CSIR NET CHEMISTRY (DEC-2015)
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
21. The biological function of cytochrome P450 and myoglobin are, respectively
(a) oxidation of alkene and O2 storage
(b) O3 transport and O2 storage
(c) O2 storage and electron carrier
(d) electron carrier and O2 transport
Ans. a
Sol. Cytochrome P450 function as monooxygenase and catalyses the insertion of oxygen in substrate

Myoglobin is found in tissue and store the oxygen in tissue transported by Haemoglobin.
Correct option is (a)
22. Deoxy – hemocyanin is
(a) heme protein and paramagnetic
(b) colorless and diamagnetic
(c) O2 transporter and paramagnetic
(d) blue colored and diamagnetic
Ans. b
Sol. In deoxyhaemocyanin Cu is in Cu(I) state i.e. have d10s0 configuration therefore it colourless and diamagnetic. Diamagnetism is due absence of unpaired electrons and colourless is due to no d–d transition as all the orbitals are filled.

Correct option is (b)
23. The oxidizing power of  , and
, and  follows the order
follows the order
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
All have +6 oxidation state but due to smaller size on going from Cr to Fe. Fe has very high charge density. Hence, it has very high tendency to accept electron. Hence, strongest oxidising agent.
Correct option is (a)
24. Using crystal field theory, identify from the following complex ions that show same  (spin only) values
(spin only) values

(a) A and B
(b) B and C
(c) A and C
(d) A, B and C
Ans. c
Sol. 
Since, A and C has same number of unpaired electron. Hence, they have same magnetic moment. As A and C are 3d – block metal with weak ligand. Hence, they are high spin while Ir being 5d – metal is low spin. Because 5d has greater splitting power than 3d.
Correct option is (c)
25. The W – W bond order in 
is
(a) three
(b) two
(c) one
(d) zero
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
26. The correct statement for Mn – O bond lengths in  is
is
(a) all bonds are equal
(b) four bonds are longer than two others
(c) two bonds are longer than four other
(d) they are shorter than the Mn–O bond in 
Ans. a
Sol. 
As all the levels are electronically non – degenerate. Hence, No Jahn – Teller distortion. Therefore, all the Mn – O bond length will be equal.
27. For the reaction of  with PMe3, the main intermediate is
with PMe3, the main intermediate is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Example of migratory insertion reaction in which alkyl group inser to CO. A new ligand create acycl a vaccancy is created which is occupied by new ligand.
Correct option is (b)
28. Identify the complex ions in sequential order when ferroin is used as an indicator in the titration of iron (II) with potassium dichromate, (phen = 1, 10 – phenathroline)
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
In presence of oxidising agent like  changes it colours from red to blue hence, they are used in redox titration.
changes it colours from red to blue hence, they are used in redox titration.
Correct option is (a)
29. The structures of XeF2 and XeO2F2 respectively are
(a) bent, tetrahedral
(b) linear, square planar
(c) linear, see – saw
(d) bent, see –saw
Ans. c
Sol. 
Therefore, G = Geometry = trigonal bipyramidal (TBP)
Hence, the shape = linear

Correct option is (c)
30. Spin motion of which of the following gives magnetic moment
(A) electron, (B) poton (C) neutron
(a) A and B
(b) B and C
(c) A and C
(d) A, B and C
Ans. d
Sol. Correct option is (d)
31. Correct statement for coulometry is
(a) it is based on Faraday's law of electrolysis
(b) it is a type of voltammetry
(c) it is based on Ohm's law
(d) it uses ion selective electrode
Ans. a
Sol. Columetry is based on Faraday's law of electrolysis
Correct option is (a)
32. The order of increasing Bronsted acidity for boron hydrides is
(a) B5H9 < B6H10 < B10H14
(b) B10H14 < B5H9 < B6H10
(c) B6H10 < B0H14 < B5H9
(d) B10H14 < B6H10 < B5H9
Ans. a
Sol. Acidic strength of Borane depends upon
(i)  number of Boron atoms
number of Boron atoms
(ii)  decapping
decapping
Hence, the correct order of acidity is B5H9 < B6H10 < B10H14
Therefore, correct option is (a)
33. Among the following, species expected to show fluxional behaviour are




(a) B and C
(b) B and D
(c) C and D
(d) A and D
Ans. b
Sol. In IF7 and Fe(CO)5, the rearrangement is so fast that axial and equatorial legands can not be differential by spectroscopy). The molecules in which rearrangement leads to configuration which are chemically equivalent are called fluxional molecule.
Correct option is (b)
34. The ring size and the number of linked tetrahedral present in  are, respectively
are, respectively
(a) 6 and 6
(b) 12 and 6
(c) 12 and 12
(d) 6 and 12
Ans. b
Sol. The structure of  is
is

