CSIR NET CHEMISTRY (JUNE - 2014)
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
21. The correct order of basicity for the following anions is

(a) II > III > I
(b) I > II > III
(c) II > I > III
(d) III > II > I
Ans. a
Sol. 
In case of the first operate resonance as well as more inductive effect, so less basic.
In case of ortho and para resonance as well as inductive effect both operate. Thus, electron withdrawl will be more in the case of ortho and para substituted intro phenol.
Thus, conjugate base of ortho and para will be less basic.
Meta substituted phenoxide (II) will be most basic.
Now, is between I and IIII, since H – bonding (intramolecular) occurs in the case of I, It is less acidic as compared to para, thus it will be more basic as compared III. II > I > III.
22. The major product formed in the reaction of 2, 5 – hexanedione with P2O5 is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Mechanism:
P2O5 is a dehydrating agent. Reacts with 1, 4 – dicarbonyl compound to form substituted furan. This reaction is known as Paal Knorr synthesis.
Correct answer is (a)
23. The absolute configuration of the two stereogenic (chiral) centres in the following molecule is
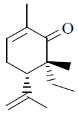
(a) 5R, 6R
(b) 5R, 6S
(c) 5S, 6R
(d) 5S, 6S
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
24. The correct statement about the following molecule is

(a) Molecular is chiral and possesses a chiral plane
(b) Molecular is chiral and possesses a chiral axis
(c) Molecular is achiral as it possesses a plane of symmetry
(d) Molecular is achiral as it possesses a centre of symmetry
Ans. a
Sol. In Biphenyl system chirality is due to presence of plane that is why it comes under planar chirality. Since, the given molecule possesses a chiral plane. Thus it is optically active.
Correct answer is (a)
25. Consider the following statements about cis- and trans – decalins
(A) cis – isomer is more stable than trans – isomer
(B) trans – isomer is more stable than cis – isomer
(C) trans – isomer undergoes ring – flip
(D) cis – isomer undergoes ring – flip
trans correct statements among the above are
(a) B and D
(b) A and C
(c) A and D
(d) B and C
Ans. a
Sol. • Trans – Decalin is more stable about 2.7 kcal / mole as compared with cis – decalin.
• Trans – Decalin has a unique and rigid conformation ring fliping is not possible as it would other wise afford a highly strained system with one ring attached to other by two axial bond.
• Cis – Decalin exists as an equilibrium between two enantiomeric all chair conformation. So, flip into one other.


Correct answer is (a)
26. In bis (dimethylglyoximato) nickel (II), the number of Ni – N, Ni – O and intramolecular hydrogen bond (s), respectively are
(a) 4, 0 and 2
(b) 2, 2 and 2
(c) 2, 2 and 0
(d) 4, 0 and 1
Ans. a
Sol. Ni++ is tested by dmg.

The structure of complex is

Therefore,

Correct answer is (a)
27. Among the following species, (A) Ni(II) dimeth dimethylglyoximate, (BI) Al(III) as oximate, (C) Ag(I) as chloride, those that precipitate with the urea hydrolysis method are
(a) A, B and C
(b) A and B
(c) A and C
(d) B and C
Ans. b
Sol. Correct answer is (b)
28. If an enzyme fixes N2 in plants by evolving H2, the number of electrons and protons associated with that, respectively are
(a) 6 and 6
(b) 8 and 8
(c) 6 and 8
(d) 8 and 6
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct answer is (b)
29. The particles postulated to always accompany the positron emission among
(A) neutrino
(B) anti – neutrion
(C) electron
(a) A, B and C
(b) A and B
(c) A and C
(d) B and C
Ans. c
Sol. Particles that are always to emit during positron emission

Correct answer is (c)
30. Toxicity of cadmium and mercury in the body is being reversed by proteins, mainly using the amino acid residue,
(a) Glycine
(b) Leucine
(c) Lysine
(d) Cysteine
Ans. d
Sol. Toxicity of cadmium and mercury in the body is being reversed by cysteine amino acid.
Correct answer is (d)
31. NiBr2 reacts with (Et) Ph2)P at – 780C in CS2 to give red compound 'A', which upon standing at room temperature turns green to give compound, 'B' of the same formula. The measured magnetic moments of 'A' and 'B' are 0.0 and 3.2 BM, respectively. The geometries of 'A' and 'B' are
(a) square planar and tetrahedral
(b) tetrahedral and square planar
(c) square planar and octahedral
(d) tetrahedral and octahedral
Ans. a
Sol. 


(A) and (B) are polytopal isomers.
Correct answer is (a)
32. The correct non – linear and iso – structural pair is
(a) SCl2 and I 3–
(b) SCl2 and I 3+
(c) SCl2 and CIF 2–
(d) I2+ and CIF 2–
Ans. b
Sol. 
Shapes of species are

Correct answer is (b)
33. Ozone present in upper atmosphere protects people on the earth
(a) due to its diamagnetic nature
(b) due to its blue coour
(c) due to absorption of radiation of wavelength at 255 nm
(d) by destroying chloro fluoro carbons
Ans. c
Sol. Ozone is a diamagnetic gas which is of dark blue coloured due to absorption of red light. 
Ozone depliction discovered by J.C. Farman over Halley Bay in Antarctica.
Ozone also show strong absorption in  which is good for earth and living beings as this 'UV–b' most dangerous
which is good for earth and living beings as this 'UV–b' most dangerous

Correct option is (c)
34. If L is a neutral monodentate ligand, the species,  , respectively are
, respectively are
(a) paramagnetic, paramagnetic and diamagnetic
(b) paramagnetic, diamagnetic and paramagnetic
(c) diamagnetic, paramagnetic and diamagnetic
(d) paramagnetic, diamagnetic and diamagnetic
Ans. a
Sol. In  has d9 configuration, hence have unpaired electron. Hence paramagnetic.
has d9 configuration, hence have unpaired electron. Hence paramagnetic.
 has d8 configuration and dsp2 hydridization (square planar so pairing of electron).
has d8 configuration and dsp2 hydridization (square planar so pairing of electron).
Hence, diamagnetic in nature.
Correct option is (a)
35. Chromite ore on fusion with sodium carbonate gives
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Chromium is extracted from chromite ore:


Correct option is (a)
36. The ligand(s) that is (are fluxional in  in the temperature range 221-298K, is (are
in the temperature range 221-298K, is (are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
37.  is red in colour whereas
is red in colour whereas  is green.
is green.  respectively corresponds to,
respectively corresponds to,
(a) NH3 and H2O
(b) NH3 and 1, 10 – phenanthroline
(c) NH3 and 1, 10 – phenanthroline
(d) H2O and NH3
Ans. a
Sol. 
Energy of green radiations > energy of red radiations.

