CSIR NET CHEMISTRY (JUNE - 2013)
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
21. Which of the following pairs has the highest difference in their first ionization energy?
(a) Xe, Cs
(b) Kr, Rb
(c) Ar, K
(d) Ne, Na
Ans. d
Sol. First ionization potential of Ne = 2080
First ionization potential of Na = Ne – 495
= 1585 eV
Inoisation Energy = Difference in ionization potential of Neon and Sodium (Ne – Na)
So, 1585eV is the largest difference in given pairs. The reason being as we move down the group number of electrons and proton increases simultaneously with addition of new energy shells so increase in distance from Nucleus to electron is more pronounced as that of increases in electron and proton resultantly Zeff (effective nuclear charge) decreases and first ionization potential also decreases down the group.
Correct answer is (d)
22. The ligand in uranocene is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Uranocene U(C8H8)2 is the most notable cyclo octatetraenidl of f– block elements and first organouranium compounds.


Correct answer is (a)
23. In metal – olefinineraction, the extent of increase in metal  olefin
olefin  π– back – donation would
π– back – donation would
(a) lead to a decrease in C = C bond length
(b) change the formal oxidation state of the metal
(c) change the hybridisation of the olefin carbon from sp2 to sp3.
(d) increase with the presence of electron donating substituent on the olefin.
Ans. c
Sol. Isolated  sp2 hybridisation
sp2 hybridisation
But when olefin attach to metal the hybridization of olefin carbon change sp2 sp3
sp3

Correct option is (c)
24. The oxidation state of molybdenum in  is:
is:
(a) +2
(b) +1
(c) 0
(d) –1
Ans. c
Sol. 
Mo in zero oxidation state.
Correct answer is (c)
25. The reaction of  with two equivalents of NH3 produces
with two equivalents of NH3 produces
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Trans effect Cl– has larger trans effect than NH3.

Correct option is (a)
26. The electronic transition responsible for the color of the transition metal ions is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. The electronic transition responsible for the colour of the transition metal ions is  which is in according to LFT.
which is in according to LFT.

Correct option is (b)
27. The number of metal-metal bonds in [W2(OPh)6] is:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans. c
Sol. Total valency electron = 12 + 18 = 30 (A) [(Oph) in bridging donate 3 electron]
B = (n × 18 – A) = 36 – 30 = 6
Metal – metal bond = B/2 = 6/2 = 3
Correct answer is (c)
28. The Mulliken symbols for the spectroscopic states arising from the free-ion term F are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. The mulliken symbols for the spectroscopio states arising from free ion term F are

Correct answer is (a)
29. Which of the following is used as propellant for whipping creams?
(a) N2O
(b) NO
(c) N2O3
(d) N2O3
Ans. a
Sol. Nitrous acid (N2O) which is commonly known as laughing gas used as a propellent in whipping cream. So, also known as whippits or nangs.
Correct answer is (a)
30. Flame proof fabrices contain
(a) H2NC(O)NH2.Na2SO4
(b) H2NC(S)NH2.Na2SO4
(c) H2NC(O)NH2.P3PO4
(d) N2NC(S)NH2.H3PO4
Ans. c
Sol. The Flame proof fabrices contain urea and phosphoric acid (H2NC(O) NH2.H3PO4)
Correct answer is (c)
31. Among the compounds A–D, those which hydrolyse easily are
(a) NCl3
(b) NF3
(c) BiCl3
(d) PC13
Ans. d
Sol. BiCl3 is not readily hydrolysed by water to give BiOCl.
BiCl3 + H2O  BiOCl + 2HCl
BiOCl + 2HCl
But BiOCl redissolve in cone. HCl to produce BiCl3 after evaporation. It has quasi molecular structure. PCl3 is is easily hydrolysed by water.
Correct answer is (d)
32. The coordination geometry of copper (II) in the type I copper protein plastocyanin is:
(a) square planar
(b) tetrahedral
(c) octahedral
(d) distorted tetrahedral
Ans. d
Sol. The coordination geometry of copper (II) in coper (I) protein plastcoyanin is distorted tetrahedral.
Correct answer is (d)
33. The metal ions present in the active site of nitrogenase enzyme co-factor are
(a) Fe, Mo
(b) Fe, W
(c) Fe, Cu
(d) Fe, Ni
Ans. a
Sol. Nitrogenase enzyme cofactor contains Fe, Mo also known as Iron – molebdenum cofactor.
Correct answer is (a)
34. The reaction,  is an example for
is an example for
(a) oxidative addition
(b) electrophilic substitution
(c) nucleophilic substitution
(d) migratory insertion
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct answer is (d)
35. The number of EPR signals observed for octahedral Ni(II) complexes is
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Zero
Ans. a
Sol. If the system has an even number of unpaired electrons then zero field splitting within the ground state may result in the EPR transitions being undetectable and only one EPR signal is observed. Since Ni(II) octahedral complex has two unpaired electrons, therefore, number EPR signals is one
Correct answer is (a)
36. For neutron activation analysis of an element, the favourable characteristics of both the target and the product are from the following.
(a) high neutron cross-sections area of target
(b) long half-life of the product
(c) low neutron cross-section area of target
(d) low half-life time of the product
Ans. a
Sol. For an element the favourable characteristics both the target and the product in neutron activation is high neutron cross – section area of the target and long half – line of the product.
Correct answer is (a)
37. The concentrations of a species A undergoing the reaction  is 1.0, 0.5, 0.33, 0.25 mol dm–3 at t = 0, 1, 2 and 3 seconds respectively. The order of the reaction is:
is 1.0, 0.5, 0.33, 0.25 mol dm–3 at t = 0, 1, 2 and 3 seconds respectively. The order of the reaction is:
(a) two
(b) one
(c) zero
(d) three
Ans. a
Sol. From given, we observe that, on reducing the concentration to half of its initial value. the half – life becomes double.

