CSIR NET CHEMISTRY (DEC-2014)
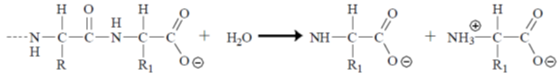
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
21. The reaction between SbF5 and two equivalents of HF leads to the formation of
(a) H2SBF3 + 2F2
(b) H SbF2 + 3F2
(c) SbF3 + H2 + 2F2
(d) [SbF6]–[H2F]+
Ans. d
Sol. HF exist as H2F2 and it act as fluoride donar if strong fluoride acceptor is present like SbF3, AsF5.
Therefore, the reaction will be
HF 2 moles = H2F2.

SbF5 act as Lewis acids as it has vacant 'd' orbital of suitable energy.
Correct answer is (d)
22. The  is formed via the overlap of
is formed via the overlap of
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. A  – bond involves the overlapping of eight lobes by facewise overlapping. This can take place by 'd' – orbitals and 'f' orbitals.
– bond involves the overlapping of eight lobes by facewise overlapping. This can take place by 'd' – orbitals and 'f' orbitals.
In 'd' orbitals following two possibilities are



Both cases are reported in many examples like.
Case – I is reported in dimeric copper acetate (II)
Case – II is reported in 

Hence, options (c) is correct.
23. Among  ions, those having the highest and the lowest ionic radii respectively are
ions, those having the highest and the lowest ionic radii respectively are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. All the ions are isoelectronic. Therefore, the size depends upon effective nuclear charge.
Size of isoelectronic ions 

Since, atomic number increases.
Therefore, Zeff increases and size decreases
Correct answer is (c)
24. The extent of  conjugation in macrocylic rings of (1) heme, (2) coenzyme B12 and (3) chlorophyll follows the order
conjugation in macrocylic rings of (1) heme, (2) coenzyme B12 and (3) chlorophyll follows the order
(a) (1) > (3) > (2)
(b) (1) > (2) >3
(c) (3) > (1) > (2)
(d) (2) (1) > (3)
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
25. The correct order of the retention of cations on a sulfonated cation exchange resin column is
(a) A+ > K+ Na+ > Li+
(b) K+ > Na+ Ag+ > Li+
(c) Li+ > Na+ K+ > Ag+
(d) Li+ > Na+ Ag+ > K+
Ans. a
Sol. The retention of ion in exchanges column depends upon the size of ion. Smaller the size of cation, stronger will be its binding ability. In cation exchanger column the aqueous solution of ion is passed where binding ability depends upon hydrated radii.

Ag+(aq) show polarization effect, hence, has high binding ability.
Correct option is (a)
26. In a polarographic measurement, (aqueous KCl solution used as supporting electrolyte) an applied potential more than +0.4 V, results mainlyin the formation of
(a) HgI
(b) HgII
(c) CI2
(d) O2
Ans. a
Sol. Mercury can be easily oxidised to Hg(I) above + 0.4 versus SCE (Standard Chemical Potential). This property restricts the use of Mercury as anode. This is the limitation of DME (Droping Mercury Electrode). DME can be applied over the range + 2.4 to – 3.0 V with reference to SCE.Above +0.4V mercury dissolves, gives an anode wave and begins to oxidise to mercurous ion.
Correct answer is (a)
27. The correct order of the isomeric shift in Mössbauer spectra (57Fe source) of iron compounds is
(a) Fe(II) > Fe(III) > Fe(IV)
(b) Fe(III) > Fe(II) > Fe(IV)
(c) Fe(IV) > Fe(III) > Fe(II)
(d) Fe(IV) > Fe(II) > Fe(III)
Ans. a
Sol. 
Isomer shift in Mössbauer spectra depend on the s – electron density and d – electron density increase the s – electron density decrease the isomer shift increase the d – electron density increase the isomer shift.
So, so correct order, Fe (II) > Fe (III) > Fe (IV).
Correct answer is (a)
28. The hapticities 'x' and 'y' of the arene moieties in the diamagnetic complex  respectively are
respectively are
(a) 6 and 6
(b) 4 and 4
(c) 4 and 6
(d) 6 and 2
Ans. c
Sol. 
Total electron = 4 + 8 + 6 = 18 electron. (Diamagnetic complex)
Example 
Correct answer is (c)
29. The rare of the reaction  depends on
depends on
(a) Concentration of both the reactants
(b) Concentration of Ni(CO)4 only
(c) Concentration of PPP3 only
(d) The steric bulk of PPh3
Ans. b
Sol. 
Since Ni(CO)4 follows 18 electron rule. So, it follow substitution via dissociation mechanism i.e.
So, the rate of reaction depends upon the concentration of Ni(CO)4 only because this stepis slowest step.
Correct answer is (b)
30. The product of the reaction of propene CO and H2 in the presence of CO2(CO)8 as a atalyst is
(a) Butanoic acid
(b) Butanal
(c) 2 – butanone
(d) Methylpropanoate
Ans. b
Sol. 
Hydroformylation.
Correct answer is (b)
31. The S and L values for 15N atom respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 1 and 0
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
32. The point group symmetries for trans–[Cr(en)2F2]+ and [TiCl6]3–, respectively, are
(a) D4d and D3d
(b) D3d and D4d
(c) D4h and D3h
(d) D3h and D4h
Ans. a
Sol. Correct answer is (a)
33. Co4(CO)12 adopts the
(a) closo–structure
(b) nido–structure
(c) arachno–structure
(d) hypho–structure
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct answer is (b)
34. Reductive elimination step in hydrogeneration of alkenes by Wilkinson catalyst results in (neglecting solvent in coordination sphere of Rh)
(a) T – shaped [Rh(PPh3)2Cl]
(b) Trigonal – planer [Rh(PPh3)2Cl]2+
(c) T – shaped [Rh(H)(PPh3)Cl]+
(d) Trigonal – planer [Rh(H)(PPh3)2]
Ans. a
Sol.  Cl is a Wilkinson catalysts in hydrogenation step one PPh3 loss due to steric factor and form
Cl is a Wilkinson catalysts in hydrogenation step one PPh3 loss due to steric factor and form 