Therefore, L will be stronger ligand and than  Thus, L and
Thus, L and 
Correct answer is (a)
38. The oxidation state of Ni and the number of metal – metal bonds in  that are consistent with the 18 electron rule are
that are consistent with the 18 electron rule are
(a) Ni(–II), 1 bond
(b) Ni(IV), 2 bonds
(c) Ni(–I), 1 bond
(d) Ni (IV), 3 bonds
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct answer is (c)
39. Structure of SbPh5 and PPh5 respectively are
(a) trigonal bipyramidal, square pyramidal
(b) square pyramidal, trigonal bipyramidal
(c) trigonal bipyramidal, trigonal bipyramidal
(d) square pyramidal, square pyramidal
Ans. b
Sol. SbPh5 is square pyramidal while PPh5 is trigonal bipyramidal.

This is due to size of central atom. 'Sb' is bigger than 'P', therefore favour square planar while small sized 'P' favour trigonal bipyramidal.
Correct answer is (b)
40. The typical electronic configurations of the transition metal centre for oxidative addition
(a) d0 and d8
(b) d6 and d8
(c) d8 and d10
(d) d5 and d10
Ans. c
Sol. Most commonly the metal in the complexes in their low oxidation state with d8 or d10 configuration undergo oxidative addition.

Correct option is (c)
41. Gelatin added during the polarographic measurement carried out using dropping mercury electrode
(a) reduces streaming motion of Hg drop
(b) decreases viscosity of the solution
(c) eliminates migrating current
(d) prevents oxidation of Hg
Ans. a
Sol. Correct answer is (a)
42. The pKa values of the following salt of aspartic acid are indicated below. The predominant species that would exist at pH = 5 is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
It is aspartic acid (amino acid) which contains ionizable side chain.
When pH = 5; since both COOH group have  It will be deportonated form.
It will be deportonated form.
Thus the predominant species that would exist at pH = 5 is

Correct answer is (b)
43. The major product formed in the following photochemical reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
44. The pair of solvents in which PC15 does NOT ionize, is
(a) CH3CN, CH3NO2
(b) CH3CN, CCl4
(c) C6H6, CCl4
(d) CH3CN, C6H6
Ans. c
Sol. PCl5 is a polar solvent which will dissolve only in polar solvent.
Therefore, since benzene and carbon tetrachloride both are non – polar solvent. Thus, PCl5 will not dissolve in it
Correct answer is (c)
45. The major product formed in the following reaction is
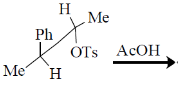
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

In the presence of neighbouring phenyl group (OTs) depart.
Correct option is (a)
46. The correct order for the rates of electrophilic aromatic substitution of the following compound is

(a) I > II > III
(b) II > I > III
(c) III > II > I
(d) I > III > II
Ans. d
Sol. Since N is a electronegative element, thus it decreases the electron density in the ring and thus the ring is less prone to be attacked by the electrophile in electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Hence, pyridine (I) will be least reactive in which the electronegative element N is present N is present in the same ring.
Since in structure (I) N is outside the ring and thus it increases the electrophilicity of the ring by donating electron pair through its lone pair.
Thus it will be most prone to electrophilic attack.
Correct order will be I > III > II
Correct option is (d)
47. The commutator of the kinetic energy operator,  and the momentum operator,
and the momentum operator,  for the one dimensional case is
for the one dimensional case is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 0
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
48. The major product formed in the reaction of trans-1-bromo-3-methylcyclobutane with sodium iodide in DMF is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Strong base and polar solvent (aprotic) favour SN2 mechanism.
• Since, SN3 mechanism proceed via inversion of configuration.
• Thus, the product formed will have confirmation opposite to that of reactant i.e.

Correct option is (c)
49. When Si is doped with a Group V element,
(a) donor levels is are created close to the valance band
(b) donor levels are created close to the conduction band
(c) acceptor levels are created close to the valence bond
(d) acceptor levels are created close to the conductionband
Ans. b
Sol. When Si is doped with group V elements like P, then at each P centre there is extra electron which constitute a donor band that lies close to empty conduction band.

Correct option is (b)
50. The symmetry point group of propyne is
(a) c3
(b) C3v
(c) D3
(d) D3d
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
51. For a first order reaction  products, the plot of ln
products, the plot of ln  vs time, where
vs time, where  refer to concentration at time t = 0 and t respectively, is
refer to concentration at time t = 0 and t respectively, is
(a) a straight line with a positive slope passing through origin
(b) a straight line with a negative slope passing through origin.
(c) an exponential curve asymptotic to the time axis
(d) a curve asymptotic to the ln  axis.
axis.
Ans. b
Sol. For a 1st order reaction

So, the plot of  is straight line with negative slope passing through the origin.
is straight line with negative slope passing through the origin.
Correct answer is (b)
52. In radical chain polymerization, the quantity given by the rate of monomer depletion, divided by the rate of propagating radical formation is called
(a) kinetic chain length
(b) propagation efficiency
(c) propagation rate constant
(d) polymerization time
Ans. a
Sol. Kinetic chain length describes the number of chain propagation steps in between the chain initiation step and the chain termination step.
Mathematically it is defined as
Kinetic chain length 
Correct option is (a)
53. Number of rotational symmetry axes for triclinic crystal system is
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 0
Ans. d
Sol. The triclinic crystal with parameters  and
and  is least symmetric.
is least symmetric.
Therefore, no axis of symmetry
Correct answer is (d)
54. Generally, hydrophobic colloids are flocculated efficiently by ions of opposite type a high charge number. This is consistent with the
(a) peptization principle
(b) krafft theory
(c) Hardy – Schulze rule
(d) Langmuir adsorption mechanism
Ans. c
Sol. Correct answer is (c)
55. Examine the following first order consecutive reactions. The rate constant (in s–1 units) for each step is given above the arrow mark
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Steady state approximation can be applied to?
Ans. d
Sol. Steady state approximation for consecutive reactions

is applied when first step is slow and second step is fast.
Correct answer is (d)
56. The figure below represents the path followed by a gas during expansion from  The work done is (L atm)
The work done is (L atm)

