CSIR NET CHEMISTRY (June-2016)
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
21. Identify the species, those obey the 18 electron rule, from the following:
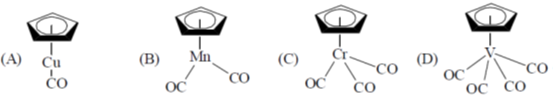
(a) A and B
(b) B and C
(c) C and D
(d) A and D
Ans. d
Sol. 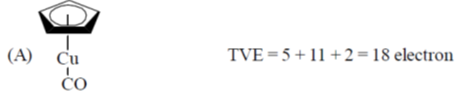
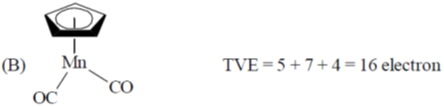
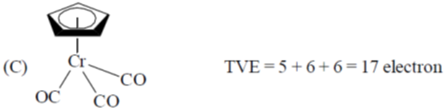
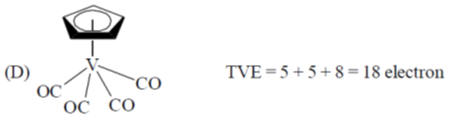
Correct option is (d)
22. The following transformation
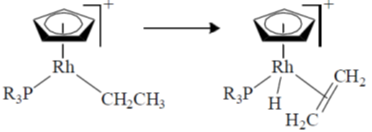
is an example of
(a) oxidative addition
(b) insertion
(c) 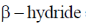
(d) reductive elimination
Ans. c
Sol. 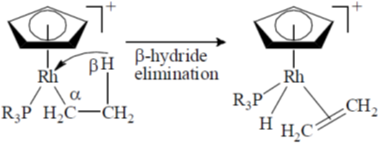
Correct option is (c)
23. 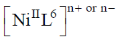 shows absorption bands at 8500, 15400, and 26000 cm–1 whereas
shows absorption bands at 8500, 15400, and 26000 cm–1 whereas 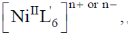 at 10750, 17500 and 28200 cm–1. L and L´ are respectively.
at 10750, 17500 and 28200 cm–1. L and L´ are respectively.
(a) 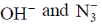
(b) 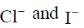
(c) 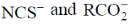
(d) 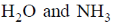
Ans. d
Sol. 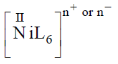 has absorption bonds at 8500, 15400, 26000 cm–1
has absorption bonds at 8500, 15400, 26000 cm–1
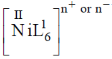 at 10750, 17500 and 28200 cm–1
at 10750, 17500 and 28200 cm–1
as for first complex absorptions bands are at low energy i.e. it has weak splitting therefore, it has weak ligand and for IInd complex high energy absorption bands corresponds to strong ligand. Thus, L is weak and L1 is strong ligand.
Correct option is (d)
24. The number of microstates present in 3F term is
(a) 3
(b) 21
(c) 9
(d) 28
Ans. b
Sol. Number of microstate in 3F is calculated as (2S + 1) (2L + 1)
For F, L = 3
Hence, (3) (2 × 3 + 1) = 21
Correct option is (b)
25. 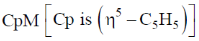 fragment isolabal with a BH fragment is
fragment isolabal with a BH fragment is
(a) CpGe
(b) CpMn
(c) 5
(d) 6
Ans. d
Sol. B – H = 4e– fragment isolobal fragment should have 14 electron.
Cp + Co = 5 + 9 = 14
Correct option is (d)
26. The number of metal – metal bonds in 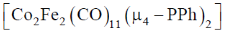 is
is
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
Ans. b
Sol. TVE = 18 + 16 + 22 + 8 = 64 = A
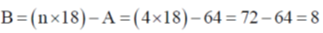
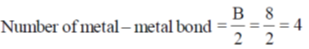
Correct option is (b)
27. Correct combination for 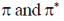 orbitals in B2 molecule is
orbitals in B2 molecule is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 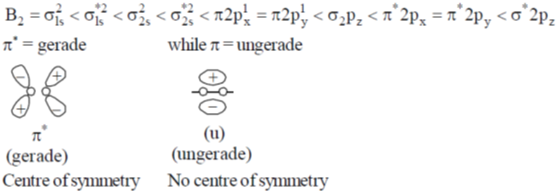
Correct option is (b)
28. The correct shape of 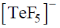 ion on the basis of VSEPR theory is
ion on the basis of VSEPR theory is
(a) trigonal bipyramidal
(b) square pyramidal
(c) pentagonal planar
(d) see – saw
Ans. b
Sol. 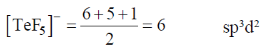
Number of lone pair = 1
Structure is square pyramidal
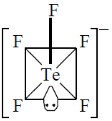
Correct option is (b)
29. The number of P–S and P–P bonds in the compounds P4S3 are, respectively
(a) 6 and 3
(b) 4 and 3
(c) 3 and 6
(d) 6 and 2
Ans. a
Sol. Structure of P4S3 is
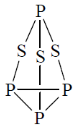
Number of P – S bond = 6
Number of P – P bond = 3
30. In the iodometric titration of sodium thiosulfate (Na2S2O3) with acidic dichromate solution, 25 mL of 0.01 M dichromate requires 25 mL of 'x' M thiosulfate. The value of 'x' is
(a) 0.2
(b) 0.1
(c) 0.6
(d) 0.4
Ans. c
Sol. In acidic medium dichromate changes into Cr+++ and in titration 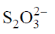 changes into
changes into 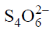 (tetrathionate).
(tetrathionate).
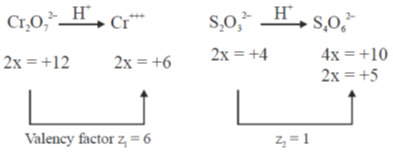
Now, milliequivalent of Cr2O72– = milli equivalent of S2O32–
Z1M1V1 = Z2M2V2
6 × 0.1 × 25 = 1 × x × 25 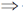 x = 0.6
x = 0.6
Correct option is (c)
31. Decomposition temperature of CaCO3 in thermogravimetric analysis will be highest in dynamic atmosphere of
(a) nitrogen
(b) synthesis gas
(c) 1 : 1 mixture of O2 and CO
(d) water gas
Ans. c
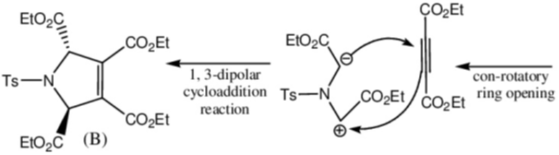
Sol. Decomposition temperature of CaCO3 in thermogravimetric analysis will be highest in dynamic atmosphere due to the presence of 1 : 1 mixture of O2 and CO.
Correct option is (c)
32. On two sequential electron capture, 56Ba131 will give
(a) 54Xe131
(b) 54Xe130
(c) 56Ce131
(d) 56Ce130
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
33. The compound which dissolves in POCl3 to give a solution with highest chloride ion concentration, is
(a) Et3N
(b) KCl
(c) FeCl3
(d) SbCl5
Ans. b
Sol. 
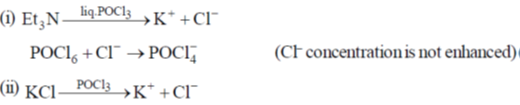
The Cl– ion produced in this reaction increases the concentration of Cl– and it is not consumed by POCl3.
Correct option is (a)
34. In the absence of bound globin chain, heme group on exposure to O2 gives the iron – oxygen species
(a) 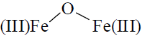
(b) 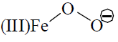
(c) 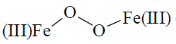
(d) 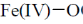
Ans. a
Sol. Absence of globin chain following reaction is occur
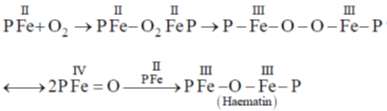
Correct option is (a)
35. For monoionic complex 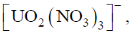 the correct coordination number and geometry respectively, are
the correct coordination number and geometry respectively, are
(a) 8 and hexagonal bipyramidal
(b) 5 and square pyramidal
(c) 8 and square antiprism
(d) 5 and trigonal bipyramidal
Ans. a
Sol. Co-ordinate number is 8 and geometry is hexagonal bipyramidal.
Correct option is (a)
36. Chelate effect is
(a) predominantly due to enthalpy change
(b) predominantly due to entropy change
(c) independent of ring size
(d) due to equal contribution of entropy and enthalpy change
Ans. b
Sol. Chelate effect if predominately due to entropy change
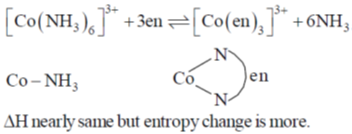
Correct option is (b)
37. The major product formed in the following reaction is
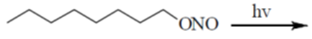
(a) 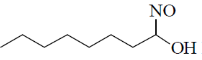
(b) 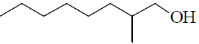
(c) 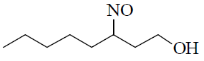
(d) 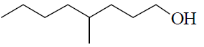
Ans. d
Sol. 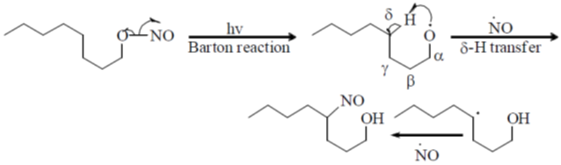
Correct option is (d)
38. The major product formed in the following reaction is
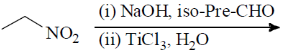
(a) 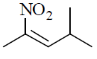
(b) 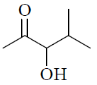
(c) 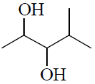
(d) 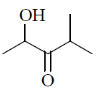
Ans. b
Sol. 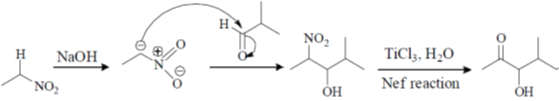
Correct option is (b)
39. The major product formed in the following reaction is
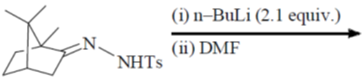
(a) 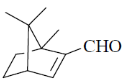
(b) 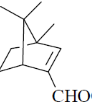
(c) 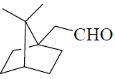
(d) 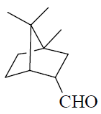
Ans. a
Sol. 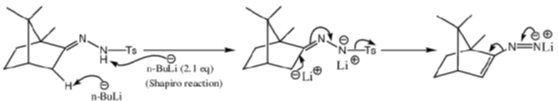
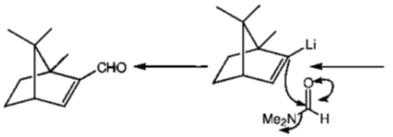
Correct option is (a)
40. Among the following, the compound that displays an IR band at 2150 cm–1 is
(a) 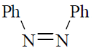
(b) 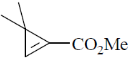
(c) 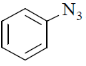
(d) 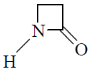
Ans. c
Sol. 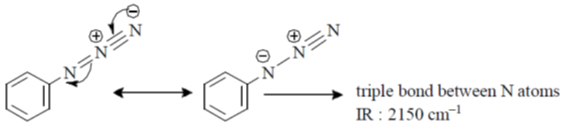
Correct option is (c)
41. In the 1H NMR spectrum of myrtenal, the two methyl groups are expected to display signals at (chemical shift values  in ppm)
in ppm)
(a) 1.35 (s, 3H) and 5.0 (s, 3H)
(b) 0.74 (s, 3H) and 1.33 (s, 3H)
(c) 1.22 (s, 6H)
(d) 0.70 (s, 6H)
Ans. b
Sol. 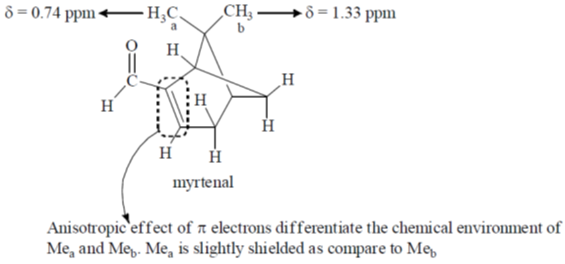
Correct option is (b)
42. Among the following, the compound(s) that can be classified as terpene derivative is(are)
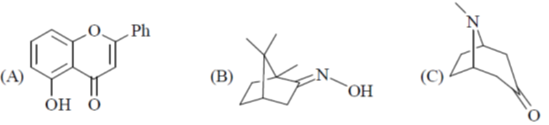
(a) A and B
(b) A only
(c) B only
(d) B and C
Ans. c
Sol. 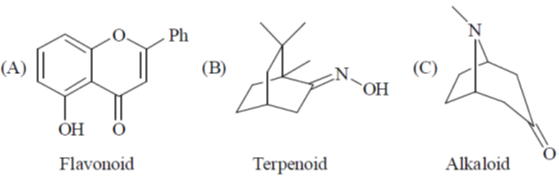
Correct option is (c)
43. The frontier orbital interactions involved in the formation of the carbocation intermediate in the reaction of isobutylene with HCl are
(a) 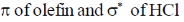
(b) 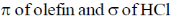
(c) 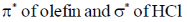
(d) 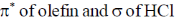
Ans. a
Sol. 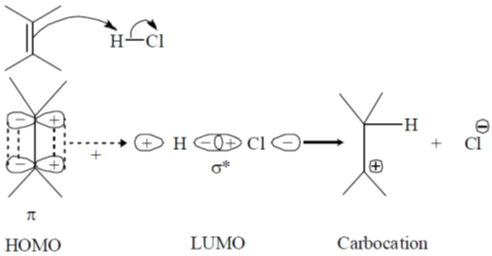
Correct option is (a)
44. The major product formed in the following reaction is
(a) 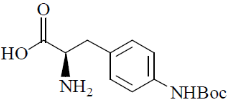
(b) 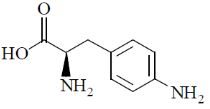
(c) 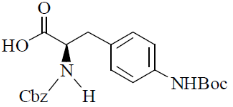
(d) 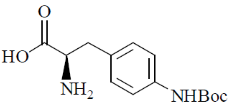
Ans. d
Sol. 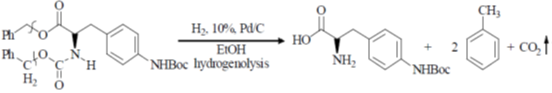
Correct option is (d)
45. In the UN – visible absorption spectrum of an 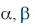 – unsaturated carbonyl compound, with increasing solvent polarity,
– unsaturated carbonyl compound, with increasing solvent polarity,
(a) 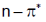 transitions undergo hypsochromic shift,
transitions undergo hypsochromic shift, 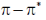 undergo bathochromic shift
undergo bathochromic shift
(b) 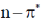 transitions undergo hypsochromic shift,
transitions undergo hypsochromic shift, 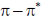 undergo hypsochromic shift
undergo hypsochromic shift
(c) both 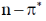 and
and 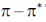 transitions undergo bathochromic shift
transitions undergo bathochromic shift
(d) both  and
and  transitions undergo hypsochromic shift.