Hence, the number of linked tetrahedrals = 6
The size of ring = 12
Therefore, Correct option is (b)
35. The molecule C3O2 has a linear structure. This compound has
(a) 
(b) 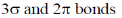
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. The structure of C3O2 (carbon suboxide) is

Correct option is (a)
36. The metallic radii are abnormally high for which of the following pairs?
(a) Eu, Yb
(b) Sm, Tm
(c) Gd, Lu
(d) Nd, Ho
Ans. a
Sol. The Eu and Yb donate two electrons in their metallic bonding unlike other lanthanoids which donate three electrons.
This is due to  stable configurations
stable configurations


Hence, they show abnormally larger sizes than other lanthanoids.
Eu 1.99Å, Yb = 1.94Å
Correct option is (a)
37. Identify two enantiomers among the following compounds

(a) A and B
(b) A and C
(c) B and D
(d) C and D
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
38. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 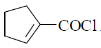
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
39. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
40. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
41. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Correct option is (a)
42. The major product A and B in the following reactions are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
43. D-Mannose upon refluxing in acetone with CuSO4 and H2SO4 gives

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 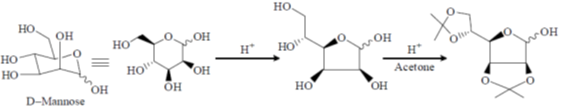
Correct option is (c)
44. The major product formed by photochemical reaction of (2E, 4Z, 6E) – decatriene is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
45. The correct statement about the following reaction is that

(a) 
and the reaction proceeds through carbene intermediate.
(b) 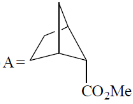 and the reaction proceeds through nitrene intermediate.
and the reaction proceeds through nitrene intermediate.
(c)  and the reaction proceeds through Norrish type II path.
and the reaction proceeds through Norrish type II path.
(d)  and the reaction proceeds through Norrish type I path.
and the reaction proceeds through Norrish type I path.
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
46. The structure of the compounds that matches the 1H NMR data given below is
1H NMR (DMSO – d6): 
7.75 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.70 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 6.50 (broad s, 2H), 3.80 (s, 3H).
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
47. Correctly matched structure and carbonyl stretching frequency set is
COLUMN – A COLUMN – B

(a) P – Y, Q – Z, R – X
(b) P – Y, Q – X, R – Z
(c) P – Z, Q – Y, R – X
(d) P – X, Q – Z, R – Y
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
48. The number of chemical shift non – equivalent protons expected in 1H NMR spectrum of  – pinene is
– pinene is

(a) 7
(b) 8
(c) 9
(d) 10
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
49. In the mass spectrum of 1, 2 – dichloroethane, approximate ratio of peaks at m/z values 98, 100, 102 will be
(a) 3 : 1 : 1
(b) 9 : 6 : 1
(c) 1 : 1 : 2
(d) 1 : 2 : 1
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
50. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
51. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 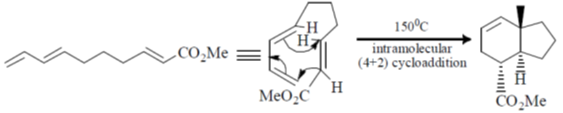
Correct option is (a)
52. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
53. The concentration of a reactant R varies with time for two different reactions as shown in the following plots:

The order of these two reactions I and II, respectively are
(a) zero and one
(b) one and zero
(c) zero and two
(d) two and zero
Ans. c
Sol. ct vs t straight line is observed for '0' order and 
vs t straight line is observed for second order.
Correct option is (c)
54. For a simple cubic crystal lattice, the angle between the [2 0 1], plane and the xy plane is
(a) less than 300
(b) between 300 and 450
(c) between 450 and 600
(d) greater than 600
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
55. 
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol.  Rate of formation of B – Rate of deformation of B
Rate of formation of B – Rate of deformation of B
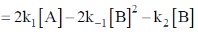
Correct option is (b)
56. If the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule is doubled without changing its force constant, the vibrational frequency of the molecule will be
(a) 
times the original frequency
(b)  times the vibrational frequency
times the vibrational frequency
(c) twice the original frequency
(d) unchanged
Ans. b
Sol. 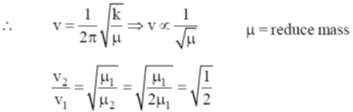
 times the original frequency.
times the original frequency.
Correct option is (b)
57. The standard deviation of speed  for Maxwell's distribution satisfies the relation
for Maxwell's distribution satisfies the relation
(a) 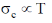
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
58. The value of  for the reaction
for the reaction 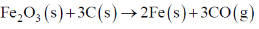 is
is
(a) –3RT
(b) +3RT
(c) +RT
(d) –RT
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
59. If the pressure p(system) is greater than the p(surroundings), then
(a) work is done on the system by the surroundings
(b) work is down on the surroundings by the systems
(c) work done on the system by the surroundings is equal to the work done on the surroundings by the system
(d) internal energy of the system increases
Ans. b
Sol. 
Process of expansion takes place. Work is done by the system on the surrounding.
Correct option is (b)
60. The different non – zero operators  satisfy the reaction
satisfy the reaction 
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
61. The degeneracy of an excited state of a particle in 3 – dimensional cubic box with energy 3 times its ground state energy is
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 4
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
62.  of a reaction is equal to slope of the plot of
of a reaction is equal to slope of the plot of
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. According to Gibbs – Helmholtz equation