(a) 0
(b) 9
(c) 5
(d) 4
Ans. d
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
57. An aqueous solution of an optically pure compound of concentration 100 mg in 1 mL of water and measured in a quartz tube of 5 cm length was found to be –30. The specific rotation is
(a) –300
(b) –600
(c) –60
(d) +60
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct answer is (b)
58. Two phase  of a species are in equilibrium. The correct relations observed among the variables, T. p and
of a species are in equilibrium. The correct relations observed among the variables, T. p and  are
are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. It two phases  of a species are in equilibrium then temperature, pressure and chemical potential for both phases are in same type.
of a species are in equilibrium then temperature, pressure and chemical potential for both phases are in same type.

Correct answer is (c)
59. The number of configurations in the most probable state, according to Boltzmann formula is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 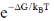
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
60. The correct match of the 1H NMr chemical shifts  of the following species / compounds is
of the following species / compounds is

(a) I : 5.4; II : 7.2; III : 9.2
(b) I : 9.2; II : 7.2; III : 5.4
(c) I : 9.2; II : 5.4; III : 7.2
(d) I : 7.2; II : 9.2; III : 5.4
Ans. a
Sol. 1H NMR chemical shift of these species can be explained on the basis of ring current leads to desielding effect.
When these species are placed in magnetic field,  – electrons in the aromatic ring system are induced to circulate around the ring. Thus, hydrogen corresponds to these ring are said to be deshielded by the diamagnetic anisotropy of the ring.
– electrons in the aromatic ring system are induced to circulate around the ring. Thus, hydrogen corresponds to these ring are said to be deshielded by the diamagnetic anisotropy of the ring.
Since, in cylopentadiene ring  are there and also it is not aromatic, thus, its proton are least deshielded compared to rest two ring. Thus
are there and also it is not aromatic, thus, its proton are least deshielded compared to rest two ring. Thus  value is lowest among three.
value is lowest among three.
Since, benzene and tropylium cation both are aromatic and contains  but since in the case of tropylium cation positive charge is there, its proton are more deshielded as compared to benzene. Thus,
but since in the case of tropylium cation positive charge is there, its proton are more deshielded as compared to benzene. Thus,  value will be in order.
value will be in order.
III > II > I
Correct answer is (a)
61. The major products formed in the following are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
62. In a Diels – Alder reaction, the most reactive diene amongst the following is
(a) (4E) – 1 4 – hexadiene
(b) (4Z) – 1, 4 – hexadiene
(c) (2E, 4E) – 2, 4 – hexadiene
(d) (2Z, 4Z) – 2, 4 hexadiene
Ans. c
Sol. 
Now, for better overlap in Diels – Alder reaction, the diene must be in cisoid fashion. Thus, favourable configuration is (2E – 4E) –2, 4 hexadiene.
Correct answer is (c)
63. Consider the statements about the following structures X and Y

(A) X and Y are resonance structures
(B) X and Y are tautomers
(C) Y is more basic than X
(D) X is more basic than Y
The correct statement(s) among teh above is/are
(a) A and C
(b) C
(c) B and D
(d) B and C
Ans. d
Sol. 
Thus, X and Y are tautomers.
Also, it is clear from the structure of X and Y that Y is more basic than X.
Correct option is (d)
64. Pericyclic reaction involved in one of the steps of the following reaction sequence is

(a) [1, 3] sigmatropic shift
(b) [3, 3] sigmatropic shift
(c) [1, 5] sigmatropic shift
(d) [2, 3] sigmatropic shift
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
65. Atrovastatin (structure given below) is a

(a) cholesterol lowering drug
(b) blood sugar lowering drug
(c) anti-plasmodial drug
(d) anti-HIV drug
Ans. a
Sol. Atorvastatin is a cholesterol lowering drug.
Correct answer is (a)
66. The maximum bond order obtained from the molecular orbitals of a transition metal dimer, formed as linear combinations of d-orbitals alone, is
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
Ans. c
Sol. A maximum five 'd' orbitals can form bonding with each other

Firstly reported in 2007 in chromium complexes.

Ar = Substituted aromatic rings.
Correct option is (c)
67. The term symbol that is NOT allowed for the np2 configuration is
(a) 1D
(b) 3P
(c) 1S
(d) 3D
Ans. d
Sol. For np2 configuration (microstates)

The configuration (IV) violets the Pauli's Principle. Hence term symbol 3D is not possible.
Correct answer is (d)
68. If the ionization energy of H atom is x, the ionization energy of Li2+, is
(a) 2x
(b) 3x
(c) 9x
(d) 27x
Ans. c
Sol. The formula for ionisation energy is
 (Z = atomic number, n = shell number)
(Z = atomic number, n = shell number)
This is for one electron 'H' atom like system
Hence, for Li++ = 1s1 (one electron system)
I. E.  For 'H' atom, I. E.
For 'H' atom, I. E. 
Therefore, I.E. of Li++ = 9x
Correct answer is (c)
69. If temperature is doubled and the mass of the gaseous molecule is halved, the rms speed of the molecular will change by a factor of
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 1/2
(d) – 1/4
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
70. In the graph below, the correct option, according to Kohlrausch law, is
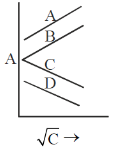
(a) A is a weak electrolyte and B is a strong electrolyte
(b) A is a strong electrolyte and B is a weak electrolyte
(c) C is a strong electrolyte and D is a weak electrolyte
(d) C is weak electrolyte and D is a strong electrolyte
Ans. c
Sol. According to Kohlrausch law molar conductance of strong electrolyte decreases linearly with square root of concentration while that of weak electrolyte decreases exponentially. Hence, (c) is strong electrolyte while D is a weak electrolyte.
Correct answer is (c)
71. Reaction of [Ru(NH3)5(isonicotinamide]3+ with [Cr(H2O6)]2+ occurs by inner sphere mechanism and rate of the reaction is determined by dissociation of the successor complex. It is due to the
(a) Inert ruthenium birdged to inert chromium centre
(b) Inert ruthenium bridged to labile chromium centre
(c) Labile ruthenium bridged to inert chromium centre
(d) Labile ruthenium bridged to labile chromium centre
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct answer is (a)
72. Consider the second order rate constants for the following outer - sphere electron transfer reactions:

(phen = 1, 10 – phenathroline)
The enhanced rate constant for the second reaction is due to the fact that
(a) The 'phen' is a  π– acceptor ligand that allows mixing of electron donor and acceptor orbitals that enhances the rate of electron transfer
π– acceptor ligand that allows mixing of electron donor and acceptor orbitals that enhances the rate of electron transfer
(b) The 'phen' is a  π– donor ligand that enhances the rate of electron transfer
π– donor ligand that enhances the rate of electron transfer
(c) The 'phen' forms charge transfer complex with iron and facilitates the electron transfer
(d) The 'phen' forms kinetically labile complex with iron and facilitates the electron transfer.
Ans. a
Sol. (Phen) is an  – acceptor ligands hence there is mixing of donor and acceptor orbital having similar symmetry this leads to fast transfer of electron leading to enhance rate of reaction.
– acceptor ligands hence there is mixing of donor and acceptor orbital having similar symmetry this leads to fast transfer of electron leading to enhance rate of reaction.


Correct option is (a)
73. The compound [Re2(Me2PPh)4Cl] (M) having a configuration  can be oxidized to M+ and M2. The formal metal-metal order in M, M+ and M2+ respectively, are
can be oxidized to M+ and M2. The formal metal-metal order in M, M+ and M2+ respectively, are
(a) 3.0, 3.5 and 4.0
(b) 3.5, 4.0 and 3.0
(c) 4.0, 3.5 and 3.0
(d) 3.0, 4.0 and 3.5
Ans. a
Sol. [Re2(Me2PPh)4Cl4] –(M)



Correct option is (a)
74. In low chloride ion concentration, the anticancer drug cis – platin hydrolyses to give a diaqua complex and this binds to DNA via adjacent guanine

The coordinating atom of guanine to Pt(II) is
(a) N1
(b) N3
(c) N7
(d) N9
Ans. c
Sol. Correct answer is (c)
75. The 19F NMR spectrum of CIF3 shows
(a) doublet and triplet for a T-shaped structure
(b) singlet for a trigonal planar structure
(c) singlet for a trigonal pyramidal structure
(d) doublet and singlet for a T-shaped structure
Ans. a
Sol. 
19F – 2F doublet
19F 1F triplet
T shaped triplet
Correct answer is (a)
76. The low temperature (–980C) 19F NMR spectrum of SF4 shows doublet of triplets. It is consistent with the point group symmetry.
(a) C3v
(b) C4v
(c) 5d
(d) C2v
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
77. Amongst organolithium (A), Grignard (B) and organoaluminium (C) compounds, those react with SiCl4 to give compound containing Si-C bond are
(a) A and B
(b) B and C
(c) A and C
(d) A, B and C
Ans. d
Sol. 
In all case there is electrostatic interaction between Si and R

Correct option is (d)
78. In its electronic spectrum,  exihibits two absorption bands, one at 17,800 (vi) and the second at 25,700 (v2) cm–1. The correct assignment of these bands, respectively, is
exihibits two absorption bands, one at 17,800 (vi) and the second at 25,700 (v2) cm–1. The correct assignment of these bands, respectively, is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
79. Reaction of elemental As with hot and conc. HNO3 and H2SO4, respectively, give
(a) As4O6 and As2(SO4)3
(b) As(NO3)5 and As2(SO4)3
(c) As4O6 and H3AsO4
(d) H3AsO4 and As4O6
Ans. d
Sol. 
The reason is that HNO3 is better oxidising agent than H2SO4 also acts as dehydrating agent.
Correct answer is (d)
80. The total valence electron count and the structure type adopted by the complex  respectively, are
respectively, are
(a) 74 and nido
(b) 60 and closo
(c) 84 and arachno
(d) 62 and nido
Ans. a
Sol. 
Total valency electron = 8 × 5 + 15 × 2 + 4 = 74
PEC = TEC – n × 12
PEC = 74 – 5 × 12 = 74 – 60 = 14