and as for a second order reaction 
So, on reducing the concentration to half of its initial value. the half – life becomes double.
Since, order of reaction is 2
Correct option is (a).
38. The difference in energy levels of n=2 and n=1 of a particle – in – a one dimensional box is 6 units of energy. In the same units, what is the difference in energy levels of n = 3 and n = 2 for the above system?
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 9
(d) 10
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
39. The wave function  of a certain system is the linear combination
of a certain system is the linear combination

Where  are energy eigen functions with eigen values (non-degnerate) E1 and E2, respectively. What is the probability that the system energy will be observed to be E1?
are energy eigen functions with eigen values (non-degnerate) E1 and E2, respectively. What is the probability that the system energy will be observed to be E1?
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
40. What is the atomic term symbol for helium atom with electronic configuration Is2?
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
41. A molecules contains the following symmetry operations:  The number of classes and order of the symmetry point group is:
The number of classes and order of the symmetry point group is:
(a) 3, 12
(b) 5, 12
(c) 6, 12
(d) 6, 6
Ans. c
Sol. 
Total operation = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 6
Order = 1 + 2 + 2 + 1 + 3 + 3 = 12
Correct option is (c)
42. A triatomic molecule of the type AB2 shows two IR absorption line and IR-Raman line. The structure of the molecule is:
(a) B – B – A
(b) B – A – B
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. Molecule contains two IR absorption lines and one Raman line. So, molecule contains centre of symmetry and follow the mutual exclusion principle, because in this type of molecule if IR band is present then Raman band absent. The common band or line is always zero. e.g. Co2 type molecule.
Correct option is (b)
43. In NMR spectroscopy, the product of the nuclear 'g' factor (gN), the nuclear magneton 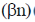 and the magnetic field strength (B0) gives the
and the magnetic field strength (B0) gives the
(a) energy of transition from  state
state
(b) chemical shift
(c) spin–spin coupling constant
(d) magnetogyric ratio
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
44. An aqueous mixed solution of NaCl and HCl is exactly neutralized by an aqueous NaOH solution. The number of components in the final mixture is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans. b
Sol. 
Mix neutralized by NaOH

For component C = N – E = 3 – 1 = 2
Or total ion = Na+, OH–, H+, Cl– and total N = 4

Correct answer is (b)
45. The lowest pressure at which the liquid phase of a pure substance can exist is known as
(a) critical point pressure
(b) super – incumbent pressure
(c) triple – point pressure
(d) saturation vapour pressure
Ans. c
Sol. At the triple point pressure the liquid phase of a pure substance exist.
Correct answer is (c)
46. A chemical reaction involving nonlinear molecule + nonlinear molecule  nonlinear activated complex
nonlinear activated complex
(a) 3N – 5
(b) 3N – 6
(c) 3N – 7
(d) 3N – 8
Ans. c
Sol. According to transition state theory, for activated complex, one of its vibrational degree of freedom is being converted into translational degree of freedom.
Therefore, required vibration degree of freedom = (3N – 6) – 1 = 3N – 7
Correct answer is (c)
47. Calculate the total number of microstates for 6 identical particles with their occupation numbers {1, 2, 3} in three states is:
(a) 6
(b) 12
(c) 60
(d) 720
Ans. c
Sol. Given : total particles = 6 (N) and states {1, 2, 3}
n1 = 1, n2 = 2, n3 = 3
So, possible arrangements 
Correct answer is (c)
48. If the concentration (c) is increased to 4 times its original value (c), the change in molar conductivity for strong electrolytes is (where b is Kohlrausch constant)
(a) 0
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
If the concentration four times increased.

From equation (1) and (2), we get

Correct option is (b)
49. In atom recombination reactions
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. For atom recombination, there is a relatively small amount of rearrangement of energy among the various defracts in the activated complex, Consequently,  is expected to have a small negative value. Such process occurs with zero activation energy and negative enthalpy change. e.g. dimerization of nitric oxide.
is expected to have a small negative value. Such process occurs with zero activation energy and negative enthalpy change. e.g. dimerization of nitric oxide.

Correct option is (b)
50. In the Lindemann mechanism of unimolecular reactions, the observed order at low concentration is
(a) 0.5
(b) 1
(c) 1.5
(d) 2
Ans. d
Sol. In the Lindeman mechanism, unimolecular reaction at low concentration or pressure follows second order kinetics.
Correct answer is (d)
51. The aggregation of surfactant molecules is known as
(a) micelles
(b) clusters
(c) gel
(d) colloid
Ans. a
Sol. The aggregation of surfactant molecules is defined as micelles.
Correct answer is (a)
52. The coordinates for the atoms in a body centred cubic unit cell are
(a) (0, 0, 0) and (1/2, 0, 0)
(b) (0, 0, 0) and (1/2, 1/2, 1/2)
(c) (0, 0, 0) and (0, 1/2, 0)
(d) (0, 0, 0) and (0, 0, 1/2)
Ans. b
Sol. 
Consider one particle at origin and second one at body center (0, 0, 0), (1/2,1/2,1/2)
Correct answer is (b)
53. The inter planar distance (Å) for a (100) plane in a cubic structure with the lattice parameter of 4Å is:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 8
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
54. The correlation coefficient of two parameters is found to be – 0.99. It may be concluded that the two parameters are
(a) strongly correlated
(b) almost uncorrelated
(c) connected by a cause – effect relationship
(d) not connected by a cause – effect relationship
Ans. a
Sol. The value of correlation coefficient lie between –1 to +1.
The value found – 0.99 near by –1 mean strongly correlate if value out side of –1 to +1 almost on correlated.
Correct answer is (a)
55. The IUPAC name for the compound given below is