Correct answer is (a)
35. In the following reaction  compound B is
compound B is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
36. The number of histidine amino acid nitrogen atoms coordinated to bimetallic active site of oxhyemocyanin and oxyhemerythrin, respectively, are
(a) 2, 3 and 3, 3
(b) 3, 3 and 2, 3
(c) 3, 3 and 2, 2
(d) 2, 4 and 3, 2
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
37. Identify correct statements for mercury as an environment pollutant.
A. Carbanionic biomethylation converts it to MeHg+.
B. Thiol group of cysteine has strong affinity for mercury.
C. Mercury containing industrial catalyst release caused Minamata disaster.
The correct answer is
(a) A and B
(b) A and C
(c) B and C
(d) A, B and C
Ans. d
Sol. In 1956, in Japan minamata disaster had been broken out in coastal area. This is a neurological syndrome caused by mercury pollution. The Hg++ get converted into MeHg+ by carbonic blomethylation. Which form strong bonding with thiol (–SH) group of protein having cysteine amino acid. Hence, A, B and C are correct.
Correct answer is (d)
38. The configurations of carbon atoms C3 and C4 in D – ribose, respectively, are
(a) R and S
(b) S and R
(c) R and R
(d) S and S
Ans. c
Sol. 
Both 3rd and 4th carbon have same configuration which is R
Correct answer is (c)
39. The compound that is antiaromatic is

(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Ans. c
Sol. For antiaromaticity, there are  and there must be delocalization. Since boron is electron deficient, it has vaccant p – orbital and thus electron can be decoalized.
and there must be delocalization. Since boron is electron deficient, it has vaccant p – orbital and thus electron can be decoalized.
In the given compound I species has 
Thus it is antiaromatic.

Correct answer is (c)
40. The increasing order of pKa values of the circled hydrogens in the following compounds is

(a) I < II < III
(b) I < III < II
(c) II < I < III
(d) II < III < I
Ans. c
Sol. 
Thus, the hydrogen which will be more acidic, will have lower pKa.

It is clear from above that III will generate as unstable anion which is vinyl anion. Thus it will less acidic and thus having highest pKa value among three.
Now, between I and II, II will have lower pKa value because the conjugate base obtained after removal of hydrogen from II will be more stabilized.

Thus the order will be III > I > II.
Correct answer is (c)
41. The decreasing order of basicity of the following compounds is

(a) I > II > III > IV
(b) IV > I > II > III
(c) III > II > I > IV
(d) IV > III > II > I
Ans. c
Sol. 
sp3 hydridized N is less electronegative than sp2 hybridized nitrogen. That is why sp3 hydridized. Nitrogen will be moe basic as compare to sp2 hydrized nitrogen.
Hence, II and III will be more basic as compared to I and IV.
Since III contains 3 nitrogen, it will be more basic as compared to II.
Imidazale is more basic than pyridine. This is because protonation of N of imidazole that does not takes part in resonance does not break up the aromatic ring. Thus, its confugated acid will be more stable as compared to corresponding conjugate acid of pyridine, which eliminates the aromaticity in pyridine.
Correct answer is (c)
42. In the most stable conformation of neomenthol, stereochemical orientation of the three substituents on the cyclohexane ring are
(a) OH : equatorial ; i – Pr : equatorial and Me : equatorial
(b) OH : axial ; i – Pr : equatorial and Me : equatorial
(c) OH : equatorial; i – Pr : equatorial and Me : axial
(d) OH : equatorial; i – Pr : axial and Me : equatorial
Ans. b
Sol. The most stable conformation of neomenthal is

which can be also written as

thus, option (b) is correct.
43. The absolute configurations of the chiral centres of starting ketone in the following reaction is

(a) 3R, 6S
(b) 3S, 6S
(c) 3R 6R
(d) 3S, 6R
Ans. a
Sol. 
According to Cram's rule formation of S alcohol at 2 indicated 3rd will have R configuration.
Thus, option (a) is correct.
44. The reaction of 1 – bromo – 2 – fluorobenzene with furan in the presence of one equivalent of Mg gives.
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 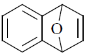
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 


Correct answer is (c)
45. The product for the following sequence of reactions is

(a) 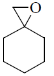
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
46. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct answer is (c)
47. The major producer of the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. This is known as Birch reduction. When electron withdrawing group substituted aromatic ring are subjected to Birch reduction, they are found mainly on the reduced position of product. Birch reduction reduces alkyne to trans alkene. Thus.

Correct answer is (a)
48. The major product of the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. Electrophilic aromatic substitutionis benzothiophene will occur preferably at 3 – position. But in excess of reagent substitution also takes place at 2 – position


Correct answer is (c)
49. The cyclic product (s) of the following photochemical reaction is(are)

(a) only cis – 1, 2 – dimethylcylopentane
(b) only trans –, 2 – dimethylcylopentane
(c) a mixture of cis – and trans – 1, 2 – dimethylcylopentane
(d) only 2, 6 – dimethylcylopentane
Ans. c
Sol. 
It will produce a mixture of product, because during the reaction caurse C–C  bond rotation can takes place
bond rotation can takes place

Correct answer is (c)
50. A compound with molecular formula C4H6O2 shows band at 1770 cm–1 in IR spectrum and peacks at 178, 68, 28 and 22 ppm in 13C NMR spectrum. The correct structure of the compound is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. M. F. = C4H6O2
IR = 1770 cm–1
 value for 13C NMR = 178, 68, 28, 22 ppm. From 13C
value for 13C NMR = 178, 68, 28, 22 ppm. From 13C 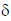 value it is clear that there are 4 types of carbon IR value indicates towards ester functional group
value it is clear that there are 4 types of carbon IR value indicates towards ester functional group  value at 28 and 22 shows that in the structure two carbon are nearly at similar environment.
value at 28 and 22 shows that in the structure two carbon are nearly at similar environment.
 value at 178 ppm indicates
value at 178 ppm indicates  carbon and 68 ppm indicates C–O carbon.
carbon and 68 ppm indicates C–O carbon.
All this observation will be well explained and satisfied by

