CSIR NET CHEMISTRY (DEC-2012)
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
21. For an odd nucleon in 'g' nuclear orbital and parallel to I, spin and parity are
(a) 9/2 and (+)
(b) 7/2 and (+)
(c) 9/2 and (–)
(d) 7/2 and (–)
Ans. a
Sol. In 'g' nuclear orbital total subshell is nine.

One odd nucleon finding in g – subshell
Total spin = 9/2

Correct option is (a)
22. For the deposition of Pb by electroplating, the best suited compound among the following is
(a) PbCl2
(b) PbSO4
(c) Pb(Et)4
(d) Pb(BF4)2
Ans. d
Sol. PbCl2 and PbSO4 are ionic compounds and insoluble in cold water. Therefore, cannot be used for deposition of Pb and Pb (Et4) is toxic.
Correct answer is (d)
23. Appropriate reasons for the deviation form the Beer's law among the following are
(A) Monochromaticity of light
(B) Very high concentration of analyte
(B) Association of analyte
(D) Dissociation of analyte
(a) A, B and D
(b) B, C and D
(c) A, C and D
(d) A, B and C
Ans. b
Sol. Beer's law is subjected to certain real and apparent deviation.
Real deviations are most usually encountered in relatively concentrated solutions of the absorbing compound (> 0.01 M). These deviations are due to interactions between the absorbing species and to attractions of the refractive index of the medium.
Most common are the apparent deviations. These deviations are due to:
Chemical reasons arising when the absorbing compound dissociates, associated or reacts with a solvent to produce a product having a different absorption spectrum.
Strict adherence to Beer's law is observed only with truely monochromatic radiation.
Correct option is (b)
24. Which one of the following shows the highest solubility in hot concentrated aqueous NaOH?
(a) La(OH)3
(b) Nd(OH)3
(c) Sm(OH)3
(d) Lu(OH)3
Ans. d
Sol. Since size of Lu3+ is smallest, therefore Lu(OH)3 complex most easily formed with NaOH and dissolves.

Correct answer is (d)
25. In the vibrational spectrum of CO2, the number of fundamental vibrational modes common in both infrared and Raman are
(a) Three
(b) Two
(c) One
(d) Zero
Ans. d
Sol. CO2 has centre of symmetry so on per exclusion principle all the IR active vibration will be Raman inactive. Hence, fundamental vibrational modes common in both IR/ and Raman will be zero.
Correct answer is (d)
26. The light pink colour of [Co(H2O)6]2+ and the deep blue colour of [CoCl4]2– are due to
(a) MLCT transition in the first and d-d transition in the second
(b) LMCT transition in both
(c) d-d transition in both
(d) d-d transition in the first and MLCT transition in the second.
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
27. In [Mo2(S2)6]2– cluster the number of bridging S22– and coordination number of Mo respectively, are
(a) 2 and 8
(b) 2 and 6
(c) 1 and 8
(d) 1 and 6
Ans. a
Sol. 

So, the bridging S22– is two and co-ordination number of Mo is 8.
Correct option is (a)
28. 1H NMR spectrum of HD would show
(a) a singlet
(b) a doublet
(c) a triplet with intensity ratio 1 : 2 : 1
(d) a triplet with intensity ratio 1 : 1 : 1
Ans. d
Sol. Duterium D Spin I = 1
Multiplicity = 2nI + 1 = 2 × 1 × 1 + 1 = 3
Where, n = number of duterium atom
I = spin of duterium atom.
Intensity ratio will be non – pascal.
Hence, 1H NMR of HD will appear as triplet with intensity ratio 1 : 1 : 1.
Correct answer is (d)
29. The number of possible isomers of [Ru(PPh3)2(acac)2] (acac = acetylacetonate) is:
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
30. The total number of Cu–O bonds present in the crystalline copper (II) acetate monohydrate is
(a) 10
(b) 6
(c) 8
(d) 4
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
31. The electronegativity differences is the highest for the pair
(a) Li, Cl
(b) K, F
(c) Na, Cl
(d) Li, F
Ans. b
Sol. Among these elements K is least electronegative and F is most electronegative. Therefore electronegativity difference is highest for the pair K, F.
Correct answer is (b)
32. Which ones among CO32–, SO3, XeO3 and NO3– have planar structure?
(a) CO32–, SO3 and XeO3
(b) SO3, XeO3 and NO3–
(c) CO32–, XeO3 and NO3–
(d) CO32–, SO3 and NO3–
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
33. The substitution of  group with nitric oxide is the easiest for
group with nitric oxide is the easiest for
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
34. 
obeys 18 electron rule. The two 'M' satisfying the condition are
(a) Cr, Re+
(b) Mo, V
(c) V, Re+
(d) Cr, V
Ans. a
Sol. 
2 × 5 + M + 2 = 18 , M = 18 – 12 = 6
So, M = Cr, and Re+.
Correct option is (a)
35. The correct set of the biologically essential elements is,
(a) Fe, Mo, Cu, Zn
(b) Fe, Cu, Co, Ru
(c) Cu, Mn, Zn, Ag
(d) Fe, Ru, Zn, Mg
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
36. The number of lines exhibited by a high resolution EPR spectrum EPR spectrum of the species, [Cu(ethylenediamine)2]2+ is [Nuclear spin (I) of Cu=3/2 and that of N=1]
(a) 12
(b) 15
(c) 20
(d) 36
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
37. Degradation of penicillin G