(a) (2R, 3Z) - 7 - phenylhept - 3 - en - 2 - ol
(b) (2S, 3Z) - 7 - phenylhept - 3 - en - 2 - ol
(c) (2R, 3E) - 7 - phenylhept - 3 - en - 2 - ol
(d) (2S, 3E) - 7 - phenylhept - 3 - en - 2 - ol
Ans. d
Sol. 
Configuration at the chiral centre at C–2 is S geometry at the double bond is E.
Therefore, IUPAC name is (2S, 3E) – 7 – phenylhept – 3 – en – 2 – ol.
Correct answer is (d)
56. Among the following esters, the one that undergoes acid hydrolysis fastest is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as


More stabilization of reaction intermediate, enhances the rate of hydrolysis.
Correct answer is (b)
57. Reaction of cyclohexyl benzyl ether with hydrogen in the presence of 10% Pd/C yields
(a) cyclohexanol and toluene
(b) cyclohexanol and benzyl alcohol
(c) cyclohexane and benzyl alcohol
(d) cyclohexane and toluene
Ans. a
Sol. 
The above case belong to hydrogenolys is. Bond cleavage by the more electrongative atom in the presence of catalyst is known as hydrogenolysis.

Z = High electronegative
Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (a)
58. Among the following dibromocyclohexanes, the one that reacts fastest with sodium iodide to give cyclohexene is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. Vicinal dibromides may be dibrominated by treating them with reducing agents like, Iodide ion or zinc. Debromination using sodium iodide is found to be an anti – elimination.

This iodine induced reduction is essentially the reverse of a halogenation. Application of the principle of microsope reversibility suggest that the reaction proceeds through a bridged intermediate as shown above.
Out of four options only (b) and (c) are vicinal and out of (b) and (c) only in (c) the two Br are anti thus the correct answer is (c)


Correct answer is (c)
59. Match the following drugs with their medicinal activity

(a) A-i, B-ii
(b) A-iv, B-iii
(c) A-iii, B-iv
(d) A-iii, B-i
Ans. d
Sol. 
The 5 – fluorauracel is anticanceragent.
Correct answer is (d)
60. The major product formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as


LiAlH4 is a reducing agent and it reduces ester group into alcohol.
Here lactone i.e. cyclic ester is converted into corresponding alcohol.
Correct option is (b)
61. The biosynthetic precursor for the steroids is
(a) secologanin
(b) shikimic acid
(c) mevalonic acid
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. The biosynthetic precursor for the steroids is Mevalonic acid.

Correct answer is (c)
62. The major product formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 


Correct option is (b)
63. In the compound given below, the hydrogenes marked A and B are

(a) homotopic
(b) isotopic
(c) enantiotopic
(d) diastereotopic
Ans. c
Sol. Homomorphic ligands: Ligands are called homomorphic, if they are indistinguishable when considered in isolation. Here HA and HB are thus homomorphic.
Two homomorphic ligands are homotopic, if substitution of first one and then the other by an atom or a group, which is not already attached to the ligend centre, gives identical product, else heterotopic. Since substitution of HA and HB by D gives different products, thus HA and HB are heterotopic.

Also, two heterotopic ligands are enantiotopic if replacement of first one and then the other by a different achiral ligand gives rise to two enantiomers.
Correct answer is (c)
64. In the IR spectrum, the absorption band due to carbonyl group in phenyl acetate appears at
(a) 1800 cm–1
(b) 1760 cm–1
(c) 1710 cm–1
(d) 1660 cm–1
Ans. b
Sol. 
Normal ester gives 1735 – 1750 but due to phenyl group some extend frequency of  group upto 1765 cm–1.
group upto 1765 cm–1.
Correct option is (b)
65. The reactive intermediate involved in the following reaction is:

(a) a carbocation
(b) a carbanion
(c) a free radical
(d) an aryne
Ans. d
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (d)
66. Number of isoprene units present in lupeol is

(a) two
(b) four
(c) six
(d) eight
Ans. c
Sol. The Terpene Lupeol contains 30 carbons, dividing by 5 (5 carbons in one Isoprene) we get 6.

Hence, lupeal contains 5 isoprene unit.
Correct answer is (c)
67. The heterocyclic ring present in the amino acid histidine is:
(a) pyridine
(b) tetrahydropyrrole
(c) indole
(d) imidazole
Ans. d
Sol. The structure of Amino acid Histidine is 
Correct option is (d)
68. The gauche conformation  of n-butane posseses
of n-butane posseses
(a) plane of symmetry; and is achiral
(b) C2 – axis of symmetry; and is chiral
(c) centre of symmertry; and is achiral
(d) plane of symmetry; and is chiral
Ans. b
Sol. The Gauche conformations of n–Butane are non – superimposable mirror image of each other, thus Gauche conformation is chiral.

If contains neither plane nor centre of symmetry.
A C2 axis passes through the mid – point of C2 – C3 bond and bisecting the dihedral angle between the two methyls.
Correct option is (b)
69. The following photochemical conversion proceeds through

(a) Barton reaction
(b) Paterno - Büchi reaction
(c) Norrish type I reaction
(d) Norrish type II reaction
Ans. d
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as



The above reaction takes place via Norrish type – II mechanism.
Correct option is (d)
70. Among the following dienes, the one that undergoes a degenerate Cope rearrangement is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. A degenerate rearrangement is a reaction process in which no overall change in structure occurs and the product is structually identical to the starting material. An example is the homotropilidene rearrangement.

