

Correct option is (c)
78. A reaction proceeds through the formation of an intermediate B in an unimolecular reaction

The integrated rate law for this reaction is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 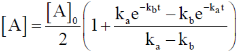
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 



Correct option is (a)
79. If ka >> kb , then concentration vs. time plot for the above reaction is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 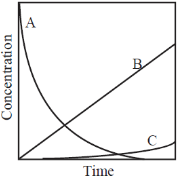
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
The net effect on [B] is the accumulation or increases to some maximum value and then it starts decreasing.
correct option is (b)
Linked Answer Q. 80 and Q. 81:
80. Identify the major product P in the following reaction

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
81. Product P of the reaction transforms to a product Q on treatment with n-Bu3SnH in the presence of AIBN in benzene solution. Identify Q.

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
Linked Answer Q. 82 and Q. 83.
82. In the following wittig reaction, the strucutre of the major product P and the intermediate [X], respectively, are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
83. Which of the following set of characteristic NMR signals will be compatible with the structure of P in the above reaction?
(a)  (d, J = 6 Hz, 2H), 7.01 (d, J = 6 Hz, 2H), 6.41 (d, J = 18 Hz, 1H)
(d, J = 6 Hz, 2H), 7.01 (d, J = 6 Hz, 2H), 6.41 (d, J = 18 Hz, 1H)
(b)  (d, J = 6 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 7.09 (t, J = 5 Hz, 1H)
(d, J = 6 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 7.09 (t, J = 5 Hz, 1H)
6.94 (d, J = 5 Hz, 1H), 6.41 (d, J = 17 Hz, 1H)
(c)  (d, J = 6 Hz, 2H), 7.01 (d, J = 6 Hz, 2H), 6.35 (d, J = 9 Hz, 1H)
(d, J = 6 Hz, 2H), 7.01 (d, J = 6 Hz, 2H), 6.35 (d, J = 9 Hz, 1H)
(d)  (d, J = 6 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 7.09 (t, J = 5 Hz, 1H),
(d, J = 6 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 7.09 (t, J = 5 Hz, 1H),
6.94 (d, J = 10 Hz, 1H), 6.35 (d, J = 10 Hz, 1H)
Ans. (d)
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
84. The prodcuts P and Q in the following sequence of reactions, respectively, are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. 

Ozonolysis occurs on electron rich double bond.
In the presence of MeH/Me2S reductive ozonolysis takes place.
Correct option is (d)
85. The reagent for selective reduction of the aldehyde group in Q obtained in the above reaction is
(a) H2, (Ph3P)3 RhCl
(b) [(H3C)2 CHCH2]2
(c) Na(CH3COO)3 BH
(d) LiAlH4
Ans. (c)
Sol. Na (CH3COO)3 BH selective reducing agent for aldehyde.
Correct option is (c)