transitions undergo hypsochromic shift.
Ans. a
Sol. 


Correct option is (a)
46. The major product formed in the following reaction is
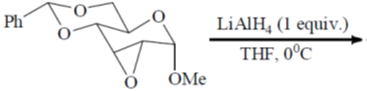
(a) 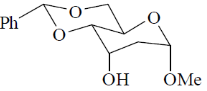
(b) 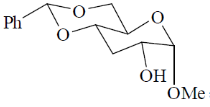
(c) 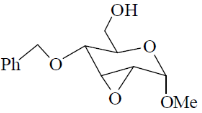
(d) 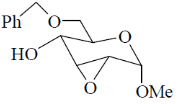
Ans. a
Sol. 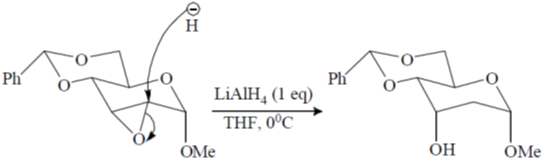
Correct option is (a)
47. In the following compound, the stereochemical descriptor for Ha and Hb is
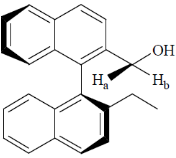
(a) enantiotopic
(b) diastereotopic
(c) homotopic
(d) constitutionally heteretopic
Ans. b
Sol. 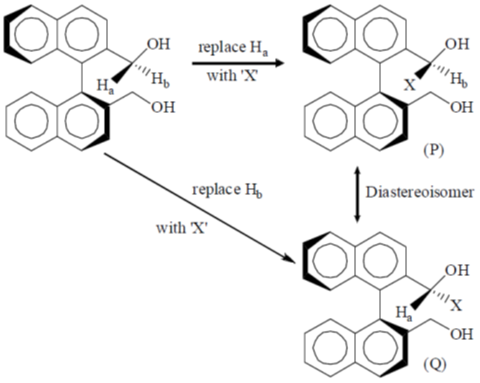
(P) and (Q) are diastereoisomers. Hence, Ha and Hb are diastereotopic.
Correct option is (b)
48. The correct statements are about the reaction of X and Y with NaNH2 are
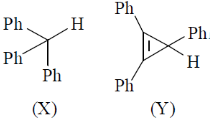
(A) X reacts faster than Y
(B) Y reacts faster than X
(C) X and Y behave as Lewis acids
(D) X is stronger Bronsted acid than Y
(a) A and C
(b) A and D
(c) B and C
(d) B and D
Ans. b
Sol. 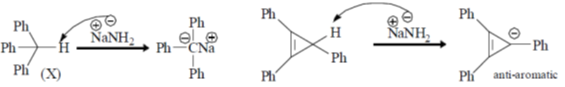
Correct option is (b)
49. The correct statements about conformations X and Y of 2–butanone are
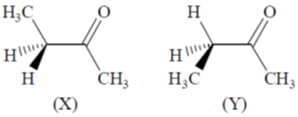
(A) X is more stable than Y
(B) Y is more stable than X
(C) Methyl groups in X are anti
(D) Methyl groups in Y are gauche
(a) A and D
(b) A and C
(c) B and C
(d) A, C and D
Ans. d
Sol. 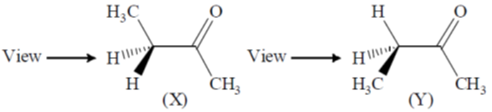
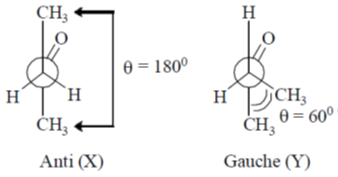
In (Y) Gauche interaction, destabilies the conformation
Correct option is (d)
50. The correct order of magnitude of 'A values' for the given substituents in cyclohexane derivatives is
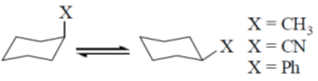
(a) Ph > CN > Me
(b) Me > Ph > CN
(c) CN > Me > Ph
(d) Ph > Me > CN
Ans. d
Sol. 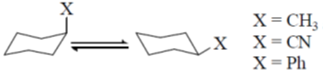
The magnitude of 'A values' dependent on the steric hinderence.
The correct order is Ph > CH3 > CN
Correct option is (d)
51. The correct order of pKa values for the compounds X, Y and Z is
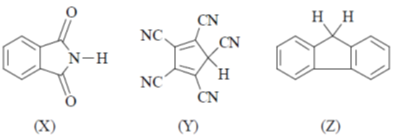
(a) X > Y > Z
(b) Y > Z > X
(c) Z > X > Y
(d) Y > X > Z
Ans. c
Sol. Higher the pKa value lower will be the acidity.
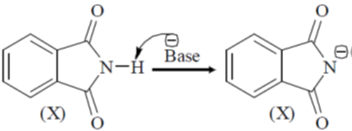
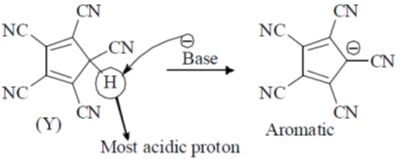
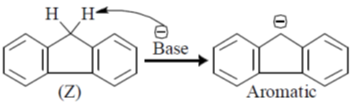
But due to annelation effect the proton will be less acidic. Hence, higher pKa value.
Correct option is (c)
52. The following transformation proceeds through two consecutive electrocyclic processes, which are
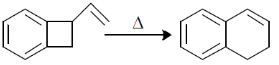
(a) 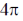 conrotatory and
conrotatory and 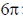 conrotatory
conrotatory
(b) 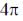 disrotatory and
disrotatory and 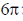 conrotatory
conrotatory
(c) 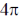 conrotatory and
conrotatory and 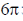 disrotatory
disrotatory
(d) 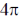 disrotatory and
disrotatory and 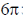 disrotatory
disrotatory
Ans. c
Sol. 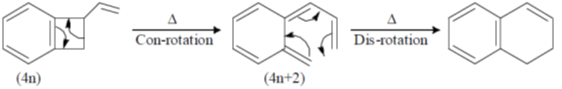
Correct option is (c)
53. The simultaneous eigenfunctions of angulra momentum operators L2 and Lz are
(a) all of 2s, 2px, 2py and 2pz orbitals
(b) only 2s, 2px and 2py orbitals
(c) only 2s and 2pz orbitals
(d) only 2pz orbital
Ans. c
Sol. 2s and 2pz orbitals are eigen function of L2 and Lz.
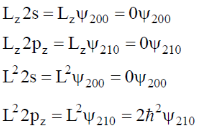
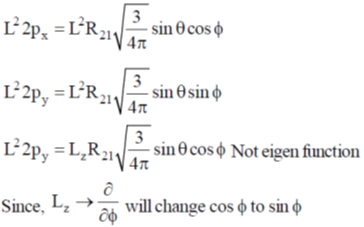
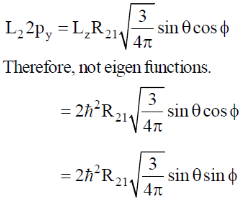
Correct option is (c)
54. An ideal gas is composed of particles of mass M in thermal equilibrium at a temperature T in one container. Another container contains ideal gas particles of mass 2M at a temperature 2T. The correct statement about the about two gases is
(a) average kinetic energy and average speed will be same in the two cases
(b) both the averages will be doubled in the second case.
(c) only the average kinetic energy will be doubled in the second case
(d) only the average speed will be doubled in the second case.
Ans. c
Sol. 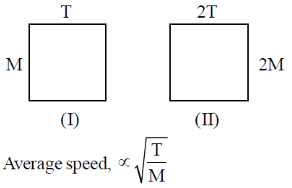
So, it will be same in both. But average kinetic energy 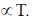
So, it will be double is second case.
Correct option is (c)
55. The lowest energy term for the d6 configuration is
(a) 2D
(b) 5D
(c) 1P
(d) 1D
Ans. b
Sol. 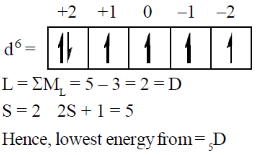
Correct option is (b)
56. If the rates of a reaction are R1 and R2 at concentrations C1 and C2 of a reactant respectively, the order of reaction, 'n' (assumping that the concentrations of all other reactants and T remain constant) with respect to the reactant is given by
(a) 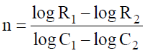
(b) 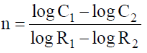
(c) 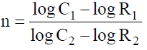
(d) 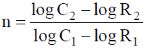
Ans. a
Sol. 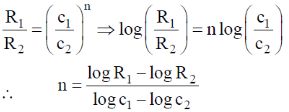
Correct option is (a)
57. Experimentally determined rate law for the chemical reaction,
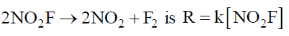
The rate determining step consistent with the rat law is
(a) 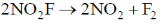
(b) 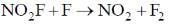
(c) 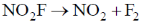
(d) 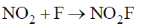
Ans. c
Sol. Given rate is in accordance with the rate of NO2F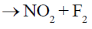
Correct option is (c)
58. The symmetry point group of the most stable geometry of the following molecule 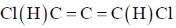 is
is
(a) C2
(b) C1
(c) C2v
(d) C2h
Ans. a
Sol. 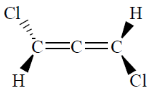
This molecule is chiral
Therefore, no plane, only one C2.