7 = n + 2 where, n = number of metal in electron.
= 5 + 2 = (n + 2) Nido
Correct answer is (a)
81. 1H NMR spectrum of  at – 200C shows a typical AA 'XX' pattern in the olefinic region. On increasing the temperature of
at – 200C shows a typical AA 'XX' pattern in the olefinic region. On increasing the temperature of  the separate lines collapse into a single line which is due to
the separate lines collapse into a single line which is due to
(a) free rotation of the ethylene ligand about the metal – olefin bond
(b) interamolecular exchange between the ethylene ligands
(c) intermolecular exchange between the ethylene ligands
(d) change in hapticity of the cyclopentadienyl ligand
Ans. a
Sol. Correct answer is (a)
82. The nuclides among the following, capable of undergoing fission by thermal neutrons, are
(A) 233U
(B) 235U
(C) 239Pu
(D) 232Th
(a) A, B and C
(b) A, C and D
(c) B, C and D
(d) 5A, B and C
Ans. d
Sol. Correct answer is (d)
83. The use of dynamic inert atmosphere in thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)
(a) decreases decomposition temperature
(b) decrease weight loss
(c) reduces rate of decomposition
(d) increases weight loss
Ans. a
Sol. In thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) use of dynamic inert atmosphere is decrease decomposition with respect to temperature.
Correct answer is (a)
84. The correct statements for hollow cathode lamp (HCL) from the following are
(A) HCL is suitable for atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS)
(B) lines emitted from HCL are very narrow
(C) the hardening of lamp makes it sunsuitable for AAS
(D) transition elements used in lamps have short life
(a) A, B and C
(b) B, C and D
(c) C, D and A
(d) D, A and B
Ans. a
Sol. Correct answer is (a)
85. Identify the correct statement about 
(a) All Ni – O and Cu – O bond lengths of individual species are equal
(b) Ni – O (equatorial) and Cu – O (equatorial)
(c) All Ni – O bond lengths are equal whereas Cu – O (equatorial) bonds are shorter than Cu – O (axial) bonds
(d) All Cu – O bond lengths are equal whereas Ni – O (equatorial) bonds are shorter than Ni – O (axial) bonds.
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
86. Reaction of nitrosyl tetrafluoroborate to Vaska's complex gives complex A with  The complex A and its N – O stretching frequency are, respectively
The complex A and its N – O stretching frequency are, respectively
(a) [IrCl(CO)(NO)(PPh3)2]BF4, 1620 cm–1
(b) [IrCl(CO)(NO)2(PPh3)](BF4)2, 1730 cm–1
(c) [IrCl(CO)(NO)2(PPh3)](BF4)2, 1520 cm–1
(d) [IrCl(CO)(NO)(PPh3)2], 1820 cm–1
Ans. a
Sol. 
Terminal NO = 1672 cm–1
Bridging NO = 1505 cm–1
Correct answer is (a)
87. The correct order of decreasing electronegativity of the following atoms is,
(a) As > Al > Ca > S
(b) S > As > Al > Ca
(c) Al > Ca > S > As
(d) S > Ca > As > Al
Ans. b
Sol. The electronegativities of elements are
Ca Al As S
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
Correct answer is (b)
88. A 1 : 2 mixture of Me2NCH2CH2CH2PPh2 and KSCN with K2[PdCl4] gives a square planar complex A. Identify the correct pairs of donor atoms trans to each other in complex A from the following combinations
(a) P, N
(b) N, S
(c) P, S
(d) N, N
Ans. a
Sol. s and p both form  – bonding with complex and
– bonding with complex and  – bonding capacity of sulphur is greater than phosphorus due to smaller size of d – orbital of sulphur. Hence, in presence of sulphur trans to phosphorus donor atom phosphorus – metal bond will be weak hence they do not lie trans to each other in the complex. As nitrogen does not involment in
– bonding capacity of sulphur is greater than phosphorus due to smaller size of d – orbital of sulphur. Hence, in presence of sulphur trans to phosphorus donor atom phosphorus – metal bond will be weak hence they do not lie trans to each other in the complex. As nitrogen does not involment in  – bonding with complex hence when nitrogen atom is trans to phosphorus, phosphorus become able to form efficient
– bonding with complex hence when nitrogen atom is trans to phosphorus, phosphorus become able to form efficient  – bond with metal hence become stable thats why P and N are trans to each other
– bond with metal hence become stable thats why P and N are trans to each other

Correct option is (a)
89. For a low energy nuclear reaction,  the correct statements from the following are
the correct statements from the following are
(A) Kinetic energy of d particle is not fully available for exciting 24Mg.
(B) Total number of protons are neutrons is conserved
(C) Q value of nuclear reaction is much higher in magnitude relative to heat of chemical reaction
(D) Threshold energy is < Q value.
(a) A, B and C
(b) A, B and D
(c) B, C and D
(d) A, C and D
Ans. a
Sol. Correct answer is (a)
90. At pH 7, the zinc (II) ion in carbonic anhydrase reacts with CO2 to give
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
91. Molybdoenzymes can both oxidize as well as reduce the substrates, because
(a) Mo(VI) is more stable than Mo(IV)
(b) Mo(IV) can transfer oxygen atom to the substrate and Mo(VI) can abstract oxygen atom from the substrate
(c) Conversion of Mo(VI) to MO(IV) is not favoured
(d) Mo(VI) can transfer oxygen atom to the substrate and Mo(IV) can abstract oxygen atom from the substrate
Ans. d
Sol. Correct answer is (d)
92. A comparison of the valence electron configuration of the elements, Sm and Eu suggests that
(a) Sm is a better one electron reductant than Eu
(b) Sm is a better one electron oxidant than Eu
(c) Facile oxidation state is +2 for both the elements
(d) Both of these display similar redox behaviour
Ans. b
Sol. 
Sm can accept one electron and become half field. So, it is better oxidant.
Correct answer is (b)
93. The cooperative binding of O2 in hemoglobin is due to
(a) a decrease in size of iron followed by changes in the protein conformation
(b) an increase in size of iron followed by changes in the protein conformation
(c) a decrease in size of iron that is NOT accompanied by the protein conformational changes
(d) an increase in size of iron that is NOT accompanied by the protein conformational changes
Ans. a
Sol. The movement of iron atom and imidazole side chain of histidine toward the prophyrin plane results in breaking of some of the salt bridges. The breaking of these salt bridges reduces the strain in hemoglobin molecule. Therefore, the oxyform of hemoglobin is called relaxed state (i.e., R state). The T form of deoxyhemoglobin discourages the addition of first dioxygen molecule.
The bonding of one dioxygen molecule to a subunit of hemoglobin reduces the steric hindrance in the other subunits (due to breaking of salt bridges) and therefore encourages the third as well as fourth subunits. This is called cooperative mechanisms.
Correct answer is (a)
94. Amongst the following which is not isolobal pairs
(a) Mn(CO)5, CH3
(b) Fe(CO)4, O
(c) Co(CO)3, R2Si
(d) Mn(CO)5, RS
Ans. c
Sol. Total electron

Correct option is (c)
95. The correct order of the size of S, S2–, S2+ and S4+ species is,
(a) S > S2+ > S4+ > S2–
(b) S2+ > S4+ > S2– > S
(c) S2– > S > S2+ > S4+
(d) S4+ > S2– > S > S2+
Ans. c
Sol. As positive charge increases the size decreases while with increase in negative charge increase the size. This is due to increase in Zeff in former case while decrease in Zeff in later case.
Hence, order of size is S2– > S > S2+ > S4+
Correct answer is (c)
96. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
97. The correct combination of reagents of effect the following conversion is