Correct answer is (c)
51. The mass of metastable ion produced due to decomposition of F1+ in the following mass fragmentation sequence is
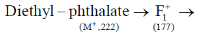
(a) 141.2
(b) 125.4
(c) 45.0
(d) 210.2
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
52. The ratio of the relative intensities of the carbon signals in the first order 13C NMR spectrum of CD3Cl is
(a) 1:4:6:4:1
(b) 1:3:3:1
(c) 1:6:15:20:15:6:1
(d) 1:3:6:7:6:3:1
Ans. d
Sol. 13C NMR
D (I = 1)
Number of time (2NI + 1) = 2 × 3 × 1 + 1 = 7 line (non pascal)
1 : 3 : 6 : 7 : 6 : 3 : 1
Correct answer is (d)
53. The biosynthetic precursor of abietic acid is
(a) Shikimic acid
(b) Mevalonic acid
(c) Chorismic acid
(d) Cinnamic acid
Ans. b
Sol. Abetic acid is a resin acid having molecular formula C20H30O2.

Its bisynthetic raute is given as follows
Mevalonic acid  geranyl – geranyl pyro phosphate
geranyl – geranyl pyro phosphate  abietic acid.
abietic acid.
Correct option is (b)
54. The amino acid constituents of artificial sweetener given below are

(a) D – Glutamic acid and L – phenylglycine
(b) L – Glutamic acid and L – phenylalanine
(c) L – Aspartic acid and L – phenylalanine
(d) L – Aspartic acid and L – tyrosine
Ans. c
Sol. This artificial sweetner is aspartame

Its IUPAC name is L–a asparty L–phenyl alanine.
Thus aspartame is a methyl ester of the dipeptide of the natural amino acid. L – aspartic acid and L – phenyl alanine.
Correct answer is (c)
55. Bond lengths of homonuclear diatomic molecules can be determined with the help of both
(a) Rotational and vibrational spectroscopy.
(b) Rotational and rotational Raman spectroscopy.
(c) Rotational Raman and electronic spectroscopy.
(d) Vibrational and electronic spectroscopy.
Ans. c
Sol. Homonuclear diatomic molecules does not have any permanent dipole moment. So, it will not show rotational spectra.
On the other hand, vibration does not make any changes in the permanent dipole moment of the homonuclear diatomic molecule. so, it will not show vibrational spectra. But the homonuclear diatomic molecules shows rotational Raman and electronic spectra and with the help of both, we can calculate the bond length.
Correct option is (c)
56. If the component of the orbital angular momentum along the molecular axis of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule is non – zero, the rotational – vibrational spectrum will show.
(a) P and R branches only
(b) P and Q branches only
(c) Q and R branches only
(d) All the P, Q and R branches
Ans. d
Sol. For a heteronuclear diatomic molecule having non – zero component of orbit angular momentum along the molecular axis, the energy levels of the vibrational rotational spectra will be

Consdering the transition from v = 0  v = 1
v = 1

Correct option is (d)
57. For a particle of mass m confined in a box of length L, assume  Assume further that
Assume further that  (min) =
(min) =  Use the uncertainity principle to obtain an estimate of the energy of the particle. The value will be
Use the uncertainity principle to obtain an estimate of the energy of the particle. The value will be
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
58. 
Identify the speed distribution functions of Ne, Ar and Kr with the curves in the figure above
(a) Ne – A, Ar – B, Kr – C
(b) Ne – B, Ar – C, Kr – A
(c) Ne – C, Ar – B, Kr – A
(d) Ne – C, Ar – A, Kr – B
Ans. c
Sol. Method – I :
As per the Maxwell's distribution.

So, higher the value of molar mass higher is the value of 

So, Ne will have lower curve and Kr will have higher.
Method – II: Maxima in the curve corresponds to most probable speed of the gas.


So, curve C corresponds to Ne, B to Ar and A to Kr.
Correct answer is (c)
59. For the cell reaction,  separate electrode reactions could be written with the respective standard electrode potential data at 250C as
separate electrode reactions could be written with the respective standard electrode potential data at 250C as

When RT/F is given as 25.7 mV, logarithm of the equilibrium constant  is
is
(a) 22.6
(b) 226
(c) 2.26
(d) 2.26 × 10–1
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
60. Hydrogen is adsorbed on many metal surfaces by dissociation (S represents a surface sit):

If the pressure of H2 (p) is small, the fraction of the surface covered by hydrogen is proportional to
(a) p
(b) p2
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. The fractional coverage for dissociative adsorption is


Correct option is (c)
61. For a process in a closed system, temperature is equal to
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
62. The exact differential df of a state function f(x, y), among the following is
(a) xdy
(b) 
(c) ydx – xdy
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. As we know, according to Euler theorem
For equation, df = Mdx = Ndy ...(i)
f is exact differential only when

Given exact differential
From equation (i) and equation (ii), we get

From equation (iii) and (iv)

Hence, both sides are equal.
Correct answer is (d)
63. The angular momentum operator  has eigen functions of the form
has eigen functions of the form  The condition that a full rotation leaves such an eigen function unchanged is satisfies for all the values of A.
The condition that a full rotation leaves such an eigen function unchanged is satisfies for all the values of A.
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. The angular momentum operator  has eigenfuction of the form exp
has eigenfuction of the form exp  where 'm' is the magnetic quantum number.
where 'm' is the magnetic quantum number.
Comparing with the eignfuction given in the question, we get
A = m
The value of m will be from 
Since, l will be a positive integer i.e. 0, 1, 2, 3,........................
Therefore, m will be 0, ± 1, ± 2,................
Correct answer is (b)
64. X–ray diffraction does not give any sturctural information for
(a) Metallic solids
(b) Ionic solids
(c) Molecular solids
(d) Amorphous solids
Ans. d
Sol. X – ray diffraction give structural information only for crystalline solids.
Correct answer is (d)
65. A reaction A + B + C  D follows the mechanism
D follows the mechanism