others examples of this rearrangement are bullvalene, semibullvalene, Barbaralane etc.
Correct answer is (a)
71. A radioisotope 41Ar initially decays at the rate of 34, 500 disintegrations/minute, but decay rate falls to 21, 500 disintegrations/minute after 75 minutes. The t1/2 for 41Ar is:
(a) 90 minutes
(b) 110 minutes
(c) 180 minutes
(d) 220 minutes
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct answer is (b)
72. The orders of reactivity of ligands, NMe3, PMe3 and CO with complexes MeTiCl3 and (CO)5Mo(thf) are
(a) CO > PMe3 > NMe3 and CO > NMe3 > PMe3
(b) PMe3 > CO > NMe3 and NMe3 > CO > PMe3
(c) NMe3 > PMe3 > CO and CO > PMe3 > NMe3
(d) NMe3 > CO > PMe3 and PMe3 > NMe3 > CO
Ans. c
Sol. 
In the first complex titanium in high oxidation state +4. So, react faster with σ – donor ligand. Correct order NMe3 > PMe3 > CO.
Where as in the second complex

Mo in low oxidation state. So, reactivity order is CO > PMe3 > NMe3
Correct answer is (c)
73. The number of lone-pairs are identical in the pairs
(a) XeF4, CIF3
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
74. Among the following, those can act as Mössbauer nuclei are:
(a) 129I
(b) 57Co
(c) 57Fe
(d) 121Sb
Ans. c
Sol. 129I, 57Fe and 121Sb
Mössbauer nuclei and they fulfuil all the properties for that 57Co is unstable nuclei which is used as  the Mössbauer spectro photometer for 57Fe study.
the Mössbauer spectro photometer for 57Fe study.
Correct answer is (c)
75. Which of the pairs will generally result in tetrahedral coordination complexes, when ligands are Ci– or OH–
(A) Be(II), Ba(II) (B)Ba(II), Co(II) (C) Co(II), Zn(II) (D) Be(II), Zn(II)
(a) A and B
(b) B and C
(c) C and D
(d) A and D
Ans. c
Sol. Co(II), Zn(II) and Be(II) form tetrahedral complexes with Cl– or OH–.
Be(II) has no d-orbitals. Therefore it form tetrahedral complexes.
Co(II) and Zn(II) form tetrahedral complexes with halides and OH–.
Correct answer is (c)
76. Silica gel contains [CoCl4]2– as an indicator. When activated, silica gel becomes dark blue while upon absorption of moisture, its colour changes to pale pink. This is because,
(a) Co(II) changes its coordination from tetrahedral to octahedral.
(b) Co(II) changes its oxidation state to Co(III)
(c) Tetrahedral crystal field splitting is NOT equal to octahedral crystal field spitting.
(d) Co(II) forms kinetically labile while Co(III) forms kinetically inert complexes.
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct answer is (a)
77. For the metalloprotein hemerythrin, the statement that is NOT TRUE is
(a) there are two ion centres per active site.
(b) both iron centres are hexacoordinated in teh active state
(c) one iron is hexacoordinated while the other is pentacoordinated in the active state.
(d) it is found in marine invertebrates.
Ans. b
Sol. 
In Hemerythrin, one iron centre is pentacoordinated and is hexacoordinated. And iron exist at peractive site found in mariene invertebrates.
Corrrect answr is (b)
78. For a tetragonally distorted Cr(III) complex, zero-field splitting results in the following number of Kramers doublets:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans. b
Sol. For systems with more than one electrons  the ground state can be split in the absence of external magnetic field due to local site symmetry – the zero field splitting. For odd electrons systems, this results in pairs of energy levels known as Kramer's doublets. Since Cr (III) has three unpaired electrons, therefore number of Kramer's doublets in tetragonally distorted Cr–(II) complex in zero field splitting is 2.
the ground state can be split in the absence of external magnetic field due to local site symmetry – the zero field splitting. For odd electrons systems, this results in pairs of energy levels known as Kramer's doublets. Since Cr (III) has three unpaired electrons, therefore number of Kramer's doublets in tetragonally distorted Cr–(II) complex in zero field splitting is 2.
Correct option is (b)
79. Intense band at 1000 cm–1 in the UV – visible spectrum of [Bu4N]2Re2Cl8 is due to the transition
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
80. Electron change in reduction of Ce(SO4)2, KMnO4, HNO2 and I2 with hydrazine in acidic medium, respectively is
(a) 1e, 1e, 2 e and 4e
(b) 1e, 3e 2e and 4e
(c) 2e, 3e, 1e and 4e
(d) 2e, 4e, l3 and 3e
Ans. a
Sol. Ce(SO4)2 and KMnO4 gives one electron on reduction with hydrazine in acidic medium and HNO2 and I2 gives two electron and four electron on reduction with hydrazine in acidic medium.
Correct answer is (a)
81. The compound that will behave as an acid in H2SO4 is
(a) CH3COOH
(b) HNO3
(c) HClO4
(d) H2O
Ans. c
Sol. HCIO4 behave as an acid in H2SO4. Because HC1O4 contain higher dissociation constant than that of H2SO4.
HC1O4 pKa value – 9, H2SO4 pKa value – 3, HNO3 pKa value –1, CH3COOH pKa value 4.7. pKa value of HC1O4 > value of H2SO4.
Correct option is (c)
82. Among the oxides of nitrogen, N2O3, N2O4 and N2O5, the compound(s) having N–N bond is/are
(a) N2O4 and N2O5
(b) N2O3 and N2O5
(c) N2O4 and N2O4
(d) N2O5 only
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
83. The treatment of PhBr with n–BuLi yields:
(a) 2 n – BuPh + Br2 + Li2
(b) PhPH + octane + 2 LiBr
(c) n – BuPh + LiBr
(d) PhLi + n – BuBr
Ans. d
Sol. This follows electron transfer (radical) process

Hence, formation of 4 – membered transition state model.