At absolute zero, i.e. when T = 0,  of reaction is equal to the slope of the plot of
of reaction is equal to the slope of the plot of  T) versus 1 / T
T) versus 1 / T
Correct option is (d)
63. The correct form for a simple Langmuir isotherm is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
64. 
(a) depend only on stoichiometry
(b) depend only on specific identify of the electrolyte
(c) are independent of specific identify of the electrolyte
(d) are mainly dependent on specific identify of the electrolyte and stoichiometry, respectively
Ans. d
Sol.  Kohlrausch's constant is specified for uni – univalent electrolyte (stoichiometry) and strong electrolyte (specific identify).
Kohlrausch's constant is specified for uni – univalent electrolyte (stoichiometry) and strong electrolyte (specific identify).
Correct option is (d)
65. The correct expression for the product  are the number – average and weight average molar masses, respectively, of a polymer] is
are the number – average and weight average molar masses, respectively, of a polymer] is
(a) 
(b) 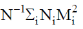
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
66. The concentration of a MgSO4 solution having the same ionic strength as that of a 0.1 M Na2SO4 solution is
(a) 0.05 M
(b) 0.067 M
(c) 0.075 M
(d) 0.133 M
Ans. c
Sol. 


Correct option is (c)
67. sp hybrid orbitals are of the form  (2s and 2pz are normalised individually). The coefficients of the normalized form of the above sp hybrid orbitals are
(2s and 2pz are normalised individually). The coefficients of the normalized form of the above sp hybrid orbitals are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
68. The correct statement among the following is
(a) N2 has higher bond order than N2+ and hence has larger bond length compared to N2+.
(b) N2+ has higher bond order than N2 and hence has larger bond length compared to N2.
(c) N2 has higher bond order than N2+ and hence has higher dissociation energy compared to N2+.
(d) N2 has lower bond order than N2+ and hence has lower dissociation energy compared to N2+ energy.
Ans. c
Sol. The Mo configuration of N2 and N2+ are



Correct option is (c)
69. The formation constant for the complexation of M+ (M = Li, Na, K and Cs) with cryptand, C222 follows the order
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. The stability (formation constant for complexation of cryptate complex depends upon)
(1) size of cavity
(2) size of metal cation

Hence, k+ ion will form most stable complex with cryptand - 222.
Correct option is (a)
70. The correct match for the compounds in column A with the description in column B is

(a) P – Y, Q – Z, R – X
(b) P – Z, Q – X, R – Y
(c) P – Z, Q – Y, R – X
(d) P – X, Q – Z, R – Y
Ans. b
Sol. 
(b) P – Z, Q – X, R – Y
Correct option is (b)
71. The resonance Raman stretching frequency  of O2 is 1580. The
of O2 is 1580. The 
for O2 in bound oxy – hemoglobin is close to
(a) 1600
(b) 1900
(c) 800
(d) 1100
Ans. d
Sol. In oxyhaemoglobin Fe is in +3 oxidation state and O2 is in in O2–