in which first step remains essentially in equilibrium. If  is the enthalpy change for the first reaction and E0 is the activation energy for the second reaction, the activation energy of the overall reaction will be given by
is the enthalpy change for the first reaction and E0 is the activation energy for the second reaction, the activation energy of the overall reaction will be given by
(a) E0
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
 is the enthalpy change for the reaction and E0 is the activation energy for the second reaction.
is the enthalpy change for the reaction and E0 is the activation energy for the second reaction.
So, the activation energy of the overall reaction is 
Correct option is (c)
66. Wavelength  of the Lyman series for an one – electron ion is in the range
of the Lyman series for an one – electron ion is in the range  The ionization energy of the ion will be closest to
The ionization energy of the ion will be closest to 
(a) 32 eV
(b) 42 eV
(c) 52 eV
(d) 62 eV
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct answer is (c)
67. A sample experiment revaled that PVC formed in the medium has  where
where  stands for the number average molar mass and
stands for the number average molar mass and  for the weight average molar mass. The variance of Mn will then be
for the weight average molar mass. The variance of Mn will then be
(a) 39
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 87
Ans. a
Sol. Variance = (Difference between molar mass and weight molar mass) × molar mass
= (16 – 3) × 13 = 3 × 13 = 39
Here molar mass represented xi and weighted molar mass fi. In this question data set and there frequency is not given. All the final values are given. So, variance 
Correct option is (a)
68. For an enzyme – substrate reaction, a plot between  yields a slope of 40s. If the enzyme concentration is 2.5 µM, then the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme is
yields a slope of 40s. If the enzyme concentration is 2.5 µM, then the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
69. For a polydispersed macromolecular colloid, osmometry gives
(a) Weight – average molecular weight
(b) Number – average molecular weight
(c) Both weight – average and number average molecular weights
(d) Viscosity – average molecular weight
Ans. b
Sol. Number average molecular weight is determined by osmometry.
Correct answer is (b)
70. 10 ml of 0.02 M NaOH is added to 10 ml of 0.02 M acetic acid (pKa = 4.75). The pH of the solution will be closest to
(a) 7.0
(b) 8.4
(c) 5.6
(d) 9.6
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
71. Which of the following will result in deviation from Beer's law:
(A) Change in refractive index of medium,
(B) Dissociation of analyte on dilution,
(C) Polychromatic light
(D) Path length of cuvette
(a) A, B and C
(b) B, C and D
(c) A, C and D
(d) A, B and D
Ans. a
Sol. Limitations of Beer's law are
Solution must be dilute, radiation must be monochromatic, temperature should not vary largely.
Analyte molecule should not undergo any kind of association or dissociation.
Refractive index of medium should not change.
Correct answer is (a)
72. The gas commonly used in generating plasma in Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICPAES) is
(a) Argon
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Nitrous oxide
(d) hydrogen
Ans. a
Sol. For ICP – OES and ICP – MS argon is most suitable gas to generate plasma
A number of gases cane be used to produce plasma, like Ar, Ne, N2, O2, H2, air and mixture of gases. The physical properties of the gases play a decisive role in this regard. Such important properties are ionization and dissociation energy, thermal conductivity, atomic weight and chemical reactivity.
Argon belongs to the group of inert gases. It means that it does not react with the material during production of plasma. Its atomic weight – the highest among all plasma gases and it generates high kinetic energy of the plasma beam. Due to its low ionization potential argon is excellently suitable for generating the plasma beam. However, argon has a low thermal conductivity and a low thermal capacity which limits its application is some specific areas only.
Correct answer is (a)
73. The geometric cross – section (in barn) of a nucleus A = 125, r0 = 1.4 × 10–15 m approximately is
(a) 1.05
(b) 1.54
(c) 2.05
(d) 2.54
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
74. The number of stereoisomers of trans [CoCl2 (triethylenetetraamine)] Br is
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct answer is (c)
75. Under physiological condition, oxygen is binding to deoxyhemoglobin and dexymyoglobin, the binding curve and its pH dependence, respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
76. Match the metalloproteins in column – A with their function in column – B

The correct answer is
(a) I – F; II – C; III – D; IV – A
(b) I – E; II – C; III – A; IV – F
(c) I – F; II – B; III – C; IV – A
(d) I – E; II – D; III – C; IV – A
Ans. a
Sol. Oxyhemocyanin stables as oxygen carrier.
Carbonic anhydrase
Carbonic anhydrase converts CO2 to H2CO3.

cytochrome P450 oxidizes alkene to epoxide.

Carboxy peptidase A catalyzes the hydrolysis of C – terminal peptide bond.
Correct option is (a)
77.  reacts with Br2 to give A. Reaction of A with LiAlH4 results in B. The proton NMR spectrum of B consists of two singlets of relative intensity 5:1. Compounds A and B, respectively, are
reacts with Br2 to give A. Reaction of A with LiAlH4 results in B. The proton NMR spectrum of B consists of two singlets of relative intensity 5:1. Compounds A and B, respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
So, in the product (B) it shows two signals in 1H NMR one for 5H of Cp ring and one for  proton with intensity ratio 5 : 1.
proton with intensity ratio 5 : 1.
Correct option is (a)
78. The compound that undergoes oxidative addition reaction in presence of H2 is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol.  is a 16 electron complex called as Vaska complex. Only show oxidative addition in the presence of
is a 16 electron complex called as Vaska complex. Only show oxidative addition in the presence of

Correct option is (c)
79. 1H NMR spectrum of free benzene shows a peak at ~ 7.2 ppm. The expected chemical shift (in ppm) of C6H6 ligand in 1H NMR spectrum of  and the reason for it, if an, is/are
and the reason for it, if an, is/are
(a) 4.5 ; disruption of ring current
(b) 9.0 ; inductive effect
(c) 7.2
(d) 2.5; combination of inductive effect and disruption of ring current
Ans. a
Sol. 
Benzene shows a peak at ~ 7.2 ppm when benzene attach to metal decrease the chemical shift due to discruten of ring current.
Correct answer is (a)
80. An aqueous solution of [Mn(H2O)6]2+ complex is pale pink in colour. The probable reasons for it are
(A) Presence of 6Alg ground state
(B) Disallowed transition by spin selection rule
(C) Presence of 2T2g ground state
(D) Charge transfer transition
The correct answer is
(a) A and B
(b) A and C
(c) B and C
(d) C and D
Ans. 1
Sol. 
Ground state term for d5 is 6S which transform into 6Alg in octahedral field.