gives penicillamine that can utilize nitrogen, oxygen or sulfer atomos as donors to bind with lead (II), mercury (II) or copper (II). The structure of penicillamine is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Degradation of penicillin G occurs at carbon hetero bond and produces

Correct option is (a)
38. The molecular that has an S6 symmetry element is
(a) B2H6
(b) CH4
(c) PH5
(d) SF6
Ans. d
Sol. B2H6 has D2h point group and S2 axis
CH4 has Td point group and S4 axis
PH5 has D3h point group and S3 axis
SF6 has Oh point group and S6 axis. Hence, SF6 has S6 symmetry element.
Correct answer is (d)
39. The electric dipole allowed transition in a d2 atomic system is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. Electric dipole allowed transition in d2
For electronic transition selection rule, spin multiplicity 
 is allowed transition because
is allowed transition because 
Correct answer is (c)
40. When a hydrogen atom is placed in an electric field along the y-axiz, the orbital that mixes most with the ground state l s orbital is
(a) 2s
(b) 2p8
(c) 2py
(d) 2pz
Ans. c
Sol. When a hydrogen atom is placed in an electric field along the y – axis. The magnetic moment i.e. electron density will be oriented along y – axis and therefore the orbital that mixes most with the ground state 1s orbital is 2py.
41. For water,  The molar entropy of vaporization at 1 atm pressure is approximately.
The molar entropy of vaporization at 1 atm pressure is approximately.
(a) 410 J K–1 mol–1
(b) 110 J K–1 mol–1
(c) 41 J K–1 mol–1
(d) 11 JK–1 mol–1.
Ans. b
Sol. Given : for water 

Correct option is (b)
42. If A and B are non-commuting hermitian operators, all eigenvalues of the operator given by the commutator [A, B] are
(a) complex
(b) real
(c) imaginary
(d) zero
Ans. c
Sol. The eigenvalues of an anti – Heritian operator are either purely imaginary or equal to zero. If A and B are non – commuting hermitian operator. So, all eigenvalues are purely imaginary or zero.
Correct answer is (c).
43. The value of commutator  is given by
is given by
(a) 2i
(b) 2ih
(c) zihx
(d) 2ih Px
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
44. The correlation coefficient between two arbitrary variables x and y is zero, if
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. If two arbitrary variables x and y then measure the intensity of correlation coefficient

They may be related in a non – linear fashion.
Correct option is (d)
45. A carnot takes up 90 J of heat from the source kept at 300K. The correct statement among the following is
(a) It transfers 60 J of heat to the sink at 200K
(b) It transfers 50 J of heat to the sink at 200K
(c) It transfers 60 J of heat to the sink at 250K
(d) It transfers 50 J of heat to the sink at 250K
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
46. The relative population in two states with energies E1 and E2 satisfying Boltzmann distribution is given by  The relative degeneracy g2/g1 is:
The relative degeneracy g2/g1 is:
(a) 2
(b) 2/3
(c) 3/2
(d) 3
Ans. b
Sol. The relative population in two states with energy E1 and E2 satisfy Boltzmann distribution law.


Correct option is (b)
47. The Daniel cell is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Daniel cell consists of two half cells. The half cell on the left contains a zinc metal electrode dipped in ZnSO4 solution. The half cell on the right consits of copper metal electrode in a solution of CuSO4. The half cell joined by a salt bridge.

Correct option is (a)
48. If the concept of half-life is generalized to quarter-life of a first order chemical reaction, it will be equal to.
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. Quarter life is the time in which the concentration decreases to  th of its initial value Rate law expression for first order reaction is
th of its initial value Rate law expression for first order reaction is

Therefore, Correct answer is (b)
49. Kohlraush's law is applicable to a dilute solution of
(a) Potassium chloride in hexane
(b) Acetic acid in water
(c) Hydrochloric acid in water
(d) Benzoic acid in benzene
Ans. c
Sol. Due to Kohlrausch' law at infinite dilution, when dissociation is complete, each ion makes a definite contribution towards molar conductance of the electrolyte irrespective of the nature of the other ion with which it is associated and that the molar conductance at infinite dilution for any electrolyte is given by the sum of the contribution of the two ions. Only hydrochloric acid in water completely dissociation and contribution with equal ion.
Correct answer is (c)
50. A dilute silver nitrate solution is added to a slight excess iodide solution. A solution of AgI is formed whose surface adsorbs.
(a) I–
(b) 
(c) Na+
(d) Ag+
Ans. a
Sol. A dilute solution of silver nitrate is add a slight excess of a dilute solution of sodium iodide, a negatively charged solution of silver iodide is formed. This is due to the adsorption of iodide ions.