Correct option is (a)
59. The eigenfunctions of the Hamiltonian 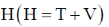 of a harmonic oscillator are (where T and V are kinetic energy and potential energy operators, respectively)
of a harmonic oscillator are (where T and V are kinetic energy and potential energy operators, respectively)
(a) eigenfunctions of T as well as V
(b) eigenfunctions of T, but not of V
(c) eigenfunctions of V, but not of T
(d) eigenfunctions of neither T nor V
Ans. d
Sol. If 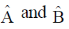 commute i.e.
commute i.e. 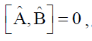 then they have same set of eigen functions.
then they have same set of eigen functions.
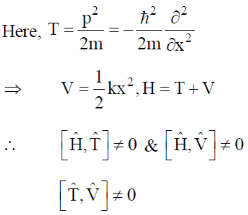
Correct option is (d)
60. In a potentiometric titration, the end point is characterised by
(a) 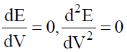
(b) 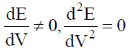
(c) 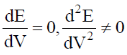
(d) 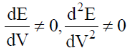
Ans. b
Sol. 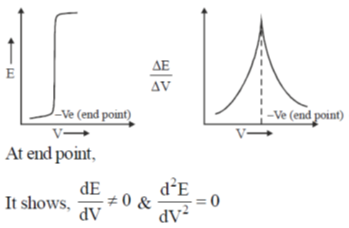
Correct option is (b)
61. On titrating conductometrically a NaOH solution with a mixture of HCl and CH3CO2H solutions, plot of the volume of mixed acid added (b) in y-axis against the conductance (a) in x-axis is expected to look like
(a) 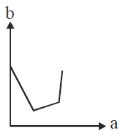
(b) 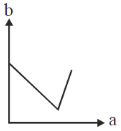
(c) 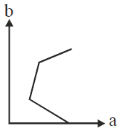
(d) 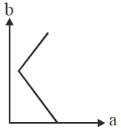
Ans. d
Sol. NaOH + (HCl + CH3COOH)
First NaOH will react with HCl will use NaOH is completely titrated during this process conductance will decrease due to less of OH– ions.
Second after that, as NaOH is completely consume. So, simple addition of mixture of HCl and CH3COOH will only increase the conductance.
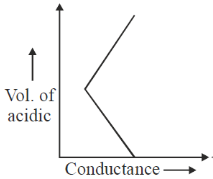
Correct option is (d)
62. 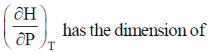
(a) pressure
(b) volume
(c) temperature
(d) heat capacity
Ans. b
Sol. 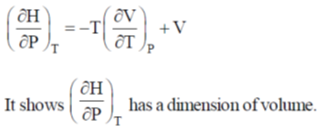
Correct option is (b)
63. In a cubic crystal, the plane [100] is equally inclined to the planes
(a) [010] and [011]
(b) [010] and [110]
(c) [001] and [101]
(d) [110] and [011]
Ans. a
Sol. Angle between (1 0 0) and (0 1 0)
And angle between (100) and (011)
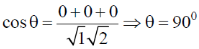
64. The standard electrode potential E0 at a fixed temperature and in a given medium is dependent on
(a) only the electrode composition
(b) the electrode composition and the extent of the reaction
(c) the extent of the electrode reaction only
(d) the electrode reaction and the electrode composition
Ans. d
Sol. The standard electrode potential E0 at a fixed temperature and in a given medium is dependent on the electrode reaction and the electrode composition.
Correct option is (d)
65. In a titration, the percentage uncertainties in the measured aliquot volume and the measured titre volume are ±x and ±y respectively. The percentage error in the calculated concentration of aliquot is
(a) x + y
(b) xy
(c) 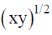
(d) 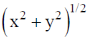
Ans. d
Sol. In a titration, the percentage uncertainties in the measured aliquot volume and the measured titre volume are ±x and ±y respectively. The percentage error in concentration of aliquot is 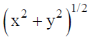
Correct option is (d)
66. For an ideal gas at 300K
(a) 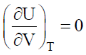
(b) 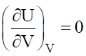
(c) 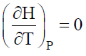
(d) 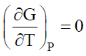
Ans. a
Sol. From Maxwell equation,
dU = TdS – PdV ...(i)
Divide the equation by (dV)T at constant T
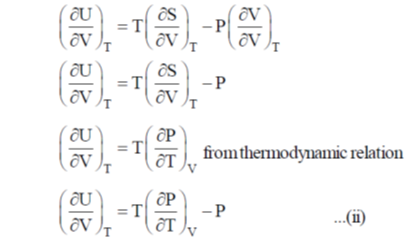


Correct option is (a)
67. The first excited state of hydrogen molecule is
(a) 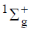
(b) 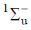
(c) 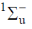
(d) 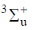
Ans. d
Sol. 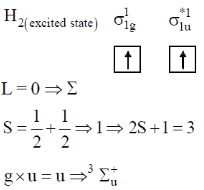
For half filled
Correct option is (d)
68. When river water containing colloidal clay flows into the sea, the major cause of silting is
(a) accumulation of sand at the bottom
(b) flocculation and coagulation
(c) decreased salinity of sea water
(d) micellization
Ans. b
Sol. When river water containing colloidal clay flows into the seac. The salt water induces flocculation and coagulation, and is a major cause of silting in estwers.
Correct option is (b)
69. Math the metal given in Column-A with its medicinal use as a compound in Column-B
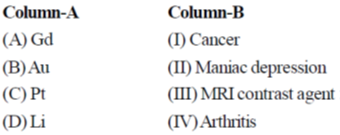
Correct match is
(a) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
(b) A – IV; B – II; C – I; D – III
(c) A – III; B – IV; C – I; D – II
(d) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV
Ans. c
Sol. Pt – complex used as anticoncern drug
Au – complex used as antiarthritis agent
Gd – complex used in MRI as contrast agent due to their strong paramagnetic behaviour
Li – complex used in Mariac depression
Correct option is (c)
70. At pH 10, tryptophan exists as
(a) 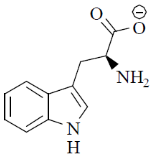
(b) 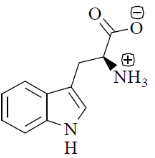
(c) 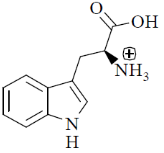
(d) 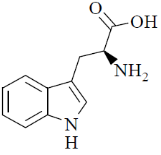
Ans. a
Sol. pH = 10 highly basic. So, there will be over all negative charge
Correct option is (a)
71. Complex 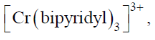 shows red phosphorescene due to transition
shows red phosphorescene due to transition
(a) 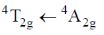
(b) 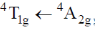
(c) 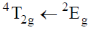
(d) 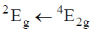
Ans. c
Sol. 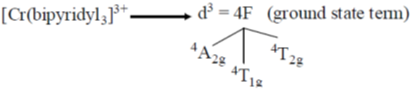
As phosphorescence is spin-forbidden transition and also occurs when electron comes from excited to ground state. Hence, transition 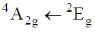 is responsible for the phosphorescence.
is responsible for the phosphorescence.
Correct option is (c)
72. Choose the correct option for carbonyl cluoride with respect to bond angle and bond length
(a) 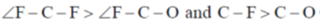
(b) 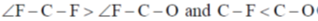
(c) 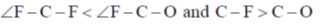
(d) 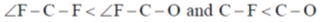
Ans. c
Sol. Structure of CoF2 =
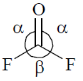
due to more space requirement for double bond the bond angle F–C–O will be higher that of F–C–F and also C–O bond order is larger than C-F hence, C–O bond length will be smaller than C–F.
Correct option is (c)
73. Which of the following react(s) with AsF5 in liquid BrF3?
(a) XeF6 only
(b) XeF6 and XeF4
(c) XeF6 and XeF2
(d) XeF4 and XeF2
Ans. c
Sol. 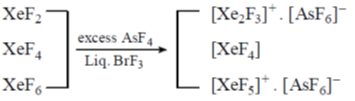
Separation of XeF4 from a mixture involves preferential complexation of XeF2 and XeF6 and XeF4 is then removed in vaccum.
Correct option is (c)
74. Consider the following reactions:

Reactions which will give  as a major product are:
as a major product are:
(a) A and B
(b) C and D
(c) A and C
(d) B and D
Ans. b
Sol. 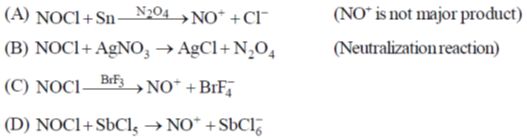
Correct option is (b)
75. The complex that shows orbital contribution to the magnetic moment, is
(a) 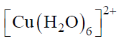
(b) 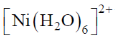
(c) 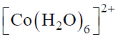
(d) 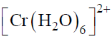
Ans. c
Sol. For orbital contribution the t2g set should be unsymmetrically filled
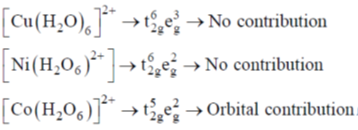
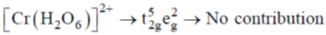
Correct option is (c)
76. Among KF, SnF4 and SbF5, solute(s) that increase(s) the concentrations of 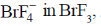 is/are
is/are
(a) KF only
(b) KF and SnF4
(c) SnF4 and SbF5
(d) KF, SnF4 and SbF5
Ans. a
Sol. 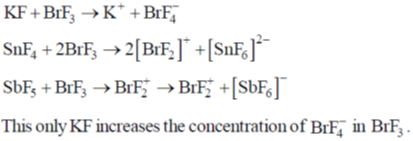
Correct option is (a)
77. Paramagnetic susceptibility of the order of 10–6 cm3 mol–1 observed for KMnO4 is due to
(a) random spin alignment
(b) antiferromagnetic exchange interaction
(c) paramagnetic impurity
(d) temperature independent paramagnetism
Ans. d
Sol. In KMnO4 all the electrons are paired. However, its paramagnetic susceptibility of the order of 10–6 cm3 mol–1 is due to the temperature independent paramagnetism.
Correct option is (d)
78. Correct order of M-C bond length of metallocenes (a–c)
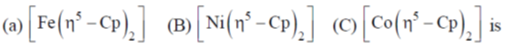
(a) A > B > C
(b) B > C > A
(c) C > B > A
(d) A > C > B
Ans. b
Sol. As the electron goes to 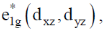 orbital of metallocene bond length increases as they are anologous eg set orbital of an octahedral complex.
orbital of metallocene bond length increases as they are anologous eg set orbital of an octahedral complex.
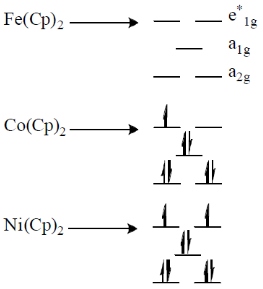
Thus, in Ni(Cp)2 there are highest number of electron in 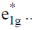 Hence, it has highest M–C bond length.
Hence, it has highest M–C bond length.
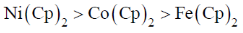
Correct option is (b)
79. A 100 mL solution of 2.5×10–3 M in Bi(III) and Cu(II) each, is photometrically titrated at 745 nm with 0.1 M EDTA solution. Identify correct statements for this titration
(A) Total volume of EDTA solution used in 5 mL.