There is spin change during electron transition. Therefore, transition in spin disallowed.
Correct option is (a)
81. The reaction of phosphorus trichloride with pheyllithium in 1:3 molar ratio yields product 'A', which on further treatment with methyl iodide produces 'B'. The reaction of B with nBuLi gives product 'C'. The products A, B and C, respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
82. The reaction between diphenyldichlorosilane and water in 1:2 molar ratio gives product A which on heating above 1000C yields a cyclic or polymeric product B. The products A and B respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. The reaction is as follows

Now, (A) undegro condensation polymerisation to yield (B), which is an inorganic silicon, polymer, as follows

Correct option is (c)
83. According to Wade's rule, anion C2B9H12– adopts
(a) closo – structure
(b) nido – structure
(c) arachno – structure
(d) hypho – structure
Ans. b
Sol. The  is potta carborane anion.
is potta carborane anion.

Now,  is equivalent to
is equivalent to  neutral borane which follows the formula
neutral borane which follows the formula  which is the general formula of nidoborane.
which is the general formula of nidoborane.

Correct answer is (b)
84. The final product in the reaction of [Cp*2 ThH] with CO in an equimolar ratio is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. It is a kind of insertion reaction of M – H (metalhydride bond between CO)

Correct option is (d)
85. Hindered  – diketonates like dpmH (dpmH = dipivaloylmethane) are used for the separation of lanthanides because complexes formed with dpmH can be separated by
– diketonates like dpmH (dpmH = dipivaloylmethane) are used for the separation of lanthanides because complexes formed with dpmH can be separated by
(a) Get permeantion chromatography
(b) Gas chromatography
(c) Gel filtration chromatography
(d) Ion exchange chromatography
Ans. b
Sol. Dipivaloylmethane  form chelats with lanthanides
form chelats with lanthanides
Correct option is (b)
86. Base hydrolysis of [CoCl(NH3)5]2+ is an overall second order reaction, whereas that of [Co(CN)6]3– is of first order. The rates depend in both cases solely on the concentrations of the cobalt complex, This may be due to
(A) Presence of ionizable proton in [CoCl(NH3)5]2+ but not in [Co(CN)6]3–
(B)  mechanism in the case of [CoCl(NH3)5]2+ only
mechanism in the case of [CoCl(NH3)5]2+ only
(C)  mechanism in the case of [CoCl(NH)6]3– only
mechanism in the case of [CoCl(NH)6]3– only
(D)  mechanism in both the complexes
mechanism in both the complexes
Correct explanations(s) is/are
(a) A and B
(b) A and C
(c) B only
(d) A and D
Ans. a
Sol. 
Base hydrolysis of  depends on the concentration of both
depends on the concentration of both  and base. In this reaction OH– abstract proton from coordinated NH3.
and base. In this reaction OH– abstract proton from coordinated NH3.
The base hydrolysis of  is independent of base because it has no ionizable proton.
is independent of base because it has no ionizable proton.
Correct option is (a)
87. AA borane (X) is reacted with ammonia to give a salt of borohydride (Y). The 11B NMR spectrum of Y consists of a triplet and a quintet. The borane X is
(a) B2H6
(b) B3H9
(c) B4H8
(d) B5H9
Ans. a
Sol. Diborane reacts with ammonia as


'Y' is actually [A+B]. In 'Y' 'B' part gives quintet and 'A' part gives triplet by 'B' and 'H' coupling.
Correct answer is (a)
88. The main products of the reaction of equimolar quantities of XeF6 with NaNO3 are
(a) XeOF4, NaF and NO2F
(b) XeO2F2, NaF, NOF and F2
(c) XeOF4, NaNO2 and F2
(d) XeF4, NaNO2 and F2O
Ans. a
Sol. The reaction of XeF6 with NaNO3 takes place as

Correct answer is (a)
89. The spin – only magnetic moment and the spectroscopic ground state term symbol of manganese center in [MnF6]3– ion respectively, are
(a) 4.9 BM and 5D
(b) 4.9 BM and 4F
(c) 3.9 BM and 3D
(d) 4.9 BM and 3F
Ans. a
Sol. 
90. The three dimensional structure of compound [Co(Co(NH3)4(OH2)3]Br6 has
(a) Twelve Co – O and twelve Co – N bonds
(b) Ten Co – O and ten C – N bonds
(c) Fourteen Co – O and ten Co – N bonds
(d) Twelve Co – O and ten Co – N bonds
Ans. a
Sol. 
It is first inorganic optically active compound discovered by Werner.
Number of Co – O bonds = 12
Number of Co – N bonds = 12
Correct option is (a)
91. The spin – only  and spin plus orbital
and spin plus orbital  magnetic moments of [CrCl6]3– are
magnetic moments of [CrCl6]3– are
(a) 3.87 BM and 5.20 BM
(b) 2.84 BM and 5.20 BM
(c) 3.87 BM and 6.34 BM
(d) 2.84 BM and 6.34 BM
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
92. Complexes HM(CO)5 and  obey 18 – electron rule. Identify M and M´ and their 1H NMR chemical shifts relative to TMS
obey 18 – electron rule. Identify M and M´ and their 1H NMR chemical shifts relative to TMS
(a) M = Mn, – 7.5; M´ = Cr, 4.10
(b) M = Cr, 4.10; M´ = Mn, – 7.5
(c) M = V, – 75; M´ = Cr, 4.10
(d) M = Mn, 10.22; M´ = Fe, 2.80
Ans. a
Sol. 