As oxygen accept electron in  orbital. Hence, bond get reduced and frequency decreases. Since, after binding to Fe in Hb bond between O–O become weaker comparison to free O–O bond in O2.
orbital. Hence, bond get reduced and frequency decreases. Since, after binding to Fe in Hb bond between O–O become weaker comparison to free O–O bond in O2.
Therefore, Force constant k decreases and 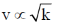
Stretching frequency would decrease
1100cm–1 is
Correct option is (d)
72. 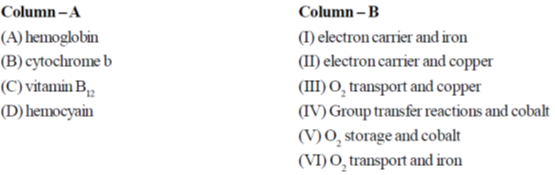
The correct match is
(a) A – VI, B – I, C – IV and D – III
(b) A – V, B – I, C – IV and D – III
(c) A – VI, B – V, C – I and D – II
(d) A – V, B – VI, C – II and D – IV
Ans. a
Sol. Hb  it functions as O2 transfer and contain Fe as active centre.
it functions as O2 transfer and contain Fe as active centre.
Cytochrome. b  it functions as electron transfer and contain Fe
it functions as electron transfer and contain Fe
Vitamin B12 it is responsible for group transfer reaction and contain cobalt.
it is responsible for group transfer reaction and contain cobalt.
Haemocyanin  it is a non – haem, non – iron, copper containing protein and functions as O2 transport system.
it is a non – haem, non – iron, copper containing protein and functions as O2 transport system.
Correct option is (a)
73. Pick the correct statements about Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS) from the following
(A) Hg lamp is not a suitable source for AAS
(B) Graphite furnace is the best atomizer for AAS
(C) Non – metals cannot be determined with AAS
(D) AAS is better than ICP – AES for simultaneous determination of metal ions.
Correct answer is
(a) A, B and C
(b) B, C and D
(c) C, D and A
(d) D, A and B
Ans. a
Sol. Inductively coupled plasma atomic spectroscopy (ICP – AES) is an analytic technique used for detection for trace metals and it is better than AAS for simultaneous determination of metal ions. Hence, option (d) is correct.
In Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy mercury lamp is not suitable cource but hollow cathode lamp (HCl) are the most common radiation source in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and atomizers most commonly used are flame and electro thermal (graphite). Solid sample is used in determination.
Correct option is (a)
74. Identify radioactive capture from the following nuclear reactions.
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 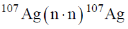
Ans. b
Sol. The reaction which involve evolution of  radiation are called radioactive capture reaction.
radiation are called radioactive capture reaction.

Correct option is (b)
75. The calibration curve in spectrofluorimetric analysis becomes non–linear when
(a) molecular weight of analyte is high
(b) intensity of light source is high
(c) concentration of analyte is high
(d) molar absorptivity of analyte is high
Ans. c
Sol. Fluorescence intensity is typically directly proportional (.inear) to concentration. There are however factor that affect tis linear relationship. When concentration is too high, light can not pass through the sample to cause excitation, thus very high concentration can have very low Fluorescence and thus calibration curves become non – linear.
Correct option is (c)
76. 
is deep purple in color whereas  is colorless. This is due to greater energy required for
is colorless. This is due to greater energy required for
(a) d–d transitions in the Re compound compared to the Mn compound
(b) d–d transitions in the Mn compound compared to the Re compound
(c) change transfer from O to Re compared to O to Mn
(d) charge transfer from O to Mn compared to O to Re
Ans. c
Sol. 
E2 > E1 hence, energy required for transfer of electron from oxygen to Re falls in UV region. Hence, 
colourless while in  due to less energy difference it falls in visible region. Hence,
due to less energy difference it falls in visible region. Hence,  coloured. Also as both Mn and Fe have +7 oxidation state i.e. they have no d – electron hence. no d – d transition and colour arises due to LMCT.
coloured. Also as both Mn and Fe have +7 oxidation state i.e. they have no d – electron hence. no d – d transition and colour arises due to LMCT.
Correct option is (c)
77. 
shows fluxional behavior. The 1H NMR spectrum of this compound when it is in the non – fluxional state shows
(a) one signal
(b) two signals in the intensity ratio of 4 : 1
(c) three signals in the intensity ratio of 2 : 2 : 1
(d) five signals of equal intensity.
Ans. c
Sol. 
Hc = central proton
Ha = is anti with respect to Hc
Hs = syn with respect to Hc
Ha, Hs, He environment are different new intensity ratio 2 : 2 : 1. When allyl is non – fluxional.
Correct option is (c)
78. The number of lone pair(s) of electrons on the central atom in  are respectively
are respectively
(a) 2, 0 and 1
(b) 1, 0 and 0
(c) 2, 1 and 1
(d) 2, 1 and 0
Ans. c
Sol. 
Hence, correct option is (c)
Note: The lone pair of 
is stereochemically inactive and the of XeF6 is boderline of stereochmically active and stereochmically inactive condition.
Correct option is (c)
79. Consider the following reaction:

The number of possible isomers for [A] is
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 5
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
80. Using Wade's rules predict the structure type of 
(a) nido
(b) closos
(c) arachno
(d) hypho
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
81. Among the following complexes



(a) A and B
(b) C and B
(c) C only
(d) A and C
Ans. d
Sol. 