(B) 3 mL of EDTA is required to complex Bi(III) and 2 mL for Cu(II)
(C) 2.5 mL of EDTA is used for each metal ion
(D) First break in titraction curve is for Cu(II)
Correct statement are
(a) A and B
(b) A and C
(c) A, B and C
(d) B, C and D
Ans. b
Sol. Milimoles of each ion are 0.25 in solution.
On titrating with 0.1 MEDTA each ion will take 2.5 ml of EDTA..
So, total EDTA used = 2.5 + 2.5 = 5
Correct option is (b)
80. On continuous exposure of 10B sample to a slow neutron flux of 1016 m2s–1, its 3% weight fraction disappears in 3 × 107 s. Cross section for neutron capture (in bans) by 10B is
(a) 1000
(b) 3000
(c) 10,000
(d) 30,000
Ans. a
Sol. Neutron incident on 10B = 1016 m2 sec–1
t = 3 × 107 sec
3% fraction disappearse i.e. 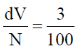
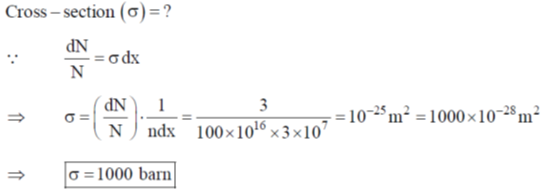
Correct option is (a)
81. The 1H NMR spectrum of 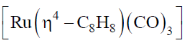 at 230C consists of a sharp single line. The number of signals observed at low temperature (– 1400C) in its spectrum is
at 230C consists of a sharp single line. The number of signals observed at low temperature (– 1400C) in its spectrum is
(a) 8
(b) 6
(c) 4
(d) 2
Ans. c
Sol. 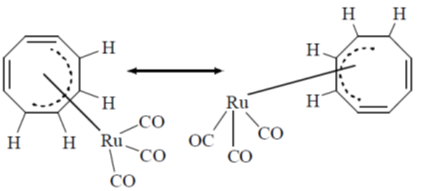
Therefore, total protons 48 but in  COT attached to the four carbon and all 4 protons show different environment at –140ºC because fluxonial behaviour slow down and hence, 4 signals will be observed.
COT attached to the four carbon and all 4 protons show different environment at –140ºC because fluxonial behaviour slow down and hence, 4 signals will be observed.
Correct option is (c)
82. The g value for Ce3+ (4f1) and Pre3+ (4f2) are, respectively
(a) 3/7 and 2/5
(b) 5/7 and 4/5
(c) 6/7 and 3/5
(d) 6/7 and 4/5
Ans. d
Sol. Lande's splitting factor g is calculated as
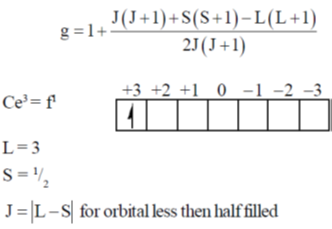
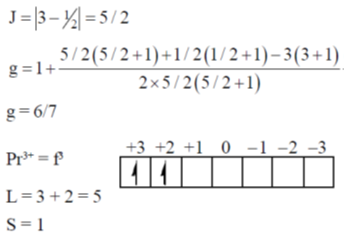
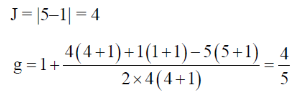
Correct option is (d)
83. The room temperature magnetic moment 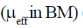 for a monomeric Cu(II) complex is greater than 1.73. This may be explained using the expression:
for a monomeric Cu(II) complex is greater than 1.73. This may be explained using the expression:
(a) 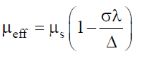
(b) 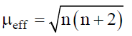
(c) 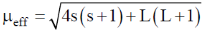
(d) 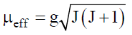
Ans. a
Sol. The complexes having T ground state have orbital contribution to magnetic moment however for complex having A or E ground state some time 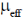 is slightly greater than
is slightly greater than 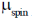 is due to mixing of first excited state T (having same spin multiplicity to ground state) mixes with A or E due to spin coupling and there
is due to mixing of first excited state T (having same spin multiplicity to ground state) mixes with A or E due to spin coupling and there 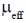 is calculated by
is calculated by
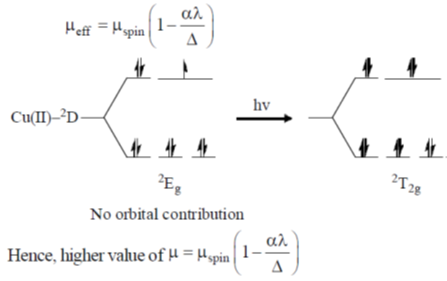
Correct option is (a)
84. The number of 3c – 2e bonds present in Al(BH4)3 is
(a) four
(b) three
(c) six
(d) zero
Ans. c
Sol. 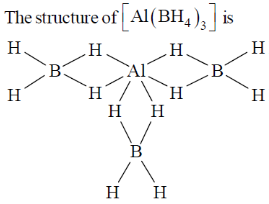
Thus, number of 3c–2e– bond is equal = 6
Correct option is (c)
85. The number of skeletal electrons present in the compounds C2B3H5, C2B4H6 and B5H9 are, respectively
(a) 10, 12 and 12
(b) 12, 14 and 14
(c) 10, 12 and 14
(d) 12, 14 and 12
Ans. b
Sol. 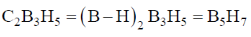
Each B–H unit give 2 electron. For cage bonding.
Hence, 5 (B – H) = 5 × 2 = 10 electron. Each hydrogen one electron,
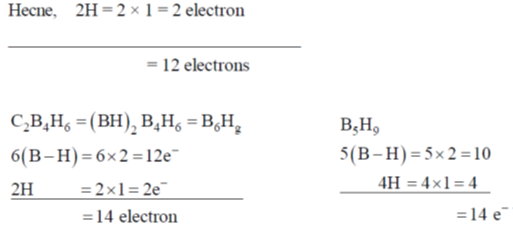
Correct option is (b)
86. Identify correct statements for the EPR spectrum of VO(acac)2 [with square pyramidal geometry at vanadium] at 77K [1(51V] = 7/2].
(A) It has two g values
(B) It has 8 lines only
(C) It has one g value
(D) It has two patterns of 8 lines each.
(a) A and D
(b) A and C
(c) B and C
(d) B and D
Ans. a
Sol. 
For vanadium, I = 7/2. So, 2NI + 1 = 2(1) (7/2) + 1 = 8
So, in EPR spectrum it has two G values and it has two patterns of 8 lines each.
Correct option is (a)
87. The number of lines shown by the BH3 part of the molecule Ph3P. 11BH3 in the 1H and 11B NMR spectra are, respectively [I(11B) = 3/2; I(31P)=1/2]
(a) 8 and 8
(b) 4 and 8
(c) 3 and 6
(d) 6 and 3
Ans. a
Sol. BH3 part of the molecule Ph3P. 11BH3
1H NMR spectrum = (2N1I + 1) × (2N2I + 1) = (2×1×3/2 + 1) × (2×1 × ½ + 1) = 4×2 = 8
11B spectrum = (2N1I + 1) × (2N2I + 1) = (2×3×½ + 1) × (2×1 × ½ + 1) = 4×2 = 8
Correct option is (a)
88. To record Mössbauer spectrum of Fe containing samples, a source 'X' is used. X after a nuclear transformation (Y), give  γ– radiation used in Mössbauer spectroscopy.
γ– radiation used in Mössbauer spectroscopy.
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 57Co, electron capture
(d) 57Fe, electron capture
Ans. c
Sol. 57Fe* can be prepared by electron capture process from radioactive 
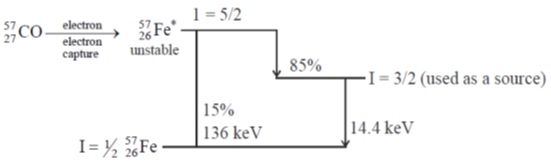
Correct option is (c)
89. Correct combination of number and size of rings present in a metal ion-porphine complex (including metal ion bearing chelate rings) is
(a) four 5 – membered and four 6 – membered
(b) two 5 – membered and four 6 – membered
(c) six 5 – membered and four 6 – membered
(d) five 5 – membered and four 6 – membered
Ans. a
Sol. Structure of m-porphyrine complex can be shown as
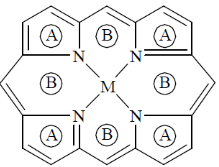
Here, (A) represents = five membered ring
(B) represents = six membered ring
Thus, these are four 5-membered ring and four-6-membered ring.
Correct option is (a)
90. In human body cis – platin hydrolyzes to diaqua complex and modifies the DNA structure by binding to
(a) N – atom of guanine base
(b) O – atom of cytosine base
(c) N – atom of adenine base
(d) O – atom of thymine base
Ans. a
Sol. cis-platin modifies the DNA structure by binding to N-7 nitrogen atom of guanine base.
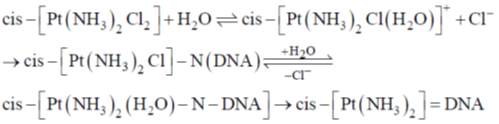
Correct option is (a)
91. For fluxional Fe(CO)5 (structure given below) in solution, the exchange of numbered CO groups will be between
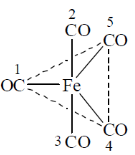
(a) 2 and 5; 3 and 4
(b) 2 and 3; 4 and 5
(c) 2 and 3; 1 and 5
(d) 1 and 2; 4 and 5
Ans. a
Sol. During fluxional axial ligands are exchanged with equatorial ligand. Hence,
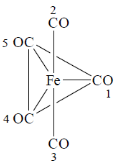
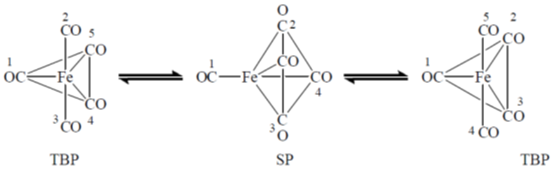
Correct option is (a)
92. In the following reaction sequence
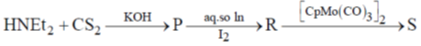
where dtc = dithiocarbamate and tds = thiuramdisulfide.
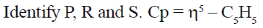
(a) P – Et2dtc –K+; R – Et4tds; S – CpMo(Et2dtc) (CO)2
(b) P – Etdtc –K+; R – Et3tds; S – CpMo(Et3dtc) (CO)2
(c) P – Et4dtc –K+; R – Et2tds; S – CpMo(Et4dtc) (CO)
(d) P – Etdtc –K+; R – Ettdc; S – CpMo(Etdtc) (CO)
Ans. a
Sol. 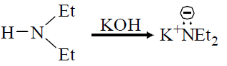
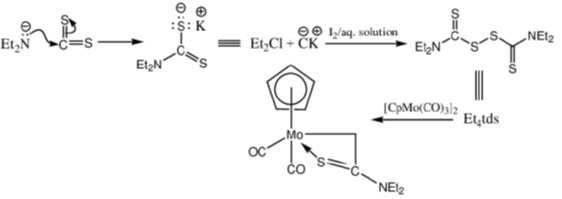
Correct option is (a)
93. Reaction of Cr(CO)6 with LiC6H5 gives A which reacts with [Me3O][BF4] to give B. The structures of A and B respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 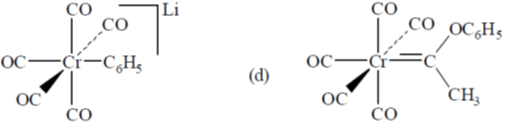
Ans. a
Sol. 