Correct option is (a)
93. 12 – Crown – 4 binds with the alkali metal ions in the following order:
Li+ >> Na+ > K+ > Cs+. It is due to the
(a) Right size of cation
(b) Change in entropy being positive
(c) Conformational flexibility of crown ether
(d) Hydrophobicity of crown ether.
Ans. a
Sol. The crown ether binds metal cation in their cavity. They are selective as they have fixed ring size.
Crown ether Metal cation
crown – 4 Li+
crown – 5 Na+
crown – 6 K+
crown – 7 Rb+
crown – 8 Cs+
Therefore, 12 – crown – 4 is best suited for Li+ cation. After then as the size increases binding capacity decreases.
Correct answer is (a)
94. The correct schmeatic molecular energy diagram for SF6 molecule is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. In the formation of SF6 the following atomic orbitals are involved.

The 3s, 3p of 'S' and 2pz of 'F' are mixed to give ten MO's. Calculations indicate that four of orbitals will be bonding and four will be antibonding. The remaining two will be non – bonding.
There are 12 electrons to be filled in ten MO's. The first two can enter l a and the next six can in it. The remaining four fill the non – bonding pair of orbitals. Thus it gives l a2 l t6 e4 as configuration.
This gives the molecular diagram of SF6 as

Therefore answer will be (a)
95. Gel permeation chromatography can be used to separate which of the following
(A) Lanthanides
(B) Alkaline earths
(C) Fatty acids
The correct answer is
(a) A and B
(b) B and C
(c) C and D
(d) A and D
Ans. c
Sol. Gel permeation chromatography is a size exclusion chromatography, that separates analytes on the basic of size. So, the size difference in fatty acids and low molecular weight peptides is greater so they can be separated by using gel permeation chromatography.
Correct option is (c)
96. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
97. The major product formed in the following transformation is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Two stereogenic centre present in the molecule direct the stereochemistry.
Correct option is (a)
98. The product of B in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Note: Bromination in hydrocarbon solvent gives crystalline trans isomer.

Correct answer is (c)
99. The major product of the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
100. The major product of the following reactions is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Hofmann Lofflar freytag reaction


Note: Five membered ring is more stable over six membered in free radical mechanism.
Correct option is (a)
101. The major product for the following sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 


Correct option is (a)
102. The products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
103. The product A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
104. The correct combinations of the reactions and the reagents are

(a) A – P, B – Q, C – R
(b) A – O, B – R, C – P
(c) A – P, B – R, C – Q
(d) A – Q, B – P, C – R
Ans. d
Sol. 



Correct option is (d)
105. The products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Trimethyl silyl chloride is used as a protecting group for alcohol functionality selectively.

106. The major product of the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 



Correct option is (a)
107. The major product of the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
108. The products A and B in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
109. The major product formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 


Correct option is (d)
110. In the following reaction sequence, the structures of A and B are, respectively.

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 


Correct option is (a)
111. In the following reaction sequence, the structure of the product is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
112. The correct combination of the following reactions and their  values is
values is

(a) A – P ; B – R ; C – P
(b) A – R ; B – Q ; C – P
(c) A – R ; B – Q ; C – P
(d) A – Q ; B – R ; C – S
Ans. b
Sol.  is called reaction constant.
is called reaction constant.
First reaction is benzoylationof aniline. the slow, rate limiting step of this reaction is found to be initial attack by the electron pair of the nitrogen atom. This develops positive charge at the reaction centre. The reaction is thus accelerated by electron donating substituents. This leads to a sufficient negative  value which will –2.69. Now base catalyzed hydrolysis of ethyl benzoates in which the slow rate limiting step in this reaction is attended by the development of –ve charge adjacent to the reaction centre in the transition state leading to the intermediate in which the reaction is accelerated by electronic withdrawing and retarded by electron donating substituents. Thus
value which will –2.69. Now base catalyzed hydrolysis of ethyl benzoates in which the slow rate limiting step in this reaction is attended by the development of –ve charge adjacent to the reaction centre in the transition state leading to the intermediate in which the reaction is accelerated by electronic withdrawing and retarded by electron donating substituents. Thus  value can be regarded as a measures susceptibility of a reaction to the electron donating or withdrawing effect exerted by a substituent. The sign of
value can be regarded as a measures susceptibility of a reaction to the electron donating or withdrawing effect exerted by a substituent. The sign of  value is of diagnostic value, –ve value indicates the development of positive charge at the reaction centre during formation of the T.S. in the rate limiting step.
value is of diagnostic value, –ve value indicates the development of positive charge at the reaction centre during formation of the T.S. in the rate limiting step.
On the other hand + value indicates developments of –ve charge at that centre. Thus in the base catalyzed hydrolysis in which –ve charge develops at reaction centre  value will be positive which is +2.09
value will be positive which is +2.09
Correct option is (b)
113. The following reactions gives a product (recemic) which exhibits the following NMR data:
1H NMR :  2.67 (2H, s), 5.60 (2H, s)
2.67 (2H, s), 5.60 (2H, s)
ppm; 13C NMR:  170.3, 129.0, 105.0, 25.4 ppm
170.3, 129.0, 105.0, 25.4 ppm
The structure of the product (racemic) is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. From 1H NMR it is clear that there is no methyl group present, because no value corresponding  value is there for three hydrogen.
value is there for three hydrogen.
Now, since the product is racemic, then it will be 3

Correct answer is (c)
114. The reactive intermediate and the product formed in the following reaction are

(a) Free radical and 4 – iodomethyloxepan – 2 – one
(b) Free radical and 5– iodooxacan – 2 – one
(c) Carbene and 3 – oxabicyclo [5.1.0] octane – 2 – one
(d) Carbene and (E) – 5 – iodopent – 3 – en – 1 – yl acetate
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
115. The major product formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
DIBAL–H does not effect triple bond. At low temperature esters and loctones are reduced directly to aldehydes or lactols.