This is the electrical property of colloid based on the concept of electrical double layer

The ions preferentially adsorbed on the surface of a particle of a colloidal system are called potential determining ions. The negatively charged surface of AgI particle attracts the positive ions (Ns+) and repels the negative ions (NO3–). The positive Na+ ion tend to form a compact layer in the vicinity of the potential determining I– ion layer. This is called stern layer. The ion present in the stern layer are called counter ions.
Correct option is (a)
51. The absorption spectrum of O2 shows a vibrational structure that becomes continuum at 56875 cm. At the continuum, it dissociates into one ground state atom (Og) and one excited state atom (Oe). The energy difference between Oe and Og is 15125 cm–1. The dissociation energy (in cm–1) of ground state of O2 is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 72000
(d) 41750
Ans. d
Sol. 
Dissociation energy, Dg = 56875 – 15125 = 41750
Correct option is (d)
52. The angle between the two planes represented by the Miller indices (1 1 0) and (1 1 1) in a simple cubic lattice is:
(a) 300
(b) 450
(c) 600
(d) 900
Ans. *
Sol. The angle between two planes having Miller Indices  is given by
is given by

53. The correct representation of the variation of molar conductivity (y-axis) with surfaciant concentration (x-axis) is [CMC = critical micelle concentration.]
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. The molar conductance of anionic surfactant of the type Na+R– in water is plooted against the square root of the normality of the solution. The curve obtained, instead of being the smoothly decreasing curve characteristic of ionic electrlytes of this type, has a shart break in it, at low concentrations. This sharp break in the curve accompanied by reduction in the conductance of the solution, indicating a sharp increase in the mass per unit charge of the material in solution, is interpreted as evidence for the formation of micelles at that point from the unassociated molecules of surfactant with part of the charge of the micelle neutralized by associated counter ions. The concentration at which this phenomenon occurs is called the critical micelle concentration (CMC)
The effect of concentration of electrolyte is given by

For homologous ionic surfactant

Correct option is (b)
54. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (a)
55. If the pKa value for p-methoxybenzoic acid is 4.46 and that of benzoic acid is 4.19, the  for methoxy group is:
for methoxy group is:
(a) 8.65
(b) 4.32
(c) 0.27
(d) –0.27
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
56. The biosynthetic precursor of cadinen is:

(a) shikimic acid
(b) mevalonic acid
(c) arachidonic acid
(d) prephenic acid.
Ans. b
Sol. Biosynthetic precursor of cardinene is mevalonic acid.
Correct option is (b)
57. The correct order of acidity of the compounds A–C is:

(a) A > B > C
(b) B > C > A
(c) C > A > B
(d) B > A > C
Ans. c
Sol. 

So, the correct order to acidity is C > A > B.
Correct option is (c)
58. The mechanism involved in the following conversion is:

(a) E2–elimination
(b) E1–elimination
(c) syn-elimination
(d) E1 CB-elimination
Ans. d
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (d)
59. The correct statements(s) – A – D are given for the following reaction. The correct one(s) is/are

(a) aromatic ipso substitution reaction
(b) aromatic nucleophilic substitution
(c) aromatic electrophilic substitution
(d) aromatic free radical substitution
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

It is an aromatic Ipso uncleophilic substitution reaction in which N–atom of reagent attacks on Ipso position leading to formation of desired product.
Correct option is (a)
60. The following photochemical transformation proceeds through

(a) Norrish type I reaction
(b) Norrish type II reaction
(c) Barton reaction
(d) Paterno–Buchi reaction
Ans. b
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Then reaction proceeds through  – transfer.
– transfer.
Correct option is (b)
61. A tripeptide gives the following products on Edman degradation.