(a) (i) Ph3P+CH2OMeCL–, BuLi, (ii) H3O+, Jones' reagent
(b) (i) H2N–NHTs; (ii) BuLi (2 equiv); (iii) DMF
(c) (i) H2N–NHTs; (ii) BuLi (2 equiv); (iii) CO2
(d) (i) ClCH2CO2Et, LDA; (ii) BF3. OEt2; (iii) DMSO, (COCl)2, Et3N, –780C to rt.
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
98. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
99. Consider the following reaction,

The appropriate intermediate involved in this reaction is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
100. The correct 13C NMR chemical  shift value of carbons labeled a – e in the following ester are
shift value of carbons labeled a – e in the following ester are

(a) a : 19; b : 143; c : 167; d : 125; e : 52
(b) a : 52; b : 143; c : 167; d : 125; e : 19
(c) a : 52; b : 167; c : 143; d : 125; e : 19
(d) a : 52, b : 167; c : 125; d : 143; e : 19
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
101. The products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Since less basic group are better leaving group. Thus, CI– will be a better leaving group as compared to methoxy group.
Thus, formation of A takes place according to following mechanism.

Correct option is (a)
102. The biosynthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate from acetyle CoA involves:
A. Four molecules of acetyl CoA
B. Three molecules of ATP
C. Two molecules of NADPH
D. Two molecules of lipoic acid
The correct options among these are
(a) A, B and D
(b) A and B
(c) B and D
(d) A, C and D
Ans. c
Sol. The biosynthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate from acetyle CoA consumes three molecule of ATP and two molecule of NADPH.
Correct answer is (c)
103. Amongst the following, the major products formed in the following photochemical reactions are


(a) A and C
(b) B and C
(c) A and D
(d) A and B
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct answer is (d)
104. The products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
105. Anthranilic acid, treament with iso-amyl nitrite furnishes a product which displays a strong peak at 76 (m/e) in its mass spectrum. The structure of the product is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Now two molecule of benzene combines to form biphenyl (dimerises)

This benzyene has m/z value 76.
Correct answer is (a)
106. The organoborane X, when reacted with Et2Zn followed by p-iodotoluene in the presence of catalytic amount of Pd (PPh3)4 furnished a tri-substituted alkene. the intermediate and the product of the reaction, respectively, are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct answer is (d)
107. Using Boltzmann distribution, the probability of an oscillator occupying the first three levels (n=0, 1 and 2) is found to be p0 = 0.633, p1 = 0.233 and p2 = 0.086.
The probability of finding an oscillator in energy levels in n > 3 is
(a) 0.032
(b) 0.048
(c) 0.952
(d) 1.000
Ans. b
Sol. Total probability = PT = 1
Probability of occupying first three levels = P0 + P1 + P2
PT = P0 + P1 + P2 + probability of finding an oscillator in energy levels in n > 3
1 = 0.952 + Pn>3 = 1 – 0.952 = 0.048
Correct answer is (b)
108. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
109. The correct combination of reagents required to effect the following conversion is

(a) (i) Na, xylene, Me3SiCl, heat; (ii) H3O+
(b) (i) Na, xylene, heat; (ii) H2O2, NaOH
(c) (i) NaOEt, EtOH; (ii) Na, xylene, heat
(d) (i) TiCl3, Zn – Cu, Me3SiCl, heat; (ii) H3O+
Ans. a
Sol. 
This reaction is acyloin condensation.
The acyloin condensation of diesters favours intramolecular cyclisation over intermolecular polymerisation.
The mechanism of acyloin condensation consist of 4 steps, which is as follows.
(i) Oxidative ionization of two sodium atoms on the double bond of two ester molecules

(ii) Intramolecular free radical coupling, followed by alkoxy elimination in both side, producing a 1, 2 diketone,

(iii) Oxidative ionization of two sodium atoms on both diketone double bonds. The sodium enodiokete is formed.

(iv) 
Note: Here along with Na, xylene TMsCl has been used to improve the yield of the product. This is because by removing the alkoxide ion formed, thereby preventing the base catalyzed side reaction.
Correct option is (a)
110. An organic compound gives following spectral data:
IR : 2210, 1724 cm–1, 1H NMR :  1.4 (t, 7 = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 4.4 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR :
1.4 (t, 7 = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 4.4 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR :  16, 62, 118, 119, 125, 127, 168
16, 62, 118, 119, 125, 127, 168
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. IR frequency indicated towards a  group
group  and a carbonyl group
and a carbonyl group 

Thus the required structure will be

Correct option is (c)
111. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
112. The correct combination of reagents for effecting the following sequence of reactions is

(a) A = O3/O2; B = K+–OOC – N = N – COOK–K+, AcOH
(b) A = O2, Rose Bengal, hv; B = K+–OOC – N = N – COOK–K+, AcOH
(c) A = O2, Rose Bengal, hv; B = H2, Pd/C
(d) A = O2, Rose Bengal, hv;  B = H2, Pd/C
B = H2, Pd/C
Ans. b
Sol. 
Rose Bengal is a dye used for catalytic purpose.
It is [4+2] cycloaddition reaction, which is favourable in photochemical condition.

Note: H2/Pd will lead to the formation of dihydroxy compound

Thus, it will not be the suitable reagent for above reaction sequence
Correct option is (b)
113. The correct combination of reagents required to effect the following conversion is

(a) I2, HNO3
(b) s – BuLi, –780C followed by KI
(c) NaOHt followed by ICH2CHI2I
(d) s – BuLi, –780C followed by ICH2CH2I
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
114. Consider the particle confined in a cubic box. The degenracy of the level, that has an energy twice that of the lowest level, is
(a) 3
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 4
Ans. a
Sol. For cubic box energy

For cubic box, lowest energy.



so, its give three degeneracy of levels.
Correct answer is (a)
115. Only two products are obtained in the following reaction sequence. The structures of the products from the list I – IV are


(a) I and II
(b) II and IV
(c) I and III
(d) III and IV
Ans. a
Sol. 