Thus, A and C are chiral and B is achiral. Hence, correct option is (d)
82. Mössbauer spectrum of a metal complex gives information about
(A) oxidation state and spin state of metal
(B) types of ligands coordinated to metal
(C) nuclear spin state of metal
(D) geometry of metal
Correct answer is
(a) A and C
(b) B and C
(c) A, B and D
(d) B and D
Ans. c
Sol. Mössbauer spectrum of a complex gives information about
(1) oxidation state and spin state of metal
(2) types of ligands co – ordinate to metal define by quardurpole splitting on the behalf of electronic environment of ligand symmetry.
(3) Also information about geometry of metal
Correct option is (c)
83. For uranocene, the correct statement(s) is/are
(A) oxidation state of uranium is '+4'
(B) it has cyclooctatetraenide ligands
(C) it is bent sandwich compound
(D) it has '–2' charge
Correct answer is
(a) A and B
(b) B and C
(c) A and D
(d) B only
Ans. a
Sol. Structure of Uranocane

Hence, oxidation state of U = +4
Thus in uranocene U is in +4 oxidation state and have cyclooctatetraenide ligand.
Correct option is (a)
84. The final products of the reaction of carbonyl metalates  with
with  respectively, are
respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
85. The correct statement about the substitution reaction of  to give
to give  is,
is,
(a) it obeys first order kinetics
(b) its rate is proportional to the concentration of both the reactants
(c) it follows the Sn1CB mechanism
(d) its rate is dependent only on the concentration of 
Ans. a
Sol. 
The reaction proceed through dissociative pathway and rate is dependent only concentration of substrates. As substate do not have acidic hydrogen. Hence, it does not undergo SN1CB mechanism.

Correct option is (a)
86. Aqueous  effects one electron reduction of
effects one electron reduction of  giving compound Y. Compound Y undergoes rapid hydrolysis. Y is,
giving compound Y. Compound Y undergoes rapid hydrolysis. Y is,
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
87. The reaction of BCl3 with NH4Cl gives product A which upon reduction by NaBH4 gives product B. Product B upon reacting with HCl affords compound C, which is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
88. The number of valence electrons provided by  fragment towards cluster bonding is
fragment towards cluster bonding is
(a) 1
(b) 14
(c) 6
(d) 2
Ans. d
Sol. Number of electron involving in metal cluster = T.V.E – 12
T.V.E in Ru(CO)3 = 8 + 6 = 14 (T.V.E = total valence electron)
Hence, number of electron provided for cluster bonding = 14 – 12 = 2
Correct option is (d)
89. Choose the correct statements about Tanabe – Sugano diagrams
(A) E/B is plotted against 
(B) The zero energy is taken as that of the lowest term
(C) Terms of the same symmetry cross each other
(D) Two terms of the same symmetry upon increases of ligand field strength bend apart from each other.
Correct answer is
(a) A and B
(b) A and C
(c) A, B and D
(d) A, B, C and D
Ans. c
Sol. Tanabe – Sugano are useful in interpretation of spectra of both high spin and low spin complexes of d2 – d8 metal cation.
In Tanabe – Sungano, the energy of excited sate (expressed as E/B) are plotted against ligand field strength (expressed as 
Zero energy is taken for the lowest term and also two form of same symmetry never cross each other and they bent for apart from each other due to repulsion.

Correct option is (c)
90. Which of the following statements are TRUE for the lanthanides?
(A) the observed magnetic moment of Eu3+ at room temperature is higher than that calculated from spin – orbit coupling
(B) Lanthanide oxides are predominantly acidic in nature.
(C) The stability of Sm(II) is due to its half – filled sub – shell.
(D) Lanthanide (III) ions can be separated by ion exchange chromatography
Correct answer is
(a) A and D
(b) A and B
(c) A and C
(d) (d) B and C
Ans. a
Sol. (a) There is no good agreement between the calculated  and experimental magnetic moments for Eu3+ and Sm3+ ions because of law value (~300 cm–1) of spin orbit coupling constant. Therefore, the ground state and the first excited states become equality populated, due to the thermal motion become equally populated due to thermal motion. Hence, the observed magnetic moment of Eu3+ at room temperature is higher than that calculated from, spin – orbit coupling.
and experimental magnetic moments for Eu3+ and Sm3+ ions because of law value (~300 cm–1) of spin orbit coupling constant. Therefore, the ground state and the first excited states become equality populated, due to the thermal motion become equally populated due to thermal motion. Hence, the observed magnetic moment of Eu3+ at room temperature is higher than that calculated from, spin – orbit coupling.
(b) Lanthanide oxides are predominantly basic in nature.
(c) The Sm(II) ion has 4f6 configuration. Thus, in Sm(II) 4f subshell is not half filled.
(d) Since the chemical properties of the tripositive lanthanide ions (due to their similar size) they can not be separated easily by chemical method. Instead they can be separated by ion exchange chromatography.
Correct option is (a)
91. The intermediate and the final major product of photolysis of Z.