Correct option is (a)
116. An organic compound having molecular formula C10H12O2 exhibits the following spectral data:
IR : 3400 (br), 1600 cm–1.
1H NMR :  1.85 (3H, d, J = 6Hz), 3.8 (3H, s), 5.0 (1H, s, D2O exchangeable), 6.0 (1H, dq, J= 18, 6 Hz),
1.85 (3H, d, J = 6Hz), 3.8 (3H, s), 5.0 (1H, s, D2O exchangeable), 6.0 (1H, dq, J= 18, 6 Hz),
6.28 (1H, d, J = 18 Hz), 6.75 (1H, d, J = 8 Hz), 6.8 (1H, s), 6.90 (1H, d, J = 8 Hz) ppm;
13C NMR :  146.5, 144.0, 131.0, 130.5, 123.0, 119.0, 114.0, 108.0, 55.0, 18.0 ppm.
146.5, 144.0, 131.0, 130.5, 123.0, 119.0, 114.0, 108.0, 55.0, 18.0 ppm.
The structure of the compound is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. • Free IR at 3400 (board) confirms presence of –OH.
• J = 18 Hz indicates the presence of trans geometry of H's. Thus, possibility of 2nd option ruled out.
•  value 3.8 (3 H,s) indicates –OMe group. Thus possibility of 4th option ruled out.
value 3.8 (3 H,s) indicates –OMe group. Thus possibility of 4th option ruled out.
•  value at 6.8 (1 H,2) rules out 3rd option.
value at 6.8 (1 H,2) rules out 3rd option.
Hence, option '(a)' is correct structure.

Correct option is (a)
117. In the following reaction sequence, the reagents X and Y are, respectively,

(a) X = PhSO2H, BF3OEt2 and Y = CH2 = CHCOOEt, BF3OEt2
(b) X = 1. PhSH, PTSA; 2. m – CPBA and Y = CH2 = CHCOOEt, BF3OEt2
(c) X = PhSO3H, BF3OEt2 and Y = LDA, CH2 = CHCOOEt
(d) X = 1, PhSP, PTSA; 2. m – CPBA and Y = LDA, CH2 = CHCOOEt
Ans. d
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
118. The major product of the following reactions is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. With zinc and acetic acid debromination takes place selectively for the bromine, which is adjacent to carbonyl group.

Correct option is (a)
119. The major product of the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 

The product have hydrogen in cis ring junction because both the hydrogen's are in same direction in the preceding compound.
Correct answer is (d)
120. The major product A and B formed in the following reaction sequence are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
121. For a gaseous reaction, 2NO(g) + Cl2(g)  Non–linear T.S.
Non–linear T.S.  2NOCl, the pre – exponential factor in the rate constant is proportional to
2NOCl, the pre – exponential factor in the rate constant is proportional to
(a) T1/2
(b) T–1/2
(c) T–5/2
(d) T–7/2
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct answer is (d)
122. Species A undergoes a unimolecular reaction as follows:

for this reaction, the first order rate constant at high pressure is  The first order the constant becomes
The first order the constant becomes  when pressure of A is [A]1/2*
when pressure of A is [A]1/2*

The value of k1 will be
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 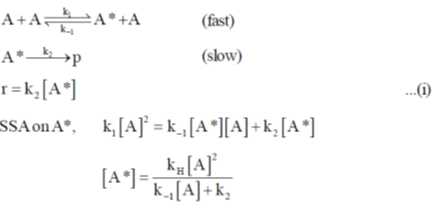



In question it is given that first order rate constant becomes  and for that,
and for that,

Correct option is (a)
123. The low and high temperature limits of vibrational partition function are 
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. For vibrational partition function 
For condition  So, from equation (i), we get
So, from equation (i), we get

Case–(i) : T is very low so that  is negligible compared with unity in the denominator of equation (ii), we get
is negligible compared with unity in the denominator of equation (ii), we get

Case – II : T is very high so that  Then the exponential in the denominator can be expand as series retaining only the first two terms.
Then the exponential in the denominator can be expand as series retaining only the first two terms.

Correct option is (b)
124. The probability of finding the harmonic oscillator in the energy level n = 1 is (neglect zero point energy and assume hv = kBT)
(a) e
(b) e2
(c) 1 – e–2
(d) e–2 (e–1)
Ans. d
Sol. Neglacting zero point energy, 

Correct option is (d)
125. A particle in a 1 – dimensional box of length L is perturbed by a delta function potential,  in the middle of the box. The first order energy correction to the ground state will be
in the middle of the box. The first order energy correction to the ground state will be 
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) L/2
(d) 2/L
Ans. d
Sol. 
So, direct put the value of  in the wavefunction and n = 1, no integration.
in the wavefunction and n = 1, no integration.

Correct option is (d)
126. The operators  are defined by
are defined by  where
where  are components of the spin angular momentum operator. The commutator [Sz,S+] is
are components of the spin angular momentum operator. The commutator [Sz,S+] is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
127. A quantum particle with fixed initial energy E0 < V is allowed to strike the following four barriers separately. The transmission probability is maximum in
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. Since for transition probability we have, 

Transmission probability is maximum if L is minimum and V is minimum.
Correct answer is (b)
128. Given the following two relations, 

for a binary liquid mixture at constant temperature and pressure, the true statement is that,
(a) Both the relations are correct
(b) Relation A is correct, but B is not
(c) Relation B is correct, but A is not
(d) Both the relations are incorrect, except for very dilute solutions
Ans. a
Sol. For a multicomponent open system

Differentiating above equation

But by the fundamental equation,

Substracting equation (i) and equation (ii)

If T and P are constant,

Gibb's – Duhem equation involving partial molar volume, we have



For a binary mixture relation (A) and (B) are correct.
Correct option is (a)
129. If the bond length of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule is greater in the upper vibrational state, the gap between the successive absorption lines of P – branch
(a) Increases non – lineraly
(b) Decreases non – lineraly
(c) Increases lineraly
(d) Decreases lineraly
Ans. a
Sol. For a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, the energy levels of the virbrational rotational spectra will be

Where 'r' is the bond length of the molecule.
If the bond length of the heteronuclear diatomic molecule is greater for upper vibrational state, the wave number corresponding to the P–branch lines will be,