Thus, P and Q are the required product.
Correct answer is (a)
116. The major product A formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
117. The product A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
SeO2 is most commonly used for allylic oxidation. First formation of allylic alcohol takes place, which can be oxidized easily to  – unsaturated carbonyl compound if desired.
– unsaturated carbonyl compound if desired.
The oxidation are belived to involved an ene reaction, between the alkene and the hyrated form of the dioxide, followed by a [2, 3] – sigmatropics rearrangement of the resulting alyl selenic acid and final hydrolysis of Se(II) ester to the allylic alcohol. Furhter, oxidation of the alcohol gives  – unsaturated carbonyl compound. A notable application of this reaction is in the oxidation of 1, 1 dimethyl alkene to the corresponding E allylic alcohols or aldehydes by selective attack on the E – methyl group.
– unsaturated carbonyl compound. A notable application of this reaction is in the oxidation of 1, 1 dimethyl alkene to the corresponding E allylic alcohols or aldehydes by selective attack on the E – methyl group.



The aldehyde formed reacts with cyanide to give cyanohydrin. Oxidation of the cyanohydrin with manganese dioxide gives the acyl nitrile. Which then reacts with the alcohol solvent to give the ester.
Correct answer is (d)
118. The spatial part of the wave function of the atom in its ground state is 1s(1) 1s(2). The spin part would be
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. According to the pauli exclusion principle the wavefunction of fermions (here electrons) must be antisymmetric 
For a triplet state, spin wavefunctions can be  which are symmetric in nature. As
which are symmetric in nature. As  So, for
So, for  to be antisymmetrical w.r.t. electron exchange,
to be antisymmetrical w.r.t. electron exchange,  the spatial part of wavefunction is symmetrical so the spin part will be antisymmetric
the spatial part of wavefunction is symmetrical so the spin part will be antisymmetric 
Correct option is (d)
119. The number of phases, components and degrees of freedom, when Ar is added to an equilibrium mixture of NO, O2 and No2 in gas phase are, respectively.
(a) 1, 3, 5
(b) 1, 4, 5
(c) 1, 3, 4
(d) 1, 4, 4
Ans. c
Sol. 
(1) Phase only (gas phase) all are gases
P = 1
(2) Component
C = N – E
C = 4 – 1 = 3
(3) F = C – P + 2
F = 3 – 1 + 2 = 4
Correct option is (c)
120. The major product formed in the followed reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
121. A particle in a one dimensional harmonic oscilator in x – direction is perturbed by a potential 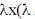 is a number). The first – order correction to the energy of the ground state.
is a number). The first – order correction to the energy of the ground state.
(a) is zero
(b) is negative
(c) is positive
(d) may be negative or positive but NOT zero
Ans. a
Sol. 
n is odd. So, total integration is zero.

Correct answer is (a)
122. The points A and B in the following sequence of reactions are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Thus, this nothing but  glucose. (cyclic form of
glucose. (cyclic form of  glucose).
glucose).
Now, methylation with MeOH in the presence of acid leads to the formation of mono – methylated  glucose.
glucose.

Correct option is (b)
123. The mass spectrum of the product A, formed in the following reaction, exhibits M, M + 2, M + 4 peacks in the ratio of about 1 : 2 : 1. The reagent HX and the product A are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. Natural abudance of Cl35 is 100% while C37 is 32.5. While natural abudance of 79Br is 100 while 81Br is 98.0.
Thus, relative intensitites of isotope peacks for various combination of bromine and chlorine will be as follows.

Since in given problem M, M + 2, M + 4 peack is in ratio 1 : 2 : 1.
Thus, two Br atom is present in compound A

Correct answer is (c)
124. Match the following natural products in column A with their structural features in column B

Identify the correct match from the following
(a) I – C, II – A, III – E, IV – D
(b) I – F, II – A, III – B IV – E
(c) I – A, II – D, III – F, IV – D
(d) I – C, II – A, III – E, IV – F
Ans. a
Sol. Correct answer is (a)
125. A particle in a one – dimensional box (potential zero between to a and infinite outside) has the ground state energy  The expectation value of the above Hamiltonian with
The expectation value of the above Hamiltonian with  yields an energy E1. Using a linear combination of two even functions
yields an energy E1. Using a linear combination of two even functions  and
and  we obtain variational minimum to the ground state energy as E2. Which of the following relations holds for E0, E1 and E2?
we obtain variational minimum to the ground state energy as E2. Which of the following relations holds for E0, E1 and E2?
(a) E0 < E1 < E2
(b) E0 < E2 < E1
(c) E1 < E0 < E2
(d) E2 < E0 < E1
Ans. b
Sol. When the variational term are increased the energy come closer to ground state energy. So, the energy of two even function  correspond to there energy E2 come closer to E0. Because the system are very complicated and not solve easily.
correspond to there energy E2 come closer to E0. Because the system are very complicated and not solve easily.
Correct option is (b)
126. The dissociation constant of a weak acid HX at a given temperature is 2.5×10–5. The pH of 0.01 M NaX at this temperature is
(a) 7.3
(b) 7.7
(c) 8.3
(d) 8.7
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
127. The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is – 13.598 eV. The expectation values of kinetic energy,  and potential energy,
and potential energy,  , is units of eV, are
, is units of eV, are
(a) 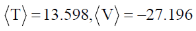
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. For hydrogen atom.
Virial Theorem.