From the following:

are
(a) A and D
(b) B and D
(c) B and C
(d) A and C
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
92. Reaction of  with results in A without loss of CO. Compound A, on heating to 1200C loses a CO ligand to give B, which does not have a Mn–Mn bond. Compound B reacts with pyridine to give 2 equivalents of C. Compounds A, B and C from the following respectively, are
with results in A without loss of CO. Compound A, on heating to 1200C loses a CO ligand to give B, which does not have a Mn–Mn bond. Compound B reacts with pyridine to give 2 equivalents of C. Compounds A, B and C from the following respectively, are



(a) II, V and IV
(b) II, III and IV
(c) V, III and IV
(d) II, V and III
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
93. The approximate positions of vCO bands (cm–1) in the solid – state infrared spectrum and the Fe–Fe bond order in 
(non – centrosymmetric) respectively, are
(a) (2020, 1980, 1800) and one
(b) (2020, 1980 1800) and two
(c) (2020, 1980) and one
(d) (2143) and one
Ans. a
Sol. 
In this complex M – M bond order = 1 and two types of CO's terminal as well as m2 – bridging. So, vC–O band lies in both range
Correct option is (a)
94. Protonated from of ZSM – 5 catalyzes the reaction of ethene with benzene to produce ethylbenzene. The correct statement for this catalytic process is
(a) alkyl carbocation is formed
(b) carbanion is formed
(c) benzene is converted (C6H5)+ group
(d) vinyl radical is formed
Ans. a
Sol. Correct option is (a)
95. Three electronic transitions at 14900, 22700 and 34400 cm–1 are observed in the absorption spectrum of 
value (in cm–1) and the corresponding transition are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 


Since,  have no fix energy therefore, they will not provide accurate value of
have no fix energy therefore, they will not provide accurate value of 
Thus, energy difference between  will be correspond to
will be correspond to 
96. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
97. The following transformation involves sequential

(a) Claisen rearrangement – Cope rearrangement – ene reaction
(b) Cope rearrangement – Claisen rearrangement – ene reaction
(c) Cope rearrangement – ene reaction – Claisen rearrangement
(d) ene reaction – Claisen rearrangement – Cope rearrangement
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
98. The major product formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
99. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
100. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. Correct option is (d)
101. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequences are

(a) A = D – threose ; B = D – glucose
(b) A = D – etythrose; B = D – glucose + D – mannose
(c) A = D – threose; B = D – glucose + D – mannose
(d) A = D – tartaric acid; B = D – glucose
Ans. b
Sol. 


Correct option is (b)
102. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Now, stablized phosphorous ylide forms Z-alkene from aldehyde.

Correct option is (d)
103. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are
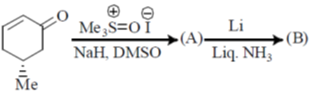
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 


Correct option is (a)
104. The major products A and B in the following reactions sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
105. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
106. The major product formed in the following reaction in
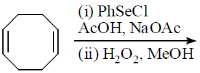
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
107. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 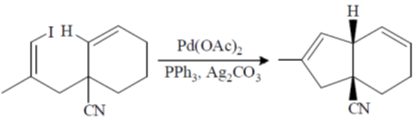
Intramolecular Heck – coupling reaction.
Correct option is (b)
108. 
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
109. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
110. The correct reagent combination to effect the following transformation is

(a) A = NaBH4, BF.OEt2; B = MeMgBr (2.5 equiv.), THF then H3O+
(b) A = BH3. THF; B = MeLi (2.5 equiv.), THF then H3O+
(c) A = BH3. THF; B = (i) aq. NaOH then H3O+, (ii) MeLi (2.5 equiv,), THF then H3O+
(d) A = (i) Me3Al, MeNHOMe, (ii) MeMgBr, THF then H3O+; B = LiAlH4, THF
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
111. The mechanism and the product formed in the following reaction, respectively, are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
112. A Concerted [1, 3]– sigmatropic rearrangement took place in the reaction shown below. The structure of the resulting product is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. A concerted [1, 3] sigmatropic shift.