Correct answer is (d)
84. Though cyclobutadiene (C4H4) is highly unstabled and readily polymerizes in its free state, its transition metal complexes could be isolated because
(a) it engages in long-range interaction with transition metals.
(b) it gains stability due to formation of C4H42– on binding to transition metal.
(c) its polymerization ability reduces in presence of transition metal.
(d) it becomes stable in presence of transition metals due to formation of C4H42+.
Ans. c
Sol. Cyclobutadiene is  which is antiaromatic and unstable due to this reasons it dimerizes, but when it attached with metal such as
which is antiaromatic and unstable due to this reasons it dimerizes, but when it attached with metal such as

The back  occurs from metal to cyclobutadienes due to this it gain electro from the metal and converted, into cyclobutadiene anion which and hence stables.
occurs from metal to cyclobutadienes due to this it gain electro from the metal and converted, into cyclobutadiene anion which and hence stables.
Correct option is (c)
85. Identify the order representing increasing  of the following ligands
of the following ligands
C2F4, NEt3, CO and C2H4
(a) CO < C2F4 < C2H4 < NEt3
(b) C2O4 < C2F4 < NEt3 < CO
(c) C2H4 < NEt3 < CO < C2F4
(d) NEt3 < C2H4 < C2F4 < CO
Ans. d
Sol. Increasing 
NEt3 < C2H4 < C2F4 < CO
Where, NEt3 = Neither 
C2H4 < C2F4 < CO = Increasing order of  ability (on the bases of LFT)
ability (on the bases of LFT)
Correct option is (d)
86. The species with highest magnetic moment (spin only value) is
(a) 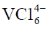
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
87. The number of metal-metal bounds in Ir4(CO)12 is
(a) 4
(b) 6
(c) 10
(d) 12
Ans. b
Sol. 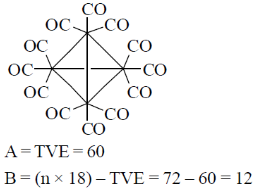
Metal metal bond = B/2 = 12/2 = 6
Correct option is (b)
88. Three bands in the electronic spectrum of  are due to the following transitions
are due to the following transitions

Identify the correct statement about them
(a) Intensity of (A) is lowest
(b) Intensity of (C) is lowest
(c) Intensities of (A), (B) and (C) are similar
(d) Intensities of (B) and (C) are similar.
Ans. b
Sol. Intensity of C  is lowest, since it is spin forbidden.
is lowest, since it is spin forbidden.
Correct answer is (b)
89. Identify the pairs in which the covalent radii of elements are almost similar
(A) Nb, Ta (B) Mo, W (C) La, Lu (D) Sc, Y
(a) A and B only
(b) A and C only
(c) B and C only
(d) A, B and C only
Ans. a
Sol. As we move from Nb – Ta and Mo – W there is introduction of electron into f – orbital. As the shielding power of f – orbital is very less. Therefore, as we move from La – Lu in 4f series the size decreases, this is termed as Lanthanide contraction. This leads to slight increase in size of 5d metal than 4d. Due to this size of d and 5d metals are neraly similar. Hence Nb – Ta and Mo – W have similar covalent radii.
Correct answer is (a)
90. Consider following lanthanide (III) ions
(A) Nd(III) (B) Gd(III) (C) Dy(III)
The magnetic moment closest to the spin only value is(are) for
(a) B only
(b) A and B only
(c) A and C only
(d) B and C only
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
91. The  of the following complexes.
of the following complexes.
 follows the order
follows the order
(a) C > A > B
(b) A > B > C
(c) B > A > C
(d) C > B > A
Ans. a
Sol. From spectro chemical series order, 

Correct option is (a)
92. In complexometric titration

The end point is estimated spectrophotometrically. If S and P have  the shape of the titration curve would look like
the shape of the titration curve would look like
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. If S and P have  then titrant shows parallely and after end point goes increasingly with respect to substate.
then titrant shows parallely and after end point goes increasingly with respect to substate.
Correct answer is (c)
93. Identify the chiral complexes from the following

(a) A only
(b) A and B only
(c) A and C only
(d) B and C only
Ans. b
Sol.  are octahedral and have no plane of symmetry. Therefore these are chiral complex,
are octahedral and have no plane of symmetry. Therefore these are chiral complex,  is square planar and has plane of symmetry. Therefore, it is achiral.
is square planar and has plane of symmetry. Therefore, it is achiral.
Correct answer is (b)
94. Distribution ratio of 'A' between CHCI3 and water is 9.0. It is extracted with several, 5 mL aliquots of CHCl3. The number of aliquots needed to extract 99.9% of 'A' from its 5 mL aqueous solution are
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Ans. c
Sol. Correct answer is (c)
95. The correct equilibrium order for the interconversion of different forms of SiO2 is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
96. The rate equation for the reaction 2AB + B2 2 AB2 is given by
2 AB2 is given by
rate = k[AB] [B2]
A possible mechanism consistent with this rate law is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Since, rate is given by slow step.
Therefore, this mechanism is consistent with the given rate law.
Correct answer is (c)
97. Observe the following statements
(I) in the H2 – O2 reaction, explosion occurs when the rate of chain branching exceeds that of chain termination.
(II) The order of the reaction, nA  products, is 2.5. For this reaction,
products, is 2.5. For this reaction, 
(III) Unimolecular gas phase reactions are second order at low pressure but becomes first order at high pressure.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) I, II and III are correct
(b) Only II is correct
(c) Only III is correct
(d) I and II are correct
Ans. a
Sol. When chain machism exceeds the chain termination, it result in uncontrolled step, chain reaction that ultimately results in explosion.
For nth order, 


Correct option is (a)
98. For the parcile-in-a-box problem in (0, L) an approximate wave function is given as x (L/2 – x) (0, L). The average energy Ē for such a state will obey
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. As we know for the particlein 1 – D box

Variation principle says.