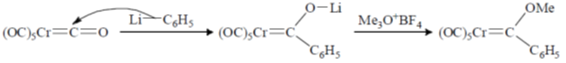
Correct option is (a)
94. Heating a sample of 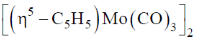 results in the formation
results in the formation 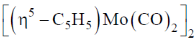 with eliminaton of 2 equivalents of CO. The Mo-Mo bond order in this reactions changes from
with eliminaton of 2 equivalents of CO. The Mo-Mo bond order in this reactions changes from
(a) 2 to 3
(b) 1 to 2
(c) 1 to 3
(d) 2 to 4
Ans. c
Sol. TVE = 10 + 12 + 12 = 34 = A
B = (n × 18) – A
B = (2×18)–34 = 36–34 = 2
Number of metal-metal bond 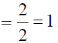
TVE = 10 + 12 + 8 = 30 = A
B = (n×18)–A = 36–30 = 6
Number of metal-metal bond 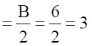
Correct option is (c)
95. A plausible intermediate involved in the self metathesis reaction of 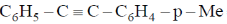 catalyzed by
catalyzed by 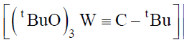 is
is
(a) 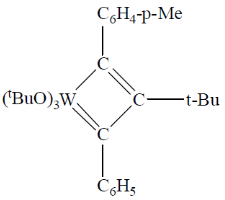
(b) 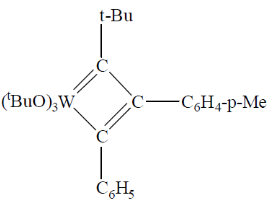
(c) 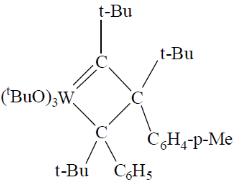
(d) 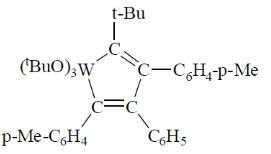
Ans. b
Sol. 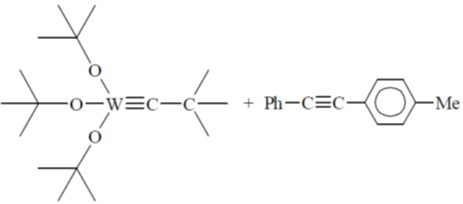
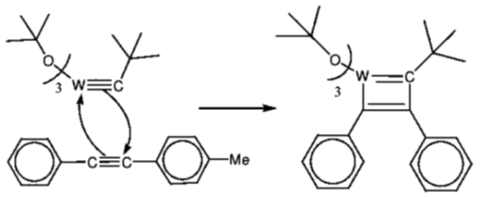
Correct option is (b)
96. The major product formed in the following reaction is
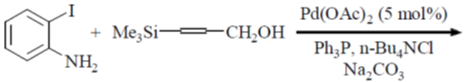
(a) 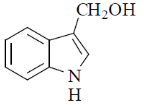
(b) 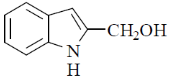
(c) 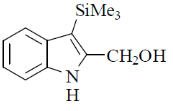
(d) 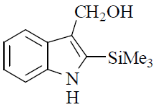
Ans. d
Sol. 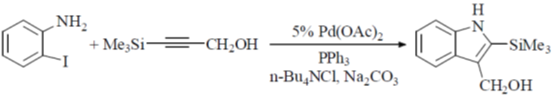
Correct option is (d)
97. The major product formed in the following reaction sequence is
(a) 
(b) 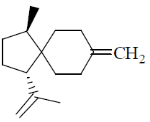
(c) 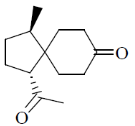
(d) 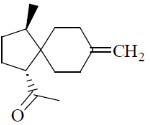
Ans. c
Sol. 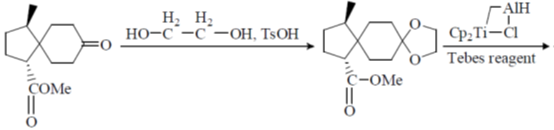
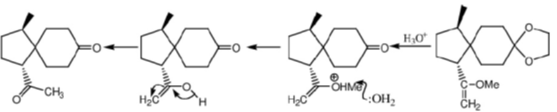
Correct option is (c)
98. The major product formed in the following reaction is
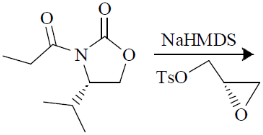
(a) 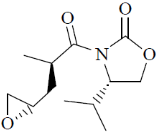
(b) 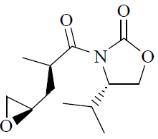
(c) 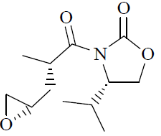
(d) 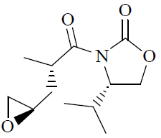
Ans. a
Sol. 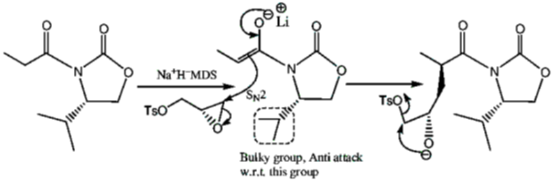
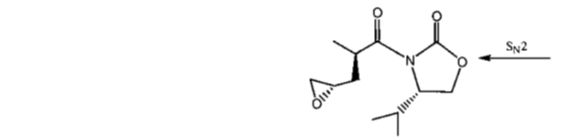
Correct option is (a)
99. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are
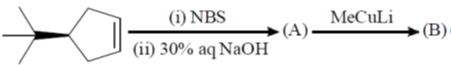
(a) 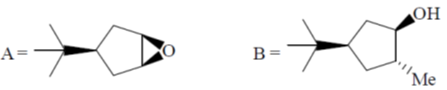
(b) 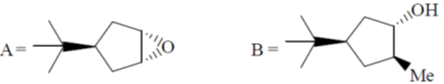
(c) 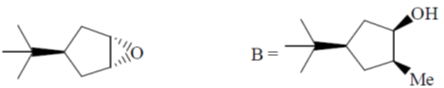
(d) 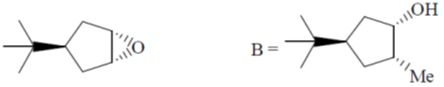
Ans. a
Sol. 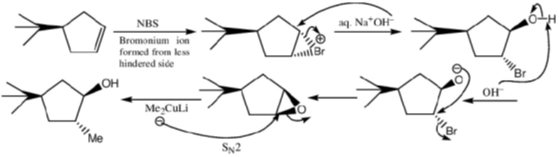
Correct option is (a)
100. The major product formed in the following reaction sequence is
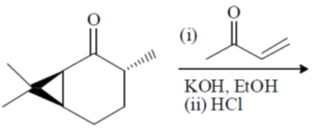
(a) 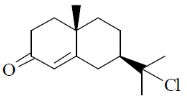
(b) 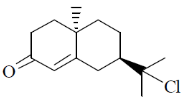
(c) 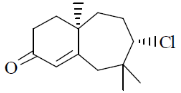
(d) 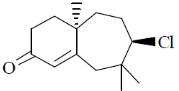
Ans. a
Sol. 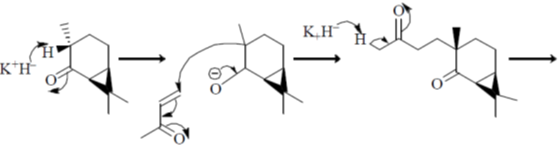
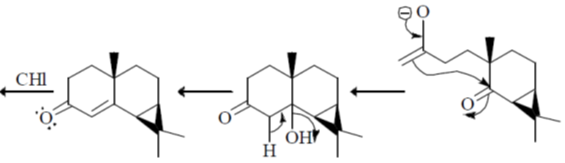
Correct option is (a)
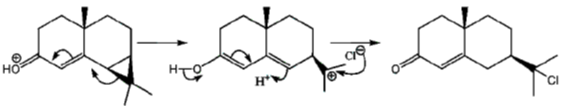
101. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 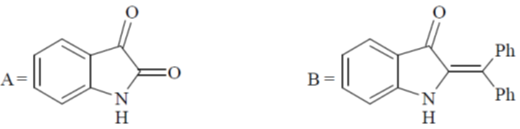
Ans. b
Sol. 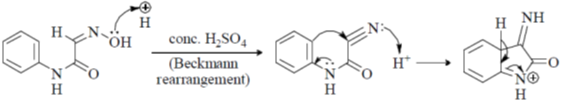
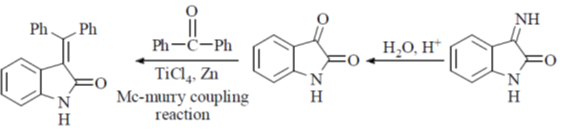
Correct option is (b)
102. The major product in the following reaction is
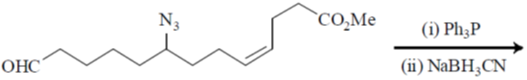
(a) 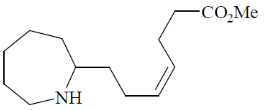
(b) 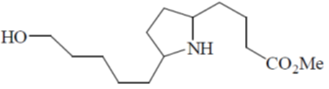
(c) 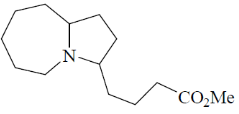
(d) 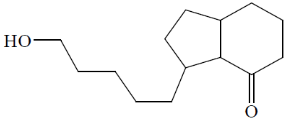
Ans. a
Sol. 
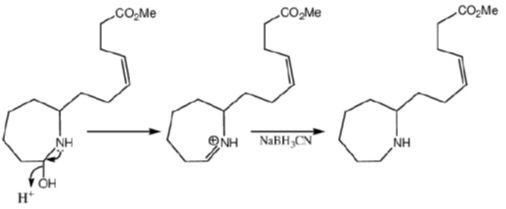
Correct option is (a)
103. The correct reagent combination to effect the following reaction is
(a) (i) NaBH4, CeCl3, MeOH, 00C; (ii) H2,[Ir(COD) (py)P(Cy)3]PF6; (iii) Ph3P, PhCO2H, DEAD; (iv) LiAlH4.