Correct option is (a)
128. If  is a normalized molecular orbital of a diaotmic molecule AB, constructed from
is a normalized molecular orbital of a diaotmic molecule AB, constructed from  which are also normalized, the overlap between
which are also normalized, the overlap between  is
is
(a) 0.11
(b) 0.31
(c) 0.51
(d) 0.71
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
129. At a given temperature consider

The equilibrium constant for the reaction

(a) 1 × 10–13
(b) 2 × 10–38
(c) 4 × 10–15
(d) 2 × 10–24
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
130. In a bomb calorimeter, the combustion of 0.5 g of compound A (molar mass = 50 g mol–1) increased the temperature by 4K. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter along with that of the material is 2.5 kJ K–1, the molar internal energy of combustion, in kJ, is
(a) 1000
(b) – 1000
(c) 20
(d) – 20
Ans. b
Sol. Molar internal energy of combination =

Note: Energy of combution has always a negative sign.
Correct answer is (b)
131. The translational, rotational and vibrational partition functions for a molecule are  at room temperature,
at room temperature,  using the approximate data given above, the frequency factor (A) for a reaction of the type: atom + diatomic molecule
using the approximate data given above, the frequency factor (A) for a reaction of the type: atom + diatomic molecule  non – linear transition state
non – linear transition state  product, according to the conventional transition state theory is
product, according to the conventional transition state theory is
(a) 2 × 103
(b) 6 × 107
(c) 2 × 1012
(d) 6 × 1013
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
132. The interplanar spacing of (110) planes in a cubic unit cell with lattice parameter a = 4.242Å is
(a) 5Å
(b) 6Å
(c) 7.35Å
(d) 2.45Å
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct answer is (d)
133. A compound AxBy has a cubic structure with A atomos occupying all corners of the cube as well as all the face centre positions. The B atoms occupy four tetrahedral voids. The values of x and y respectively, are
(a) 4, 4
(b) 4, 8
(c) 8, 4
(d) 4, 2
Ans. a
Sol. A = corners + face centres 
And B = 4 (Full 1 contribution in tetrahadral void)
Correct option is (a)
134. The number of lines in the ESR spectrum of CD3 is (the spin of D is 1)
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 7
Ans. d
Sol. CD3 (ID = 1)
(2nl + 1 ) = (2 × 3 + 1 ) = 7
Correct answer is (d)
135. The C = O bond length is 120 pm in CO2. The moment of inertia of CO2 would be close to (masses of C and O are 1.9 × 10–27 kg and 2.5 10–27 kg, respectively)
(a) 1.8 × 10–45 kgm2
(b) 3.6 × 10–45 kgm2
(c) 5.4 × 10–45 kgm2
(d) 7.2 × 10–45 kgm2
Ans. d*
Sol. The moment of inertia of CO2.


Correct answer is (d*)
136. The fluorescene lifetime of a molecule in a solution is 5×10–9 s. The sum of all the known radiative rate constant for the decay of exciting state is 1.2 × 108 s–1. The fluorescenece quantum yield of the molecule is
(a) 0.1
(b) 0.2
(c) 0.4
(d) 0.6
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
137. Solution of three electrolytes have the same ionic strength and different dielectric constants as 4, 25 and 81. The corresponding relative magnitude of Debye–Hückel screening, lengths of the three solutions are
(a) 4, 25 and 81
(b) 2, 5 and 9
(c) 1/2, 1/5 and 1/9
(d) 1, 1 and 1
Ans. b
Sol. Debye – Hückel screening length

138. Simple Hückel molecular orbital theory
(a) considers electron – electron repulsion explicitly
(b) distinguishes cis – butadiene and trans – butadiene
(c) disinguishes cis – butadiene and cyclobutadiene
(d) has different coulomb inegarals for non – equivalent carbons.
Ans. c
Sol. In simple Hückel molecular orbital theory only distinguishes between cis – butadiene and cyclobutadiene on the bases of energy correction. In cyclobutadiene delocalization energy is zero and cis butadiene is 
Correct answer is (c)
139. For the non – dissociative Langmuir type adsorption of a gas on a solid surface at a particular temperature, the fraction of surface coverage is 0.6 at 30 bar. The Langmuir isotherm constant (in bar–1 units) at this temperature is
(a) 0.05
(b) 20.20
(c) 2.0
(d) 5.0
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option (a)
140. For a set of 10 observed data points, the mean is 8 and the variance is 0.04. The 'standard deviation' and the 'coefficient of variation' of the data are, respectively
(a) 0.005, 0.1%
(b) 0.02. 0.2%
(c) 0.20, 2.5%
(d) 0.32, 1.0%
Ans. c
Sol. n = 10, variance = 0.04, 

In percentage (coefficient of variation) = 0.025 × 100% = 2.5%
Correct option is (c)
141. In the Linewaver – Burk plot of (initial rate)–1 vs. (initial substrate concentration)–1 for an enzyme catalyzed reaction following Michaelis – Menten mechanism, the y – intercept is 5000 M–1 s. If the initial enzyme concentration is 1×10–9 M, the turnover number is
(a) 2.5 × 103
(b) 1.0 × 104
(c) 2.5 × 104
(d) 2.0 × 105
Ans. d
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
142. The  direct product in D3 point group contains the irreducible representations
direct product in D3 point group contains the irreducible representations

(a) A1 + A2 + E
(b) 2A1 + E
(c) 2A2 + E
(d) 2A1 + 2A2
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
143. The result of product C2 (x) C2 (y) is
(a) E
(b) 
(c) C2(z)
(d) i
Ans. c
Sol. The product of C2 (x) C2 (y) is C2 (z)


Correct option is (c)
144. Given:
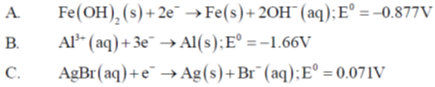
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

In this cell Fe carried negative reduction potential goes to left hand side of the half cell and in this halfs cell oxidation occur.
Fe oxidised
Note: In electrochemical series (Al+3, Al) stay below to (Fe+2, Fe) and (AgBr(s), Br– : Ag) stay above. So, (Al+3, Al) reduced and (AgBr, Br–.Ag) oxidised by (Fe+2, Fe).
Correct answer is (b)
145. The reagent A used and the major product B formed in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Catalytic hydrogenating works in the case of alkene and alkyne. Thus H2|Pd will not work here. Therefore, NaBH4 reduces aldehyde and ketones to corresponding alcohol.
Therefore, reduction of amide to amine can be beautifully done by LiAlH4, but it does not follow the same pattern an observed for ester and acids.

Correct option is (a)