The tripeptide is
(a) Phe-Ala-Gly
(b) Phe-Gly-Ala
(c) Ala-Gly-Phe
(d) Gly-Ala-Phe
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Since, Edman degradation occur from N – T – AA. So, the sequence is Phe – Ala – Gly.
Correct option is (a)
62. In the 1H NMR spectrum recorded at 293 K, an organic compound (C3H7NO), exhibited signals at  7.8 (1.H, s), 2.8 (3H, s) and 2.6 (3H, s). The compound is
7.8 (1.H, s), 2.8 (3H, s) and 2.6 (3H, s). The compound is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. DMF appears in two forms as shown below

At lower temperature DMF remains in form-2 prefentially
In form-2 methyl groups are chemically non – equivalent and they appears as singlets at 2.8 and 2.6 ppm.
Singlet at 7.8 ppm appears due to olefinic proton of form-2.
Correct option is (a)
63. In the IR spectrum of p-nitrophenyl acetate, the carbonyl absorption band appears at
(a) 1670 cm–1
(b) 1700 cm–1
(c) 1730 cm–1
(d) 1760 cm–1
Ans. d
Sol. C = O structure occurs at cm–1
1750 – 1735 cm–1 for aliphatic esters.
1740 – 1715 cm–1 if C = O conjugated with aromatic.
1765 – 1762 cm–1 if oxygen atom is conjugated with alkene or aromatic.
Example: Phenyl acetate 1765cm–1
p – nitrophenyl acetate 1761 cm–1.

Correct option is (d)
64. The absolute configuration at the two chiral centres of (–)–camphore is:

(a) 1R, 4R
(b) 1R, 4S
(c) 1S, 4R
(d) 1S, 4S
Ans. d
Sol. According to CIP Priorities

View from inside the cavity,
Bridging group always denote, above the plane.

Correct option is (d)
65. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
66. The first person to separate a racemic mixture into individual enantiomers is:
(a) J, H van't Hoff
(b) Pasteur
(c) H.E. Fischer
(d) F. Wohler
Ans. b
Sol. L. Pasteur has isolated individual isomers first time. Pasteur separated the left and right crystal shapes from each other to form two piles of crystals.

Correct option is (b)
67. Consider the following statements for [18]–annulene
(A) It is aromatic
(B) The inner protons reasonate at  in its 1H NMR spectrum
in its 1H NMR spectrum
(C) There are six protons in the shielded zone.
(a) A, B, C
(b) A and B only
(c) B and C only
(d) A and C only
Ans. d
Sol. [18] annulene is aromatic compound and shows ring current
The ring current produces strong induced magnetic field.
Outer 12 protons appears at 8.9 ppm because they remains in deshielding zone.
Inner six protons appears at – 1.8 ppm because they remains in shielding zone (up – field)
Hence, statement A and C are correct.

Correct option is (d)
68. In the compound given below, the relation between HA, HB; and between Br1, Br2 is:

(a) HA, HB are enantiotopic; and Br1, Br2 are diastereotopic
(b) HA, HB are diastereotopic; and Br1, Br2 are enantiotropic
(c) HA, HB are diastereotopic; and Br1, Br2 and homotopic
(d) HA, HB are enantiotropic; and Br1, Br2 are homotopic
Ans. b
Sol. 
Molecule has a plane of symmetry bisecting HA and HB reflecting Br1/Br2 and CH3/CH3.
Br1 and Br2 are reflected by plane so they are enantiotopic to each other.
HA and HB are bisecting by plane. Hence, they are diasterotopic to each other.
Correct option is (b)
69. The most appropriate reagent to effect the following chemoselective conversion is:

(a) HC1, EtOH, reflux
(b) Bu4NF
(c) K2CO3, MeOH
(d) CF3 COOH, EtOh, rt.
Ans. c
Sol. 
The hydrolysis of ester is faster in alkaline medium. So, the correct answer will be K2CO3, MeOH.
Correct option is (c)
70. Among the following, an example of a "Green Synthesis" is
(a) Synthesis of malachite green
(b) Friedel-Craft's acylation of anisole with Ac2O/anhydrous A1C13.
(c) Jones' oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid.
(d) Diels-Alder reaction of furan and maleic acid in water.
Ans. d
Sol. (i) Synethesis of Malachite green

(ii) Friedel – Craft's acylation of anisole with Ac2O/AlCl3.

In this reaction using reagent as well as product is toxic.
(iii) Jones oxidation of benzyl alchohol to benzoic acid.

In this reaction using reagent as hazardous for body.
(iv) Diels – Alder reaction of Furan and Maleic acid in water.