(b) (i) Li, liquid NH3; (ii) H2,[Ir(COD) (py)P(Cy)3]PF6; (iii) Ph3P, PhCO2H, DEAD; (iv) NaBH4, CeCl3, MeOH, 00C
(c) (i) H2, Pd/C; (ii) LIAlH4, –780C
(d) (i) H2, Pd/C; (ii) Li, liquid NH3
Ans. a
Sol. 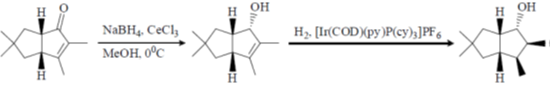
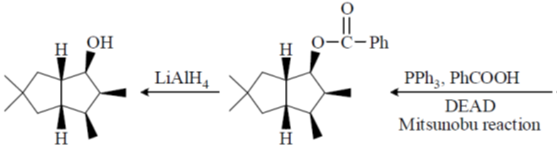
Correct option is (a)
104. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are
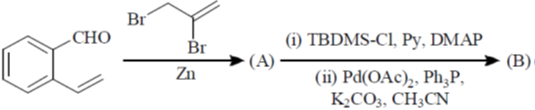
(a) 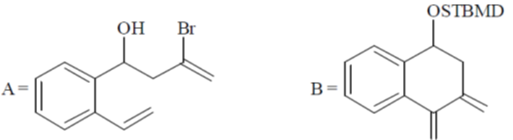
(b) 
(c) 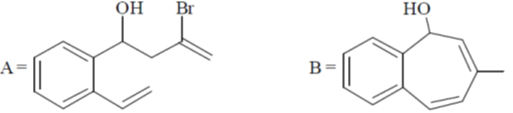
(d) 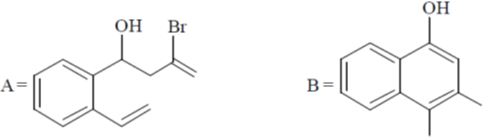
Ans. a
Sol. 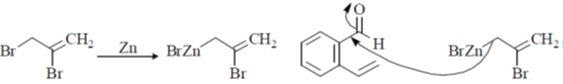
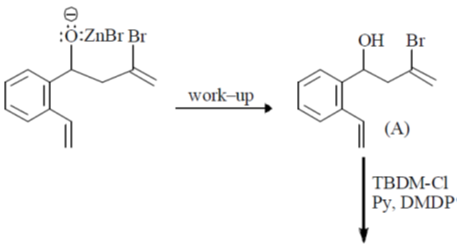
Correct option is (a)
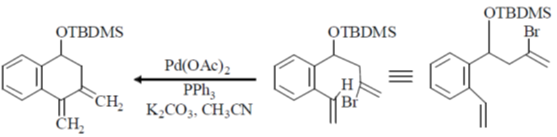
105. Structure of the intermediate A and major product B in the following reaction sequence are
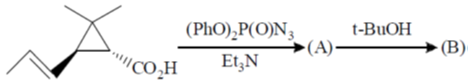
(a) 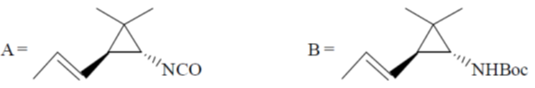
(b) 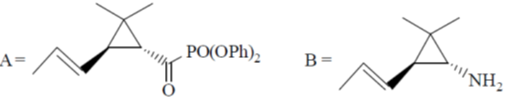
(c) 
(d) 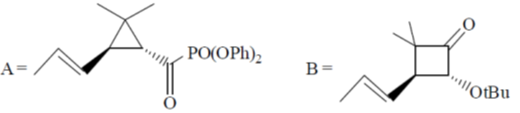
Ans. a
Sol. 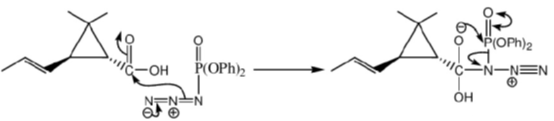
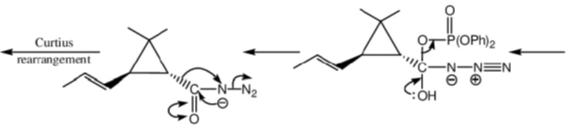
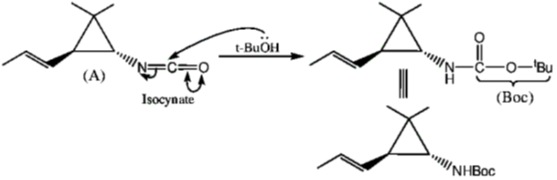
Correct option is (a)
106. The correct match for the following transformations P–S with the processes I-IV is
Reactions:
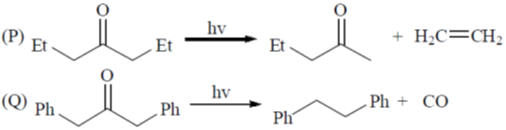
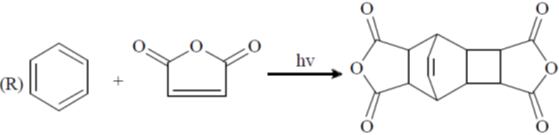
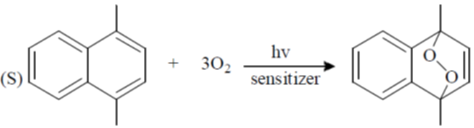
Processes:
(I) Diels – Alder
(II) Norrish Type – I
(III) Photocycloaddition followed by Diels – Alder
(IV) Norrish Type – II
(a) P – II; Q – IV; R – III; S – I
(b) P – II; Q – IV; R – I; S – II
(c) P – IV; Q – II; R – III; S – I
(d) P – IV; Q – II; R – I; S – III
Ans. c
Sol. 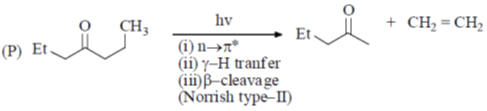
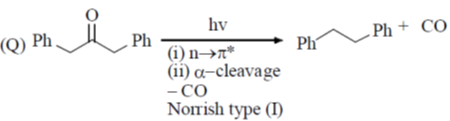
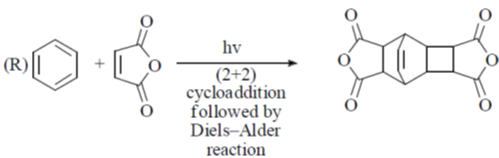
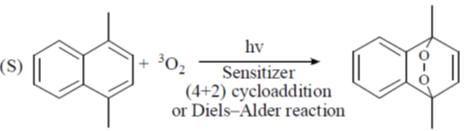
Correct option is (c)
107. The correct match for the reaction P – S with the names of cyclizations I – IV is
Reactions:
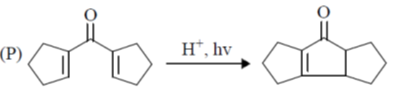
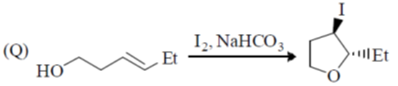
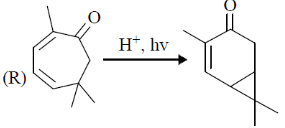
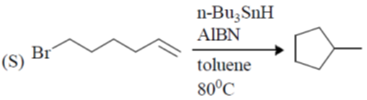
Name of Cyclization
(I) halocyclization
(II) Nazarov cyclization
(III) radical cyclization
(IV) electrocyclization
(a) P – IV; Q – I; R – II, S – II
(b) P – II; Q – I; R – IV; S – III
(c) P – IV; Q – II; R – III; S – I
(d) P – II; Q – I; R – III; S – IV
Ans. b
Sol. 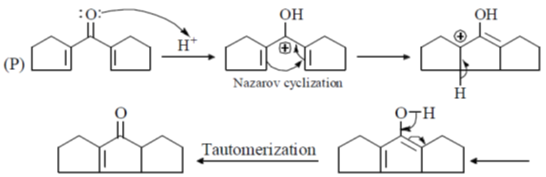
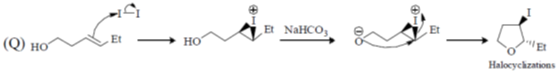
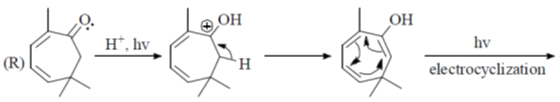
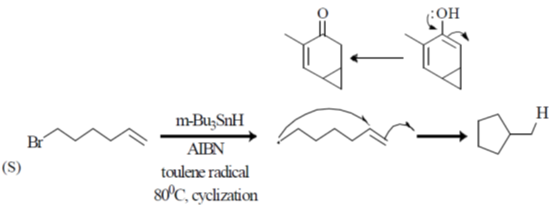
Correct option is (b)
108. The correct structure of the intermediate, which leads to the product in the following reaction is
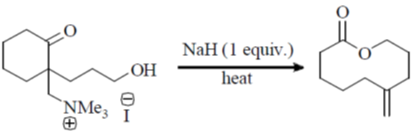
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 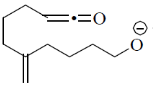
(d) 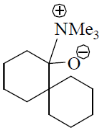
Ans. a
Sol. 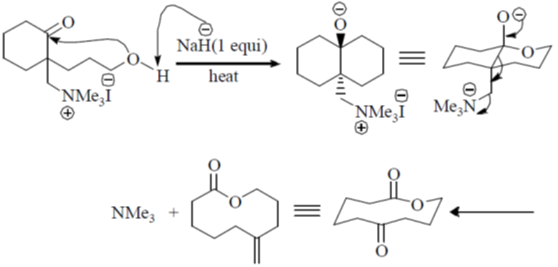
Correct option is (a)
109. The major product formed in the following reaction is
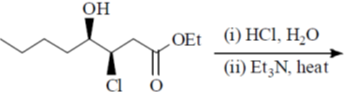
(a) 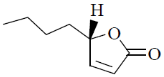
(b) 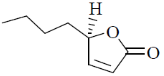
(c) 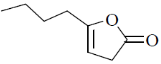
(d) 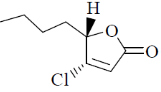
Ans. b
Sol. 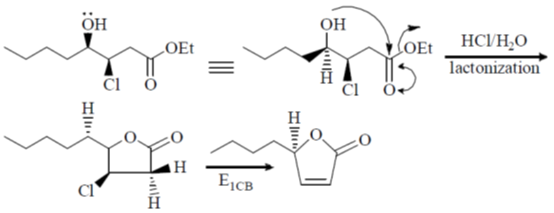
Correct option is (b)
110. The major product formed in the following reaction is
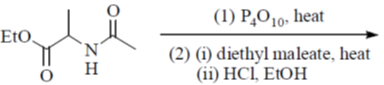
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 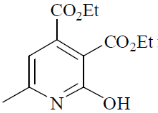
(d) 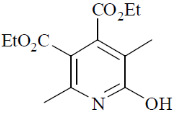
Ans. a
Sol. 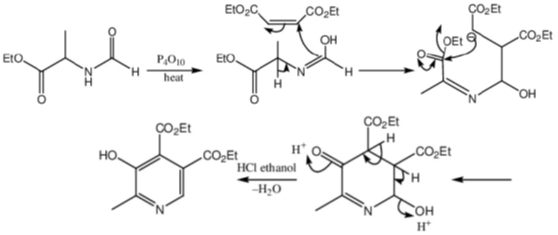
Correct option is (a)
111. The major product A and B formed in the following reaction sequence are
(a) 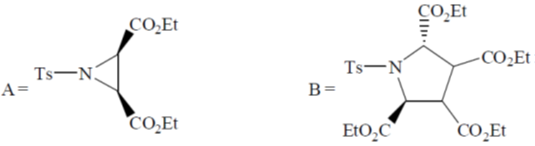
(b) 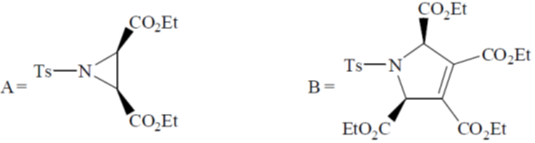
(c) 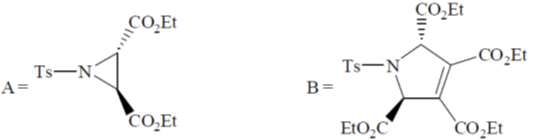
(d) 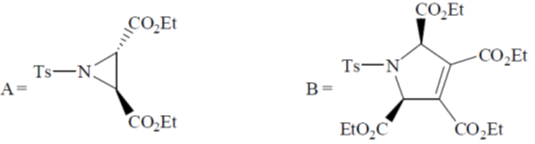
Ans. a
Sol. 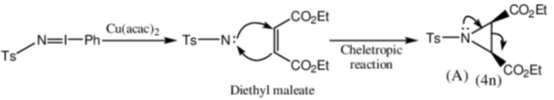
Correct option is (a)
112. The major product formed in the following reaction is
(a) 
(b) 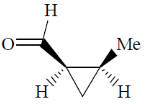
(c) 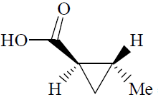
(d) 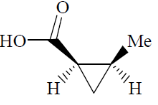
Ans. d
Sol. 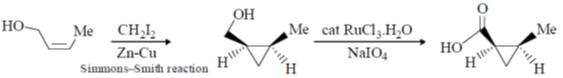
Correct option is (d)
113. The intermediate A and the major product B in the following reaction sequence are
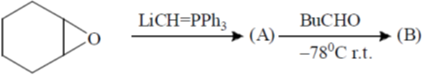
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 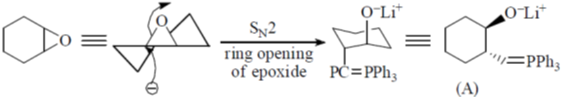
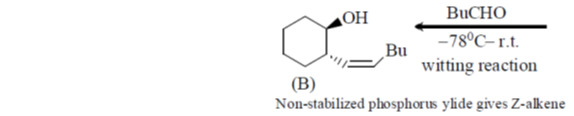
Correct option is (a)
114. The correct structure of the compound, which shows following 13C NMR DEPT-135 data is 13C NMR DEPT–135: negative peaks at  30.2, 31.9, 61.8, 114.7 ppm; positive peack at 130.4 ppm
30.2, 31.9, 61.8, 114.7 ppm; positive peack at 130.4 ppm
(a) 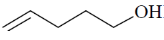
(b) 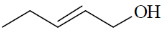
(c) 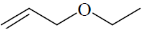
(d) 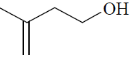
Ans. a
Sol. 13C NMR DEPT-135 shows positive CH3 and CH and negative CH2 signals.