Also at  node means given wave function represent
node means given wave function represent  one node
one node
So, 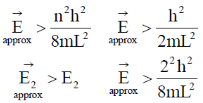
Correct option is (b)
99. For two variables X and y, the following data set is given:

The correct statement for the covariance A and correlation coefficient B of x and y is
(a) A = 2/3, B = 1
(b) A = –2/3, B = 1
(c) A = –2/3, B = –1
(d) A = 0, B = 0
Ans. a
Sol. 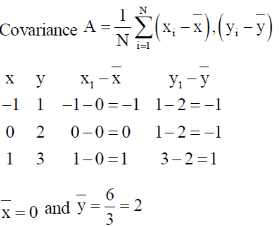



Correct option is (a)
100. The hydrogenic orbital with the form of the radial function.

are constants, may be identified as a
(a) 3d orbital
(b) 4f orbital
(c) 5d orbital
(d) 5f orbital
Ans. c
Sol. 
Where,  = represent one radical node i.e.
= represent one radical node i.e. 
 = represent one radial node i.e.
= represent one radial node i.e. 
i.e. total 2 nodes
We know that, radial node = 1 – l – = 2
For option (c), n = 5, l = 2
Radial node = 5 – 2 – 1 = 2
Correct option is (c)
101. The operator  is identified with
is identified with
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
102. For the particle -in-a-box problem in (0, L), the value of  limit would be
limit would be
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
103. Identify the Mulliken notation for the following irreducible representation

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
104. Identify the point group symmetry of the following molecule (all C–C bond lengths are equal)

(a) C2v
(b) S4
(c) D2d
(d) D4d
Ans. c
Sol. 
The structure has three C2 axis perpendicular to each other. If C2(z) is P-axis. Then there is two vertical plane also.


Correct option is (c)
105. The ground state term symbol for Nb(atomic number 41) is 6D. The electronic configuration corresponding to this term symbol is
(a) [Kr]4d35s2
(b) [Kr]4d45s1
(c) [Kr]4d55s0
(d) [Kr]4d35s15p1
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
106. In the presence of an external magnetic field (normal Zeeman effect0, the transition 1D2 1P1 splits into
1P1 splits into
(a) 9 lines
(b) 8 lines
(c) 7 lines
(d) 6 lines
Ans. a
Sol. Selection rule,  (for Zeeman Effect)
(for Zeeman Effect)

Correct option is (a)
107. Identify the Huckel determinant for cyclobutadiene
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
108. On mixing 120 ml of 0.05 M CH3COOH and 40 ml of 0.05 M of NaOH, the pH of the solution is (PKa = – log Ka)
(a) pKa + 0.69
(b) pKa + 0.301
(c) pKa
(d) pKa – 0.69
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
109. A system consists of gaseous H2, O2, H2O and CO2 where the amount of CO2 is specified and the equilibrium constant for the reaction  is known. The number of degrees of freedom of the system is
is known. The number of degrees of freedom of the system is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Ans. b
Sol. Degree of freedom F = C – P + 2
Component C = N – E
Only one phase exist i.e. gaseous phase.
C = N – E = 4 – 2 = 2
Therefore, F = 2 – 1 + 2 = 3
Correct option is (b)
110. "Colloids are thermodynamically unstable with reference to bulk but kinetically stable". Identify the correct pair

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. With reference to bulk colloid are thermdonynamically unstable but kinetically stable because interfacial surface tension form thermodynamically unstable colloid and kinetically stable colloid formed on electrical double layer
Correct option is (b)
111. An AX system gave 4 lines at 4.72, 4.6, 1.12 and 1.0 ppm away from the TMS using an nmr spectrometer operating at 100 MHz. What are the values of JAX (in Hz) and  (in ppm), respectively
(in ppm), respectively
(a) 12 and 3.6
(b) 6 and 3.6
(c) 12 and 2.86
(d) 6 and 2.86
Ans. a
Sol. Ax type mean X split with A and A split with X.
Two doubles.

Coupling constant JAX is separation between peaks of a multiplet.

Correct option is (a)
112. The equilibrium population ratio (nj / ni) of a doubly-degenerate energy level (Ej) lying at energy 2 units higher than a lower non-degenerate energy level (Ej), assuming kBT = 1 unit, will be
(a) 2e–2
(b) 2e2
(c) e2
(d) e–2
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct answer is (a)
113. Which of the following statements is true for a cyclic process?
(a) 
(b) 
(c) Heat can be completely converted into work
(d) Work can be completely converted into heat
Ans. d
Sol. 
Cyclic integral of state function (exact differential) is zero but q is path function differential). So cyclic integral of q is not zero.
 is not true as the case above.
is not true as the case above.
Heat cannot be converted completely into work in cyclic process because it is the violation of carnot cycle or carnot engine. Work can be completely converted into heat. (Second law statement)
Correct option is (d)
114. Identify, from the following, the correct ionic strengths for (A) 0.01 molal solution of NaCl and (B) a 0.01 molal solution of Na2SO4.
(a) (A) 0.010 mol kg–1 (B) 0.010 mol kg–1
(b) (A) 0.010 mol kg–1 (B) 0.030 mol kg–1
(c) (A) 0.010 mol kg–1 (B) 0.025 mol kg–1
(d) (A) 0.010 mol kg–1 (B) 0.015 mol kg–1
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
115. A system has 100 degenerate energy levels and 100 bosons are kept in it. Find the entropy of the system at equilibrium.
(a) 10–2 kB
(b) 102 kB
(c) 460.6 kB
(d) 4.606 kB
Ans. b
Sol. 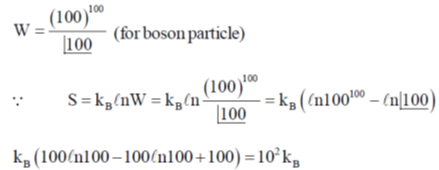
Correct option is (b)
116. Which is correct Nernst equation for redox reaction 
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
117. A plane of spacing 'd' shows first order Bragg diffraction at angle  . A plane of spacing 2d
. A plane of spacing 2d
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. From Bragg's equation, we have 