Diels – Alder reaction is the case of Green synthesis.
Correct option is (d)
71. The recoil energy of a Mossabauer nuclide of mass 139 amu is 2.5 MeV. The energy emitted by the nucleus in keV is:
(a) 12.5
(b) 15.0
(c) 20.5
(d) 25.0
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
72. Complexes of general formula, fac [Mo(CO)3(phosphite)3] have the C–O stretching bands as given below,
Phosphines: PF3(A); PCI3(B); P(Cl)Ph2(C); PMe3(D)
v(CO), cm–1,: 2090(i); 2040(ii); 1977(iii), 1945 (iv)
The correct combination of the phsphine and the stretching frequency is,
(a) (A-i), (B-ii), (C-iii), (D-iv)
(b) (A-ii), (B-i), (C-iv), (D-iii)
(c) (A-iv), (B-iii), (C-ii), (D-i)
(d) (A-iii), (B-iv), (C-i), (D-ii)
Ans. a
Sol. As the  – accepting abilities of phosphine increases vc–o stretching frequency of the complex increases. So, the order of
– accepting abilities of phosphine increases vc–o stretching frequency of the complex increases. So, the order of  – accepting abilities among the given phosphine is:
– accepting abilities among the given phosphine is:

Correct option is (a)
73. On subjecting 9.5 ml solution of Pb2+ of X M to polarographic measurements, Id was found to be  When 0.5 mL of 0.04 M pb2+ was added before the measurement, the Id was found to be 1.25
When 0.5 mL of 0.04 M pb2+ was added before the measurement, the Id was found to be 1.25 
(a) 0.0035
(b) 0.0400
(c) 0.0067
(d) 0.0080
Ans. c
Sol. Correct answer is (c).
74. Match each item from the List-I (compound in solvent) with that from the List-II (its behaviour) and select the correct combination using the codes given below.

(a) (A-i), (B-ii), (C-iii), (D-iv)
(b) (A-ii), (B-i), (C-iii), (D-iv)
(c) (A-iii), (B-iv), (C-ii), (D-i)
(d) (A-iv), (B-ii), (C-iii), (D-i)
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
75. Structure of a carborane with formula, C2B2H8 is formally derived from
(a) Closo-borane
(b) Nido-borane
(c) Arachno-borane
(d) Conjuncto-borane
Ans. b
Sol. C2B4H8
(BH)2B4H8; B2H2B4H8

Correct option is (b)
76. Boric acid is a weak acid in aqueous solution. But its acidity increases significantly in the presence of ethylene glycol, because
(a) ethylene glycol releases additional H+
(b) B(OH)4– is consumed in forming a compound with ethylene glycol.
(c) ethylene glycol neutralizes H+ released by boric acid.
(d) Boric acid dissociates better in the mixed-solvent.
Ans. b
Sol. 
In presence of ethylene glycol, B(OH)4– is consumed as shown below and boric acid behaves as strong acid.

Correct option is (b)
77. Coordination number of "C" in Be2C3 whose structure is correlated with that of CaF2, is:
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Ans. d
Sol. In Be2C3; Be+ = In tetrahedral voids.

 = In FCC arrangement (Lattice point at corner + at each face centre)
= In FCC arrangement (Lattice point at corner + at each face centre)
Therefore, coordination number of Be+ = 4
And coordination number of 
Correct option is (d)
78. For the molecule below,

Consider the following statements about its room temperature spectral data.
(A) 1H NMr has singlets at 5.48 and 3.18 ppm
(B) 1H NMR has multiplet at 5.48 and singlet at 3.18 ppm
(C) IR has CO stretching bands at 1950 and 1860 cm–1
(D) 1R has only one CO stretching band at 1900 cm–1.
The correct pair of statement is.
(a) A and C
(b) B and C
(c) A and D
(d) B and D
Ans. a
Sol. 
Since, the molecule is C2 – symmertric. So, two CO's will give two absorption band in IR spectrum
Correct option is (a)
79. In the cluster  obeying 18e rule, the number of metal-metal bonds and the bridgind ligands respectively, are.
obeying 18e rule, the number of metal-metal bonds and the bridgind ligands respectively, are.
(a) 3 and 1 CH
(b) 0 and 3 CO
(c) 3 and 1 CO
(d) 6 and 1 CH
Ans. a
Sol. The structure of cluster [Co3(CH)(CO)9]