[1, 3]- allyl shift under thermally condition occurs antrafacially and hence stereochemistry changes (inversion in configuration occurs)
Hence, stereochemistry of (D) and (OAc) will become same / cis.
Correct option is (c)
113. The major product A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
114. The major product formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
115. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
116. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 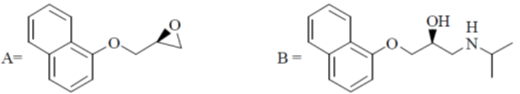
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
117. The major product of the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
118. The major product A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
119. The major products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
120. The major product of the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
121. According to the transition state theory, one of the vibrations in the activated complex is a loose vibration. The partition function for this loose vibration is equal to (kB is the Boltzmann's constant and h is the Planck's constant)
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
122. Possible term symbol(s) of the excited states of Na atom with the electronic configuration  is / are
is / are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
123. For a simple cubic crystal, X–ray diffraction shows intense reflections for angles  which are assigned to [1 0 1] and [1 1 1] planes, respectively. The ratio
which are assigned to [1 0 1] and [1 1 1] planes, respectively. The ratio  is
is
(a) 1.5
(b) 1.22
(c) 0.82
(d) 0.67
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
124. Stability of lyophobic dispersions is determined by
(a) inter – particle electric double layer repulsion and intra – particle van der walls attraction.
(b) inter – particle electric double layer attraction and intra – particle van der waals repulsion.
(c) inter – particle excluded volume repulsion and intra – particle van der waals attraction.
(d) inter – particle excluded volume attraction and intra – particle van der waals repulsion.
Ans. a
Sol. Stability of lyophobic dispersions is determined by inter – particle electric double layer repulsion and intra – particle van der waals attraction.
Correct option is (a)
125. A certain 2 – level system has stationary state energies E1 and E2 (E1 < E2) with normalized wave function  respectively. In the presence of a perturbation V, the second – order correction to the energy for the first state
respectively. In the presence of a perturbation V, the second – order correction to the energy for the first state  will be
will be
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. The second order correction to nth state


Correct option is (c)
126. The 1H NMR frequency at 1.0 T is 42.4 MHz. If the gyromagnetic ratios of 1H and 13C are 27 × 107 and 6.75 × 107 T–1S–1, respectively, what will be the 13C frequency at 1.0 T?
(a) 10.6 MHz
(b) 169.9 MHz
(c) 42.6 MHz
(d) 21.3 MHz
Ans. a
Sol. 
Equation (i) divided by equation (ii),

Correct option is (a)
127. 10 mL aliquots of a mixture of HCl HNO3 are titrated are titrated conductometrically using a 0.1M NaOH and 0.1M AgNO3 separately. The titre volumes are V1 and V2 mL, respectively. The concentration of HNO3 in the mixture is obtained from the combination.
(a) V1 – V2
(b) 2V1 – V2
(c) V2 – V1
(d) 2V2 – V1
Ans. a
Sol. First titration:
10 mL of HCl + HNO3 with NaOH
Reaction,

Suppose in 10 ml aliquots n1 mole of HCl are present, and n2 moles of HNO3 are present. (Number of moles of HCl = number of moles of NaOH + no. of moles of HNO3)
n2 + n1 = 0.1 V1
Second titration:

Number of moles of HCl = number of moles of AgNO3
n1 = 0.1V2
Number of moles of HNO3 only 
So, (V1 – V2) will give number of moles of HNO3. So, from it well get conc. 
Correct option is (a)
128. Given that  at 250C, E0 corresponding to the electrode reaction
at 250C, E0 corresponding to the electrode reaction
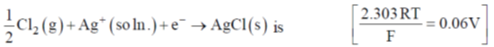
(a) 0.75V
(b) 1.05V
(c) 1.65V
(d) 1.95V
Ans. d
Sol. Reaction – 1:

Reaction – 2:

Reaction – 3: On reversing reaction – 2

On adding reaction (1) and reaction (3), we get

Correct option is (d)
129. The standard EMF of the cell 
(a) increases with T
(b) decreases with T
(c) remains unchanged with T
(d) decreases with [HCl]
Ans. b
Sol. 
As entropy of reaction decreases because gaseous is being consumed. So, 
 decreases with increase in temperature.
decreases with increase in temperature.
Correct option is (b)
130. The molecule with the smallest rotational constant (in the microwave spectrum) among the following is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
I for ClC = CF is highest
Therefore, B would be smallest for CIC = CF
Correct option is (c)
131. The spectrosopic technique that can distinghuish unambiguously between trans – 1, 2 – dichloroethylene and cis – 1, 2 – dichloroetylene without any numerical calculation is
(a) microwave spectroscopy
(b) UV – visible spectroscopy
(c) X – ray photoelectron spectroscopy
(d)  – ray spectroscopy
– ray spectroscopy
Ans. a
Sol. 
These two compound are distinguish on the behalf of dipolemoment by microwave spectroscopy without any calculation.
Correct option is (a)
132. The ground state electronic configuration of C2 using all electron is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. C2 = valence electron = 12