Then for spacing 2d, we have

Correct option is (c)
118. In the formation of H2 molecules from 2H atoms placed at positions A and B, and separated by a distance rAB, a part of the spatial wave function is

(a) This is a covalent term and is important as 
(b) This is an ionic term and is important as 
(c) This is a covalent term and is important as 
(d) This is an ionic term and is important as 
Ans. d
Sol. In molecular orbital treatment of H2, two electrons with opposite spins are assigned to the lowest molecular orbital  Thus, the spatial wave function of H2 is.
Thus, the spatial wave function of H2 is.

Opening out the above expression, we get

In the above expression, the various terms represent the structures as described below.
First and Fourth terms: The terms are  These configuration assign both the electrons either to atom Ha or Hb and hence they represent ionic structures.
These configuration assign both the electrons either to atom Ha or Hb and hence they represent ionic structures.
Second and third terms: The terms are  These configuration assign one electrons to each of the atom and hence they represent covalent structures.
These configuration assign one electrons to each of the atom and hence they represent covalent structures.
Since the coefficients of all the terms are identical, it follows that MO treatment gives equal weightage to the ionic and covalent structures. It is expected that the MO function will be poor at large internuclear separations since the dissociation products will be an equal mixture of ions and atom. In actual practice we get two hydrogen atoms. On the other hand, for very short internuclear distances one expects that there will also be some chance of finding both electrons in the same atomic orbital. Thus, MO treatment does take into account this fact, but perhaps gives more weightage to this fact than what actually exists in the molecule.
Correct option is (d)
119. A 0.1 M solution of compound A shows 50% transmittance when a cell of 1 cm width is used at  nm. Another 0.1 M solution of compound B gives the optical density value of 0.1761 using 1 cm cell at
nm. Another 0.1 M solution of compound B gives the optical density value of 0.1761 using 1 cm cell at  nm.
nm.
What will be the transmittance of a solution that is simultaneously 0.1 M in A and 0.1 M in B using the same cell and at the same wave length?
[log 20 = 1 1.301; log 30 = 1.4771; log 50 = 1.699]
(a) 33.3%
(b) 50%
(c) 66.7%
(d) 70%
Ans. a
Sol. for A, T = 0.50, c = 0.1M, b = 1 cm
for B, A = 0.01761, c = 0.1 M, b = 1cm
For solution (A).

Therefore, absorbance of solution of (A) and (B) = 0.3010 + 0.1761 = 0.4771 (as absorbance is additive in nature)
Therefore, required transmittance 
Correct option is (a)
120. Using standard equation for intrinsic viscosity  for a solution of polymer and any information from the graph identify viscosity average molar mass
for a solution of polymer and any information from the graph identify viscosity average molar mass  [given that a = 0.5, K = 5×10–5 L g–1]
[given that a = 0.5, K = 5×10–5 L g–1]

(a) 103 g/mol
(b) 104 g/mol
(c) 105 g/mol
(d) 106 g/mol
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
121. Among the following, the correct statement for the following reaction is

(a) A is the major product and it will have five signals in the proton decoupled 13C NMR spectrum
(b) A is the major product and it will have eight signals in the proton decoupled 13C NMR spectrum
(c) B is the major product and it will have five signals in the proton decoupled 13C NMR spectrum
(d) B is the major product and it will have five signals in the proton decoupled 13C NMR spectrum
Ans. d
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as


Five distinct carbon atoms, thus five signals in proton decoupled 13C NMR spectrum.

Eight distinct carbon atoms, thus eight signals inproton
Correct option is (d)
122. For the following three step conversion of A to B, the appropriate sequence of reactions is

(a) MnO2; (CH2OH)2/p–TSA; PCC
(b) PCC; MnO2; (CH2OH)2/p–TSA;
(c) PCC; (CH2OH)2/p–TSA; Jones' regent
(d) Jones' regent; (CH2OH)2/p–TSA; MnO2.
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

MnO2 (Manganese dioxide) specifically oxidizes allylic and benzylic hydroxyl groups. MnO2 does not attack carbon – carbon double bonds, triple bonds, triple bonds and saturated hydroxyl group.

PCC and Jones reagent oxidizes both primary and secondary alcohols, so cannot be used in first step, also Jones reagent oxidises primary OH into COOH thus PCC will be used in final step.

Therefore, correct sequence of steps is
(i) MnO2 (ii) (CH2OH)2/p – HSA (iii) PCC
Correct option is (a)
123. Which one of the following statements is true for the following transformation?

(a) A is the major product and it is a Cram product.
(b) A is the major product and it is anti–Cram product.
(c) B is the major product and it is a Cram product.
(d) B is the major product and it is anti–Cram product.
Ans. a
Sol. This is an example of Cram's rule having chelation.
Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Reagent attacks away from CH2Ph bulky group.
Therefore, major product is Cram's product.

Correct option is (a)
124. Which one of the following statements is true for the following transformation?

(a) Suitable regent is m-CPBA and B is the major product.
(b) Suitable regent is m-CPBA and A is the major product.
(c) Suitable regent aq. H2O2/NaOH and B is the major product.
(d) Suitable regent aq. H2O2/NaOH and A is the major product.
Ans. d
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as
Here epoxidation takes place  unsaturated double bond and we know that H2O2 / NaOH is the best reagent for epoxidation at
unsaturated double bond and we know that H2O2 / NaOH is the best reagent for epoxidation at  unsaturated double bond. This is due to nucleophilic nature of attacking spaces.
unsaturated double bond. This is due to nucleophilic nature of attacking spaces.