So, the number of M – M bond = 3 and bridging ligand = 1 CH
Correct option is (a)
80. Consider the fions Eu(III), Gd(III), Sm(II) and Lu(III). The observed and calculated magnetic moment values are closest for the pair.
(a) Gd(III), Lu(III)
(b) Eu(III), Lu(III)
(c) Sm(III), Gd(III)
(d) Sm(IIII), Eu(III)
Ans. a
Sol. The electronic configuration of Gd3+ and Lu3+ are 4f7 and 4f7 and 4f14, for this ions total angular momentum is zero i.e. there is no orbital contribution. Therefore, calculated and observed values of magnetic moment are closest for this pair.
Correct option is (a)
81. Silicates with continuous 3D frame work are
(a) Neso-silicates
(b) Soro-silicates
(c) Phyllo-silicates
(d) Tecto-silicates
Ans. d
Sol. Correct answer is (d)
82. The correct spinel structure of  is:
is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. Co3O4 is a normal spinel. In normal spinel the Co2+ ions occupy tetrahedral voids and Co3+ ions occupy octahedral voids. Therefore, spinel structure Co3O4 is (Co2+)t(2Co3+)0O4.
Correct option is (d)
83. In the solid state, the  ion has two types of bonds. These are
ion has two types of bonds. These are
(a) Three long and two short
(b) Two long and three short
(c) One long and four short
(d) Four long and one short
Ans. a
Sol. In trigonal bipyramidal complexes, the two ligands lie on z – axis and the three in xy plane somewhere in between the axes. In xy plane, there are four electrons and on z – axis there is only one electron in  orbital (Electronic Configuration,
orbital (Electronic Configuration, 
Correct option is (a)
84. In metalloenzymes, the metal centres are covalently linked through the side chains of the amino acid residues. The correct set of amino acids which are involved in the primary coordinates spheres of metalloenzymes is
(a) Ala, Leu, His
(b) Glu, His, Cys
(c) Leu, Glu, Cys
(d) Ala, His, Glu
Ans. b
Sol. So, it creat chiral environment across the catalyst.
Correct option is (b)
85. Consider the catalyst in column-I and reaction in column-II

The best match of a catalyst of column-I with the reaction nuclear column-II is
(a) (A-ii), (B-i), (C-iv), (D-iii)
(b) (A-i), (B-ii), (C-iii), (D-iv)
(c) (A-iii), (B-i), (C-iv), (D-ii)
(d) (A-iv), (B-iii), (C-ii), (D-i)
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
86. A solution of 2.0 g of brass was analysed for Cu electro gravimetrically using Pt-gauze as electrode. The weight of Pt-gauze changes from 14.5g to 16.0 g. The percentage weight of Cu in brass is
(a) 50
(b) 55
(c) 60
(d) 75
Ans. d
Sol. The weight of Pt – gauze as electrode increases by 16–14.5 = 1.5 g because 1.5 g of Cu is deposited on Pt – gauze. Therefore, weight of Cu in 2.0 gram brass is 1.5 g.
Therefore, percentage weight of Cu in brass 
Correct option is (d)
87. The platinum complex of NH3 and Cl-ligands is an anti-tumour agent. The correct isomeric formula of the complex and its precusor are.
(a) cic–Pt(NH3)2Cl2 and PtCl42–
(b) trans–Pt(NH3)2Cl and PtCl42–
(c) cis–Pt(NH3)2Cl2 and Pt(NH3)42+
(d) trans–Pt(NH3)2Cl2 and Pt(NH3)42–
Ans. a
Sol. 
Correct option is (a)
88. Successive addition of NaCl, H3PO4, KSCN and NaF to a solution of Fe(NO3)3.9H2O gives yellow, colourless, red and again colorless solutions due to the respective formation of:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. When Fe(NO3)3.9H2O) is dissolved in water, the complex ion [Fe(H2O)6]3+ is formed .

Correct option is (a)
89. Which one of the following will NOT undergo oxidative addition by methyl iodide?
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
90. In hydrofomylation reaction using  as the catalyst, addition of excess PPh3 would
as the catalyst, addition of excess PPh3 would
(a) Increase the rate of reaction
(b) decrease the rate of reaction
(c) not influence of the rate of reaction
(d) stop the reaction
Ans. b
Sol. 
18 electron species in excess PPh3 it becomes 20 electron species but the active catalyst is 16 electron species. So, in presence of excess PPh3. Teh rate of hydroformylation will be decreases.
Correct option is (b)
91. Find out the number of lines in the 31P NMR signal for

(a) 3
(b) 6
(c) 18
(d) 90
Ans. d
Sol. 
Four H1 are equivalent. Two nitrogen are equivalent.
Two flurone are equivalent. One 2H is separate.

Correct option is (d)
92. The rate of exchange of OH2 present in the coordination sphere by 18OH2 of, (i) [Cu(OH)2)6]2+, (ii) [Mn(OH2)6]2+, (iv) [Ni(OH2)6]2+, follows an order
(a) (i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv)
(b) (i) > (iv) > (iii) > (ii)
(c) (ii) > (iii) > (iv) > (i)
(d) (iii) > (i) > (iv) > (ii)
Ans. a
Sol. The rate of water exchange in  is fastest due to Jahan – Teller distortion. For other three complexes of 3d – series dipositive metal cation. The rate of water exchange decreases with increase in effective nuclear charge and decrease in size.
is fastest due to Jahan – Teller distortion. For other three complexes of 3d – series dipositive metal cation. The rate of water exchange decreases with increase in effective nuclear charge and decrease in size.
Correct option is (a)
93. Based on the behaviour of the metalloenzymes, consider the following statements
(A) In the enzymes, the zinc activates O2 to form peroxide species.
(B) In the enzymes, the zinc activates H2O and provides a zinc bound hydroxide.
(C) In the oxidases, the iron activates O2 to break the bonding between the two oxygens.
(D) Zinc ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at the peptide carbonyl
The set of correct statements is,
(a) A and B
(b) B and C
(c) C and D
(d) A and D
Ans. b
Sol. Because zinc is a Lewis acid and hence,

However, oxidase are enzyme that catalyse the reduction of O2 H2O or H2O2.
H2O or H2O2.