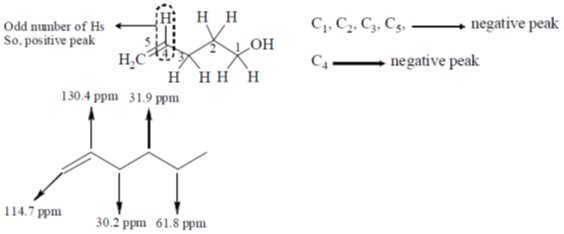
Correct option is (a)
115. A compound displays the following spectral data. The correct structure of the compound is IR : 1690 cm–1.
1H NMR :  2.5 (s, 3H), 3.8 (s, 3H), 6.9 (d, J=8Hz, 2H), 7.8 (d, J = 8 Hz, 2H) ppm
2.5 (s, 3H), 3.8 (s, 3H), 6.9 (d, J=8Hz, 2H), 7.8 (d, J = 8 Hz, 2H) ppm
13C NMR :  197, 165, 130, 129, 114, 56, 26 ppm
197, 165, 130, 129, 114, 56, 26 ppm
(a) 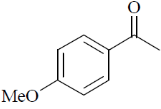
(b) 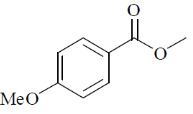
(c) 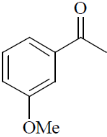
(d) 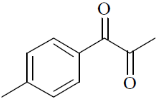
Ans. a
Sol. 6.9 (d, J = 8Hz, 2H); 7.8 (d, J = 8Hz, 2H)
Confirms the para-substitution pattern.
Since, J = 8Hz, 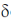 value in aromatic region, 2 doublets of 4Hs.
value in aromatic region, 2 doublets of 4Hs.

Correct option is (a)
116. The major products A and B formed in the following sequence are
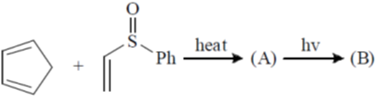
(a) 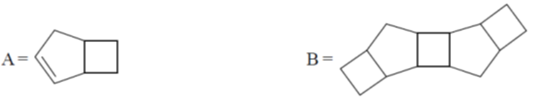
(b) 
(c) 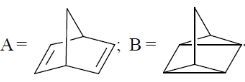
(d) 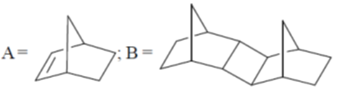
Ans. c
Sol. 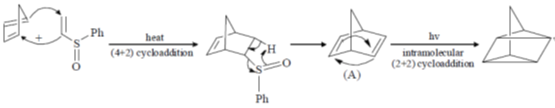
Correct option is (a)
117. The major product formed in the following reaction is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 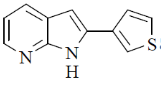
(d) 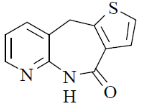
Ans. c
Sol. 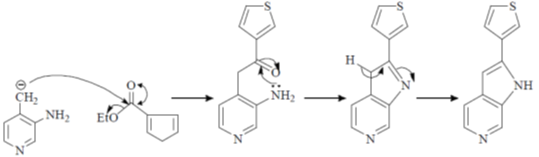
Correct option is (c)
118. The major product formed in the following reaction is
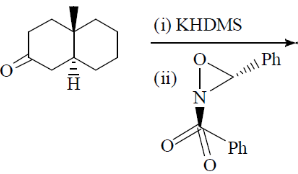
(a) 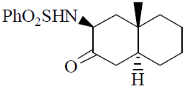
(b) 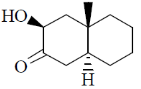
(c) 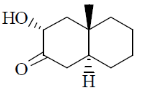
(d) 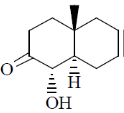
Ans. c
Sol. 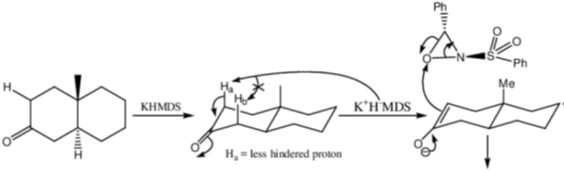
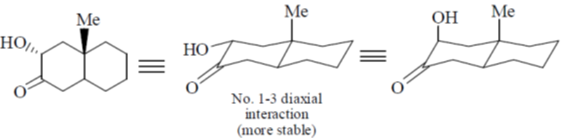
Correct option is (c)
119. The major product formed in the following reaction is
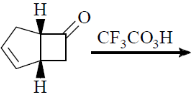
(a) 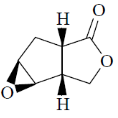
(b) 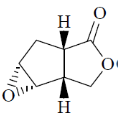
(c) 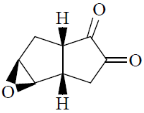
(d) 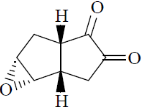
Ans. c
Sol. 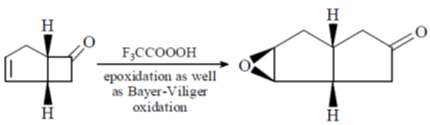
Correct option is (c)
120. The major product formed in the following reaction is
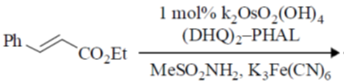
(a) 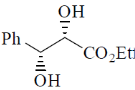
(b) 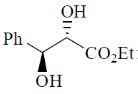
(c) 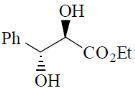
(d) 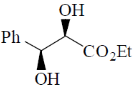
Ans. d
Sol. 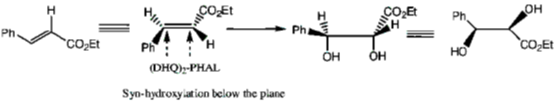
Correct option is (d)
121. The signal – particle translational partition function (f) for an ideal gas in a fixed volume V depends on the thermal de – Broglie wavelength 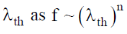 where
where
(a) n = 3
(b) n = 1
(c) n = – 1
(d) n = – 3
Ans. d
Sol. Single – particle translational partition function 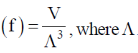 = de – Broglie wavelength
= de – Broglie wavelength
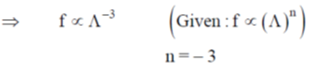
Correct option is (d)
122. 15 particles are distributed among 4 levels as shown in state I. Heat is given to the system and no work is done. The final state could be
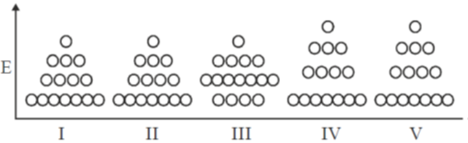
(a) I
(b) III
(c) IV
(d) V
Ans. a
Sol. Since, only heat is given to system 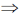 only number of particles in given states would change under the criterion of Boltzmann – Equilibrium.
only number of particles in given states would change under the criterion of Boltzmann – Equilibrium.
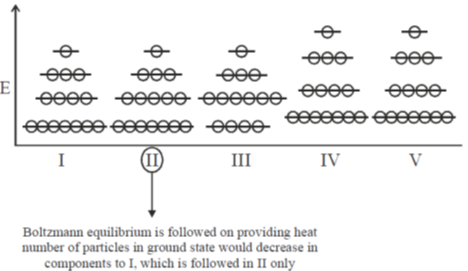
Correct option is (a)
123. In an NMR spectrometer containing a 2.5T magnet, Larmor precession frequency of 1H is 100 MHz. The radiofrequency used in this spectrometer has an associated magnetic field strength of 2.5 × 10–4T. The duration of a 900 pulse in this instrument is
(a) 25 × 10–6 s
(b) 50 × 10–6 s
(c) 25 ×10–5 s
(d) 50 × 10–5 s
Ans. a
Sol. A 900 pulse width or pulse duration is the amount of time the pulse of energy is applied to the particular sample in order to flip all the spins into the X – Y plane.
The approximate field width of excitation is given by the formula, RFfield = 1 / (4*900 pulse duration in sec.)
RFfield is frequency due associated field strength = 2.5 × 10–4 × 42.57 MHz = 10642.5 Hz
Here, 42.57 MHz/T is gyromagnetic ratio for proton
Now, 1064.5 Hz = 1/(4*pulse duration in sec.)
Pulse duration = 1/(1064.5*4) sec. = 1/42570 sec. = 23.5 × 10–6 sec.
Correct option is (a)
124. Upon application of a weak magnetic field, a line in the micirowave absorption spectrum of rigid rotor splits into 3 lines. The quantum number (J) of the rotational energy level from which the transition originates is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Ans. a
Sol. Under the section rule DMj = 0, ± 1
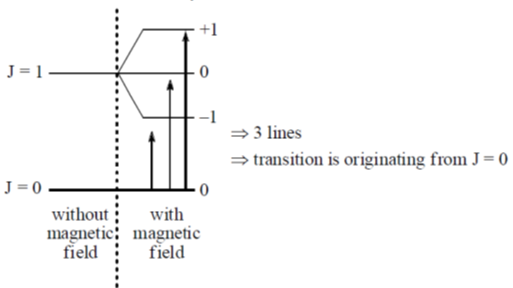
Correct option is (a)
125. Phase diagram of a compound is shown below
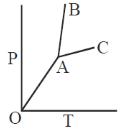
The slpes of the lines OA, AC and AB are  respectively. If melting point and
respectively. If melting point and  of melting are 300K and 3 kJ mole–1 respectively, the change in the volume on melting is
of melting are 300K and 3 kJ mole–1 respectively, the change in the volume on melting is
(a) 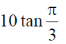
(b) 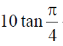
(c) 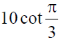
(d) 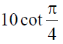
Ans. c
Sol. 