Correct option is (d)
125. The compound formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (d)
126. Among the following compounds, the one which has highest dipole moment is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. The compound which have maximum charge separation, have highest dipole moment.

This compound is aromatic in nature, ands have maximum charge separation. so, it have highest dipole moment.
Correct option is (b)
127. In the UV–visible is spectrum, a diterpenoid exhibited a  at 275 nm. The compound, among the choices given below is
at 275 nm. The compound, among the choices given below is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
For homo annular diene,
Basic value = 253
Ring residue = +20
1 exodouble bond = +5

Close to 275 nm.
Correct answer is (c)
128. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Diels – Alder reaction is ortho – para directive.
Correct answer is (a)
129. In the broad band decoupled 13C NMR spectrum, the number of signals appearing for the two pyrenediols A and B

(a) eight and eight
(b) eight and sixteen
(c) five and ten
(d) five and eight
Ans. c
Sol. To count the number of signal pass the c2 – axis, then count number of carbon on each side of c2 – axis as

Correct option is (c)
130. An organic compound exhibited the following 1H NMR spectra data:
 7.80 (2 H, d, J = 8 Hz), 6.80 (2 H, d, J = 8 Hz), 4.10 (2H, q, J = 7.2 Hz),
7.80 (2 H, d, J = 8 Hz), 6.80 (2 H, d, J = 8 Hz), 4.10 (2H, q, J = 7.2 Hz),
2.4 (3H, s), 1.25 (3 H, t, J = 7.2 (Hz)
The compound, among the choices given below is,
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol.  value and J values of corresponding H's are illustrated below as
value and J values of corresponding H's are illustrated below as

Correct option is (a)
131.  – Pinene on reaction with dilute alkaline KMnO4 produces a diol, which on further oxidation with chromium trioxide gives product A, which undergoes a positive haloform test. The compound A is
– Pinene on reaction with dilute alkaline KMnO4 produces a diol, which on further oxidation with chromium trioxide gives product A, which undergoes a positive haloform test. The compound A is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

A contains  group and will give positive haloform test.
group and will give positive haloform test.
Correct option is (c)
132. In major product formed in the reaction of guanosine with one equivalent of methyl iodide is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Because at position (1) electron density is easily available for donation to the eletrophilic reagent. Hence, electrophilic methyl will joined there.
Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (a)
133. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. [4 + 2] cycloaddition reaction is thermal allowed. So, the above reaction takes place via 4 + 2 Mechanism in thermal condition. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as


Correct option is (c)
134. Reaction of the dipeptide, given below, with hydrogen in the presence of 10% palladium over carbon, produces a mixture of

(a) Gly – Leu + toluene + carbon dioxide
(b) Phe – Leu + toluene + carbon dioxide
(c) Phe + Leu + benzyl alcohol + carbon dioxide
(d) Gly + Leu + benzyl alcohol + carbon dioxide
Ans. b
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (b)
135. Among the following, the most suitable reagent for carrying out resolution of racemic 3– methylcyclohexanone is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
The ketonic group can be resolved by the formation of diastereomeric ketal which can be prepared by diethyl tartarate (optically active) molecule.
Correct answer is (c)
136. In the following reaction sequence, structures of the major product X and Y are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (a)
137. Consider the following reaction sequence


The overall yield for the formation of p–hydroxyacetanilide and o-hydroxyacetanilides from phenol, respectively, are aproximately
(a) 57 and 20%
(b) 57 and 68%
(c) 83 and 68%
(d) 83 and 20%
Ans. a
Sol. Suppose initially we had 100 moles of

Correct answer is (a)
138. The most stable conformation of 1, 2–difluoroethane and dI – 2, 3 – butanediol are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
In general staggered conformation is stable but in case of  Gauche conformation is stable due to Gauche effect i.e. hyper conjugation.
Gauche conformation is stable due to Gauche effect i.e. hyper conjugation.

Correct option is (d)
139. Reaction of (S) – (1, 2, 4 – butanetriol with benzaldehyde in the presence of catalytic amount of p – TSA furnished the major product A. The structure of A is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. The reaction is nothing but actual formation. When there is a choice ketone, prefers to react with a 1, 2 – diol to form five – membered ring, while aldehydes prefer to react across a 1, 3 – diol to form a six membered ring and Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as


In P, both Ph and O* are syn. Here all the ring substituents are equatorial thus more stable. Whereas in Q, Ph and O* are anti and Ph is in axial position. Thus a very large syn diaxial or 1, 3 – diaxial repulsions results thus Q is very less stable and is not formed. Therefore, P is the actual product A.
Correct option is (b)
140. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
141. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

On heating this xanthate ester syn elimination results.
This is Pyrolytic cyn elimination known as chugaev reaction which can be better shown as

Correct option is (a)
142. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
143. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. Conformational preference is seen in the phtotolysis of cyclodecanone where transannular hydrogen abstraction takes place for the E – carbon, i.e. a 1, 7 – hydrogen transfer to form the cyclodecanol.

H and OH trans to each other. Because trans decalin is more stable than cis – decalin.
Correct option is (d)
144. Predict the condition A and the structure of the major product B in the following sequence.

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as


Ph3P = CHCOOEt form E alkene.
Correct answer is (a)
145. The most appropriate mode of cyclisation in the following transformation is

(a) con – rotatory in photochemical; and dis – rotatory in thermal conditions.
(b) con – rotatory in thermal; and dis – rotatory in photochemical conditions.
(c) con – rota tory in thermal; and con – rotatory in photochemical conditions.
(d) dis – rotatory in photochemical; and dis – rotatory in thermal conditions.
Ans. d
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