Correct option is (b)
94. Fe2+ –porphyrins fail to exhibit reversible oxygen transport and cannot differentiate CO from O2. However, the hemoglobin is free both these pit falls. Among the following.
(A) Fe2+ – porphyrins undergo  formation and the same is prevented in case of the hemoglobin.
formation and the same is prevented in case of the hemoglobin.
(B) Fe–CO bond strength is much low in case of hemoglobin when compared to the Fe2+ – porphyrins.
(C) While Fe–CO is linear, Fe-O, is bent and is recognized by hemoglobin.
(D) The interlinked four monomeric units in the hemoglobin are responsible to overcome the pitfalls.
The correct set of statements is
(a) A and B
(b) A and C
(c) C and D
(d) B and D
Ans. b
Sol. Free heme (i.e. without globular protein chain) if foms  oxodimer) i.e.
oxodimer) i.e.

Correct option is (b)
95. Reactions A and B are, termed as respectively.

(a) Insertion, Metathesis
(b) Metathesis, insertion
(c) Oxidative, addition, metathesis
(d) Oxidative addition, insertion
Ans. a
Sol. Since SnCl2 will behaves as a carbene and it insert into the M – M bond. So, it is a kind of insertion reaction.

Correct option is (a)
96. A metal crystallizens in fee structure with a unit cell side of 500 pm. If the density of the crystal is 1.33 g/cc, the molar mass of the metal is close to
(a) 23
(b) 24
(c) 25
(d) 26
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
97. The activation energy for the biomoecular reaction A + BC  AB + C is E0 in the gas phase. If the reaction is carried out in a confined volume
AB + C is E0 in the gas phase. If the reaction is carried out in a confined volume  the activation energy is expected to
the activation energy is expected to
(a) remain unchanged
(b) increase with decreasing 
(c) decrease with decreasing 
(d) oscillate with decreasing 
Ans. c
Sol. Smaller the volume the greater will be possibility of collisions and therefore the activation energy will decrease.
Correct answer is (c)
98. In ammany-electron atom, the total orbital angular momentum (L) and spin (S) are good quantum numbers instead of the individual orbital (l1,l2) and spin (s1, s2) angular momenta in the presence of
(a) inter-electron repulsion
(b) spin-orbit interaction
(c) hyperfine coupling
(d) external magnetic field
Ans. a
Sol. In many electron atom, there is strong electron – electron i.e. inter – electron repulsion. Due to inter – electron repulsion, the orbital angular momentum (l1, l2) as well as spin angular momenta (s1, s2) are coupled together to give total orbital angular momentum (L) and spin (S).
Correct option is (a)
99. The packing fraction of a simple cubic lattice is close to
(a) 0.94
(b) 0.76
(c) 0.52
(d) 0.45
Ans. c
Sol. 
For simple cubic lattice,
Number of particles per unit cell = 1

where, r = radius of one particle and a = unit cell edge length.
Then the total volume of the unit cell = a3.

Correct option is (c)
100. The number of IR active vibrational modes of pyridine is:

(a) 12
(b) 20
(c) 24
(d) 33
Ans. c
Sol. C5H5N

C2v point group
Reducible represented by 3N coordinates as basis sets.

R.R.= 11A1+4A2+7B1+11B2
Rotational = A2 + B1 + B2
Transitional = A1 + B1 + B2
Vibrational = 10A1 + 3A2 + 5B1 + 9B2 = 27
Out of 27 3A2 are IR inactive.
So, total IR active 10A1 + 5B1 + 9B2
Total = 24 vibrations.
Correct option is (c)
101. One of the excited states of Ti has the electric configuration  The number of microstates with zero total spin (S) for this configuration is
The number of microstates with zero total spin (S) for this configuration is
(a) 9
(b) 15
(c) 27
(d) 60
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
102. For the reaction  in a closed container, the relation between the degree of dissociation.
in a closed container, the relation between the degree of dissociation.  and the equilibrium constant Kp at a fixed temperature is given by
and the equilibrium constant Kp at a fixed temperature is given by
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
103. The fugacity of a gas depends on pressure and the compressibility factor 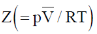 through the relation
through the relation 
For most gases at temperature T and up to moderate pressure, this equation shows that
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Correct option is (a)
104. The internal pressure  of a real gas is related to the compressibility factor
of a real gas is related to the compressibility factor  through the relation
through the relation 
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
105. Suppose, the ground stationary state of a harmonic oscillator with force constant 'k' is given by