Correct option is (d)
133. 
for an enzyme catalyzed reaction are  respectively. The rate of the reaction when the substrate concentration is 1.0 × 10–6 M is
respectively. The rate of the reaction when the substrate concentration is 1.0 × 10–6 M is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
134. The first order rate constant for a unimoleclar gas phase reaction A  products that follows Lindemann mechanism is 2.0 s–1 at pA = 1 atm and 4.0 s–1 at pA = 2 atm. The rate constant for the activation step is
products that follows Lindemann mechanism is 2.0 s–1 at pA = 1 atm and 4.0 s–1 at pA = 2 atm. The rate constant for the activation step is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
135. The molecule diborane belongs to the symmetry point group
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
136. Though a constant shift of energy levels of a system changes the partition function, the properties that do not change are
(a) average energy, entropy and heat capacity
(b) average energy and entropy
(c) average energy and heat capacity
(d) entropy and heat capacity.
Ans. d
Sol. Entropy and heat capacity
Since, entropy change in partition function is compensated by change in total energy and in heat capacity differentiation with respect to temperature lead to cancellation of constant shift in energy.
Correct option is (d)
137. The vibrational frequency of a homo – nuclear diatomic molecule is v. The temperature at which the population of the first excited state will be half that of the ground state is given by
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
138. The irreducible representations of  The Raman active modes of trans–1, 3 – butadiene belong to the irreducible representations
The Raman active modes of trans–1, 3 – butadiene belong to the irreducible representations
(a) Ag and Bg
(b) Ag and Au
(c) Au and Bg
(d) Bg and Bu
Ans. a
Sol. Raman active vibrations transform according to quadractic functions of x, y and z which are Ag and Bg.
Correct option is (a)
139. The symmetry – allowed atomic transition among the following is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Since, for allowed transition (atomic), 
Correct option is (b)
140. The average end – to – end distance of a random coil polymer 106 monomers (in units of segment length) is
(a) 106
(b) 105
(c) 104
(d) 103
Ans. d
Sol. Average end – to – end distance 
Correct option is (d)
141. The reversible expansion of 1.0 mol of an ideal gas is carried out from 1.0 L to 4.0 L under isothermal condition at 300K.  for this process is
for this process is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
142. A temperature – dependence of the vapour pressure of solid A can be represented by log  and that of liquid A by log
and that of liquid A by log  The temperature of the triple point of A is
The temperature of the triple point of A is
(a) 200 K
(b) 300 K
(c) 400 K
(d) 500 K
Ans. a
Sol. At triple point vapour pressure of solid A and liquid A are same. So,

Correct option is (a)
143. The non – spontaneous process among the following is
(a) vapourisation of superhead water at 1050C and 1 atm pressure
(b) expansion of a gas into vacuum freezing
(c) freezing of supercooled water at –100C and 1 atm pressure
(d) freezing of water at 00C and 1 atm pressure.
Ans. d
Sol. Option (a), (b) and (c) talks about the processes which are spontaneous processes.
Option (a) and (c) can be seen through phase diagram of water and (b) is free expansion which is spontaneous.
Option (d) talks about an equilibrium process.

So, this is a non - spontaneous process.
Correct option is (d)
144. The radial part of a hydrogenic wave function is given as  This function is then indentifiable as
This function is then indentifiable as
(a) 2s
(b) 3p
(c) 4d
(d) 5f
Ans. b
Sol. In radial part of wave function highest power of r denote the value of 
Here  and radial node
and radial node 
Correct option is (b)
145. A normalised state  is constructed as a linear combination of the ground state
is constructed as a linear combination of the ground state 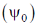 and the first excited state
and the first excited state  of some harmonic oscillator with energies 1/2 and 3/2 units, respectively. If the average energy of the state
of some harmonic oscillator with energies 1/2 and 3/2 units, respectively. If the average energy of the state  is 7/6, the probability of finding
is 7/6, the probability of finding  will be
will be
(a) 1/2
(b) 1/3
(c) 1/4
(d) 1/5
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