Where,  = rotational quantum number of upper vibrational state,
= rotational quantum number of upper vibrational state,
 = rotational constant of upper vibrational state.
= rotational constant of upper vibrational state.
Gap between two successive P – branch lines is proportional to 
As bond length r increases,  decreases and gap between successive absorptionline of branches increases non-linearly.
decreases and gap between successive absorptionline of branches increases non-linearly.
Correct answer is (a)
130. EPR spectrum of a free radical containing nuclei with non – zero nuclear spin is obtaining if the following selection rules are observed.
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
131. At high pressure, the fugacity coefficient of a raal gas is greater than one, because
(a) Attractive termoverweighs the repulsive term
(b) Repulsive termoverweighs the attractive term
(c) Repulsive term is equal to the attractive term
(d) The system is independent of both the attractive and repulsive terms
Ans. b
Sol. 
Equation (i) shows that the chemical potential varies with natural logrithm.
 vs P may be represented as
vs P may be represented as

However measurement on the real gas shows that the relation between  is not show exact at very – 2 low gas pressure all gas appear ideal behaviour at moderate pressure region. The pressure is lower than expected because real gas molecule attract each other and the measured pressure is lower than ideal.
is not show exact at very – 2 low gas pressure all gas appear ideal behaviour at moderate pressure region. The pressure is lower than expected because real gas molecule attract each other and the measured pressure is lower than ideal.
At very high P the pressure is higher than expected because gas molecule become. So, densely packed that they begin to repel each other. So, the real behaviour or actual behaviour of chemical potential vs the real pressure may be show that here is attractive palt clominate.

Correct option is (b)
132. If D0(A) and I(A) refer respectively to the dissociation energy and ionization potential of A (where A is either H, H2, species), the correct relation among the following is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
133. The character table of C2y point group is given below. in cis–butadiene molecule the vibrational modes belonging to A2 irreducible representation are IR inactive. The remaining IR active modes are

(a) 7A1 + 5B1 + 8B2
(b) 9A1 + 4B1 + 7B2
(c) 7A1 + 3B1 + 7B2
(d) 9A1 + 3B1 + 8B2
Ans. d
Sol. 



Correct option is (d)
134. The product  is the four fold improper axis o rotation around the z-axis, and
is the four fold improper axis o rotation around the z-axis, and  is the reflection in the xy plane) is
is the reflection in the xy plane) is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
135. A solid consisting of only X – atoms has a close – packed structure with X – X distance of 160 pm. Assuming it to a closed packed structure of hard spheres with radius equal to half of the X – X bond length, the number of atoms in 1 cm3 would be
(a) 6.023 × 10–27
(b) 3.45 × 1023
(c) 6.02 × 1021
(d) 3.8 × 1021
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
136. Fuel cells provide clean electrical energy to a variety of applications including automobiles and stationary power sources. Normally hydrogen combines with oxygen to give electrical energy and water. If we use butane instead of hydrogen at 1.0 bar and 298 K, the following reaction occurs:
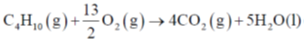
(a) 1.55 V
(b) 1.09 V
(c) 3.15 V
(d) 2.06 V
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
137. The fraction of groups condensed at time t in any stepwise condensation polymerization (overall second order) reaction is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
138. The configuration [Ne] 2p1 3p1 has at 3D term. Its levels are
(a) 3D3/2, 3D1/2
(b) 3D5/2, 3D3/2, 3D1/2
(c) 3D3, 3D2, 3D1
(d) 3D3, 3D2, 3D1, 3D0
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
139. For some one – electron system with l = 0 and m = 0, the functions  refer respectively to the ground (E0) and first excited (E1) energy levels. If a varational wave function N2(3 –
refer respectively to the ground (E0) and first excited (E1) energy levels. If a varational wave function N2(3 –  yields an average energy
yields an average energy  it will satisfy
it will satisfy
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. Ground state wave function : 
First excisted state wave function: 
The variatioanl wave function  will be good appromixation for the first excited state wave function. Since, the energy calculated from the variational wave function will be greater than or equal to that of exact energy.
will be good appromixation for the first excited state wave function. Since, the energy calculated from the variational wave function will be greater than or equal to that of exact energy.

Correct option is (c)
140. The number of microstates that are possible, when two particles are distributed in four states such that the resulting wave functions are antisymmetric with respect to exchange of the particles, is
(a) 16
(b) 12
(c) 8
(d) 6
Ans. d
Sol. 
There are 4 gives state and number of particles 2 possible distribution.
Correct option is (d)
141. A Slater determinant corresponding to the ionic part of the ground state valence bond wave function of H2 molecule is  are atomic spin – orbitals of hydrogen atoms a and b of the hydrogen molecule)
are atomic spin – orbitals of hydrogen atoms a and b of the hydrogen molecule)
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Ionic part of the ground state valence bond wave function of H2 molecule if

Correct option is (a)
142. When  value of the single – particle partition function will be (given : degeneracy of level j = g1)
value of the single – particle partition function will be (given : degeneracy of level j = g1)
(a) 1
(b) g0
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 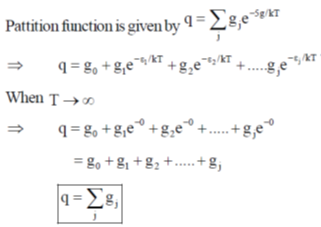
Correct option is (c)
143. The rate constant for a reaction  is measured in two different aqueous solutions of ionic strengths 0.01 M and 0.04 M. If log
is measured in two different aqueous solutions of ionic strengths 0.01 M and 0.04 M. If log  the charge n on B is closest to
the charge n on B is closest to
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 6
Ans. c
Sol. 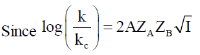

Correct option is (c)
144. According to Hückel theory, the  electron charge on the central carbon atom in propenyl cation (CH2CHCH2)+ is (in units of electronic charge)
electron charge on the central carbon atom in propenyl cation (CH2CHCH2)+ is (in units of electronic charge)
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 1
(d) 2
Ans. c
Sol. 




Correct option is (c)
145. Among the following figures, the variations of mass adsorbs with pressure for a monolayer and a multilayer are represented by

(a) A and C respectively
(b) A and B respectively
(c) C and A respectively
(d) B and A respectively
Ans. b
Sol. A = Monolayer
B = Multilayer without condensation
C = Multilayer with capillary condensation
Therefore, correction answer is (b)