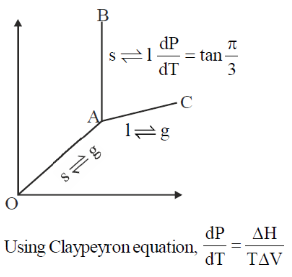
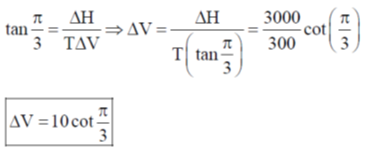
Correct option is (c)
126. The figure below describes how a Carnot eingine works. It starts from the adiabatic compression step denoted by
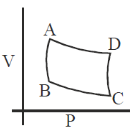
(a) AB
(b) BC
(c) DC
(d) AD
Ans. b
Sol. BC is an adiabatic compression
Correct option is (b)
127. The point group obtained by adding symmetry operation  to the point group C4 is
to the point group C4 is
(a) S4
(b) C4h
(c) D2h
(d) D4
Ans. b
Sol. 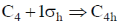
Correct option is (b)
128. For a particle of mass m confined in a rectangular box with sides 2a and a, the energy and degeneracy of the first excited state, respectively, are
(a) 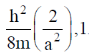
(b) 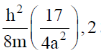
(c) 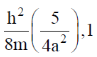
(d) 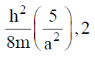
Ans. a
Sol. 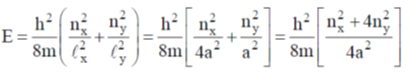
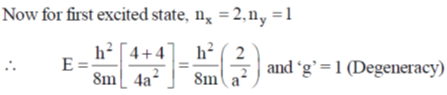
Correct option is (a)
129. The ionization energy of hydrogen atom in its ground state is approximately 1.3.6 eV. The potential energy of He+, in its ground state is approximately
(a) –54.4 eV
(b) –27.2 eV
(c) –13.6 eV
(d) –108.8 eV
Ans. d
Sol. 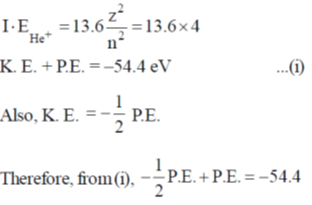

Correct option is (b)
130. The character table for the D3 point group is provided below:
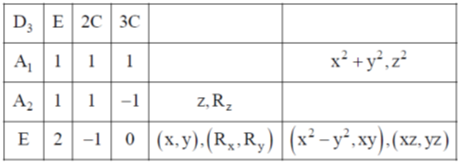
For this point group, the correct statement among the following is:
(a) it is possible to have a totally symmetric normal mode of vibration which is IR-active
(b) all IR-active normal modes are necessarily Raman inactive
(c) all Raman-active normal modes are necessarily IR-active
(d) it is possible to have a pair of IR-active normal modes that are degenerate.
Ans. d
Sol. From column '3' and column '4'
In front of 'E' irreducible representation, it is clear that there is a pair of I.R active momdes which are degenerate.
Degeneracy of 'E' = 2
Correct option is (d)
131. Suppose, 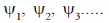 are wavefunctions of an anharmonic oscillator and
are wavefunctions of an anharmonic oscillator and 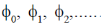 are wavefunctions of a harmonic oscillator with increasing order of energy. The subscripts denote vibrational quantum numbers in both the cases. Given.
are wavefunctions of a harmonic oscillator with increasing order of energy. The subscripts denote vibrational quantum numbers in both the cases. Given.
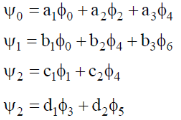
the FORBIDDEN electric dipole (assumping the dipole operator is linear in normal coordinates) transition among the following is
(a) 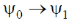
(b) 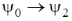
(c) 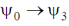
(d) 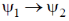
Ans. a
Sol. 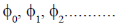 are the wavefunctions of a harmonic oscillator in ground state, first excited state, second excited state respectively.
are the wavefunctions of a harmonic oscillator in ground state, first excited state, second excited state respectively.
We know that for a harmonic oscillator 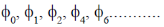 will have even parity and
will have even parity and 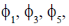
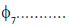 will have odd parity.
will have odd parity.
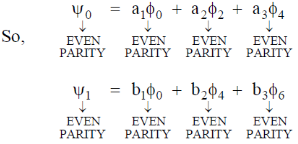
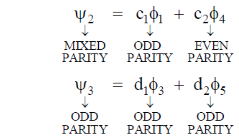
Since, the dipole operator is linear, therefore electric dipole transition is forbidden if the initial and final state have same parity.
Since, 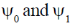 have same parity.
have same parity.
So, 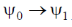 transition is FORBIDDEN.
transition is FORBIDDEN.
Correct option is (a)
132. If U is a function of V and T, 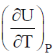 is equal to
is equal to 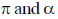 are the internal pressure and the coefficient of thermal expansion, respectively)
are the internal pressure and the coefficient of thermal expansion, respectively)
(a) CP
(b) CV
(c) 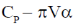
(d) 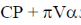
Ans. d
Sol. 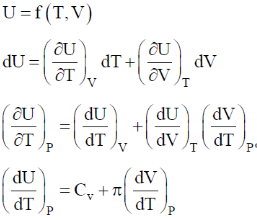
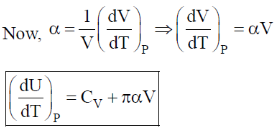
Correct option is (d)
133. The character table of C3V point group is provided below, along with an additional reducible representation, 
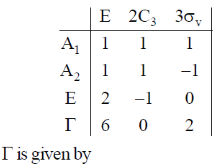
(a) A1 + A2 + 2E
(b) 2A1 + 2E
(c) 2A2 + 2E
(d) 2A1 + 2A2 + E
Ans. b
Sol. 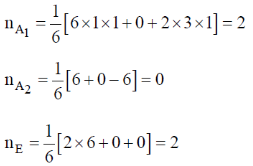
Correct option is (b)
134. For the chemical reaction in aqueous solution,
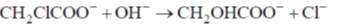
the correct statement is
(a) increase of pressure increases the rate constant
(b) increase of dielectric constant increases the rate constant
(c) increase of ionic strength decreases the rate constant
(d) the entropy of activation is positive
Ans. b
Sol. Entropy of activation for bimolecular reaction is negative. Therefore, (d) is incorrect
Here, positive salt effect is observed. Therefore, increase of ionic strength increases the rate constant, Therefore option (c) is incorrect
Increase of Dielectric constant increases rate constant.
Correct option is (b)
135. If experimentally observed rate constant is greater than the maximum value of rate constant obtained using hard – sphere model of collision theory, then relation between the impact parameter (b) and sum of the radii of two reactants is
(a) b = r1 + r2
(b) b < r1 + r2
(c) b > r1 + r2
(d) b < r1 + r2
Ans. c
Sol. If experimental rate is greater than maximum rate using collision theory then impact parameter must be greater than sum of radii of reactants.
Correct option is (c)
136. Half – life t1/2 for a third order reaction 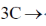 products, where C0 is the initial concentration of C, will be
products, where C0 is the initial concentration of C, will be
(a) 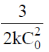
(b) 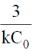
(c) 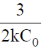
(d) 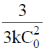
Ans. a
Sol. For a 3rd order reaction,
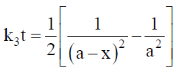
For half – life time,
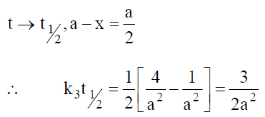
Correct option is (a)
137. For a simple cubic lattice, the ratio between the unit cell length and the separation of two adjacent parallel crystal planes can NOT have a value of
(a) 51/2
(b) 71/2
(c) 111/2
(d) 131/2
Ans. b
Sol. 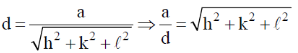
Correct option is (b)
138. Adsorption isotherm of three gases A, B and C are shown in the following figure, where  is the percentage of surface coverage
is the percentage of surface coverage
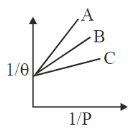
The correct order of the extent of adsorption of these gases is
(a) A > B > C
(b) B > A > C
(c) C > A > B
(d) C > B > A
Ans. d
Sol. 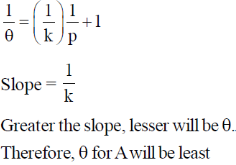
Correct option is (d)
139. Choosing some Hamiltonian H and an orthonormal basis, a linear variation is carried out to get approximately energies 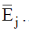 With 2 basis function, one obtains
With 2 basis function, one obtains 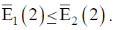 Taking 3 basis functions, similarly three ordered energies
Taking 3 basis functions, similarly three ordered energies 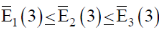 are found. The relation which holds from the following is?
are found. The relation which holds from the following is?
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. Correct option is (d)
140. Average value of momentum for the ground state of a particle in a 1 – d box is zero because
(a) [p, H] = 0
(b) V (potential) = 0
(c) H is hermitian
(d) the state is bound and stationary
Ans. d
Sol. For any bound state particle has equal and opposite value of momentum.
Correct option is (d)
141. For a hermitian operator A, which does NOT commute with the Hamiltonian H, let 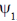 be an eigenfunction of A and
be an eigenfunction of A and 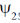 be an eigenfunction of H. The correct statement regarding the average value of commutator of A with H
be an eigenfunction of H. The correct statement regarding the average value of commutator of A with H 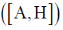 is
is
(a) 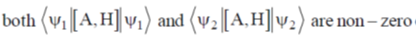
(b) 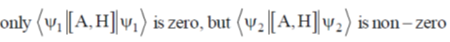
(c) 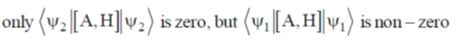
(d) 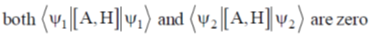
Ans. d
Sol. 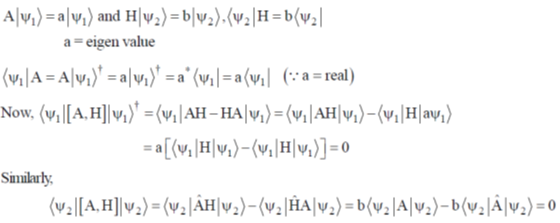
Correct option is (d)
142. The condensation of a hydroxy acid produces a polyster with the probability of linkage at both ends being p. The mole fraction of k–merchain formation is
(a) 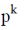
(b) 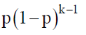
(c) 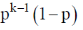
(d) 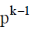
Ans. c
Sol. In Flory Schulz distribution
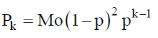
Therefore, mole fraction of polymer with a chain length k is
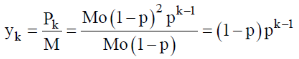
Correct option is (c)
143. In simple molecular orbital theory of hydrogen molecule, bonding 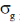 and anti – bonding
and anti – bonding 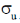 molecular orbitals are constructed as linear combinations of atomic orbitals of two hydrogen atoms. Thes spatial part of a purely covalent singlet wavefunction is obtained by
molecular orbitals are constructed as linear combinations of atomic orbitals of two hydrogen atoms. Thes spatial part of a purely covalent singlet wavefunction is obtained by
(a) 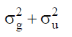
(b) 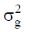
(c) 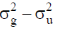
(d) 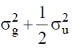
Ans. c
Sol. Correct option is (c)
144. Two aqueous 1:1 electrolyte systems A and B are at different temperature TA and TB and CA and CB concentrations, respectively. Their Debye lengths will be equal if
(a) 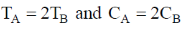
(b) 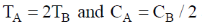
(c) 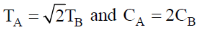
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Debye - Huckel screening legnths

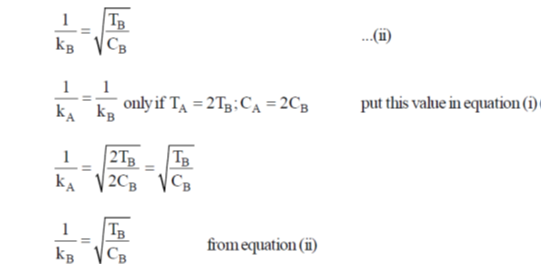
Equation (i) = equation (ii)
Correction option is (a)
145. Aqueous solutions of NaCl, CaCl2 and LaCl3 show the following plots of logarithms of mean ionic activity coefficient 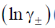 vs molar concentration (c)
vs molar concentration (c)
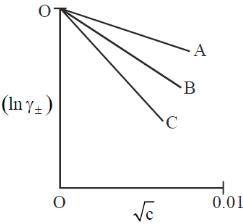
The correct option is then
(a) NaCl – C ; CaCl2 – B ; LaCl3 – C
(b) NaCl – A ; CaCl2 – B ; LaCl3 – C
(c) NaCl – A ; CaCl2 – C ; LaCl3 – B
(d) NaCl – C ; CaCl2 – A ; LaCl3 – B
Ans. b
Sol. 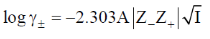
For same concentration of electrolyte 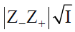 will be smallest for NaCl and largest for LaCl3. As negative sign is there so slope of NaCl will be least negative and slope of LaCl3 will be most negative.
will be smallest for NaCl and largest for LaCl3. As negative sign is there so slope of NaCl will be least negative and slope of LaCl3 will be most negative.
Correct option is (b)