Then, A should depend on k as
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. For harmonic oscillator, the ground state wave function is,

Correct option is (c)
106. Combining two real wave functions  the following functions are constructed:
the following functions are constructed: 
 The correct statement will then be
The correct statement will then be
(a) A and B represent the same state
(b) A and C represent the same state
(c) A and D represents the same state
(d) B and D represent the same state.
Ans. c
Sol. Combining two real wave function  constructed functions
constructed functions  represent the same state because if these two function multiplied by any constant, no effect on the state and on the energy because multiply only in the eigenvalue, no effect on the energy and no affect on the wavefunction. If we use any eignfunction which given eigenvalue. If multiply by any constant not change in the eignfunction and no change in the energy of the state. Energy is same, so state is same only change in eigenvalue.
represent the same state because if these two function multiplied by any constant, no effect on the state and on the energy because multiply only in the eigenvalue, no effect on the energy and no affect on the wavefunction. If we use any eignfunction which given eigenvalue. If multiply by any constant not change in the eignfunction and no change in the energy of the state. Energy is same, so state is same only change in eigenvalue.
Correct option is (c)
107. Crystal A diffracts from (1 1 1) and (2 0 0) planes but not from (1 1 0) plane, while the crystal B diffracts from (1 1 0) and (2 0 0) planes but not from the (1 1 1) plane. From the above, we may conclude that
(a) A has fcc lattice while B has bcc lattice
(b) A has bcc lattice while B has fcc lattice
(c) A and D represents the same state
(d) A and B both have bcc lattice.
Ans. a
Sol. We know that, selection rule for allowed reflection for BCC and FCC lattice is
BCC h + k + l should be even
FC h, k, l all either even or odd.
Correct option is (a)
108. The decomposition of NH3 on Mo surface follows Langmuir-Hinshelwood mechanism. The decomposition was carried out at low pressures. The initial pressure of NH3 was 10–2 torr. The pressure of NH3 was reduced to 10–4 torr in 10 minutes. The rate constant of decomposition of NH3 is:
(a) 9.9 × 10–4 torr min–1
(b) 0.4606 min–1
(c) 9.9 × 10–3 torr min–1
(d) 0.693 min–1
Ans. b
Sol. At low pressure Langmuir Hinshelwood mechanism follows first order kinetics.

Correct option is (b)
109. A polymer sample has the following composition.

The polydispersity index (P.D.I.) of the polymer is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option (c)
110. The equilibrium constant for an electrochemical reaction,

(a) 1010
(b) 1020
(c) 1030
(d) 1040
Ans. b
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
111. A bacterial colony grows most commonly by cell division. The change in the population due to cell division in an actively growing colony is  The population of bacterial colony at time 't' is
The population of bacterial colony at time 't' is 
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. Radioactive process follows first order kinetics and rate law expression is,

Here, Since bacterial colony is growing i.e. concentration is increasing with increasing time.
Correct option is (c)
112. The Arrhenius parameters for the thermal decomposition of NOCI, 2NOCl(g) 2N(g)+Cl2(g), are A = 1013M–1s–1, Ea = 105 kJ mol–1 and RT = 2.5 kJ mol–1. The enthalpy (in kJ mol–1) of the activated complex will be
2N(g)+Cl2(g), are A = 1013M–1s–1, Ea = 105 kJ mol–1 and RT = 2.5 kJ mol–1. The enthalpy (in kJ mol–1) of the activated complex will be
(a) 110
(b) 105
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
113. The rotational partition function of H2 is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. 

Correct option is (d)
114. The potential in Debye-Hückel theory is proportional to
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans.
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
115. The vibrational frequency and anharmonicity constant of an alkali halide are 300 ch–1 and 0.0025 respectively. The positions (in cm–1) of its fundamental mode and first overtone are respectively.
(a) 300, 600
(b) 298.5, 595.5
(c) 301.5, 604.5
(d) 290, 580
Ans. b
Sol. 
Correct option is (b)
116. The adsorption of a gas is described by the Langmuir isotherm with the equilibrium constant K=0.9kPa–1 at 250C. The pressure 9in kPa) at which the fractional surface coverage is 0.95, is
(a) 1/11.1
(b) 21.1
(c) 11.1
(d) 42.2
Ans. b
Sol. Langmuir isotherm is given as

Correct option is (b)
117. The energy of a harmonic oscillator in its ground state is  According to the virial theorem, the average kinetic (T) and potential (V) energies of the above are
According to the virial theorem, the average kinetic (T) and potential (V) energies of the above are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. The energy of a harmonic oscillator in its ground state is 
According to Virial Theorem for SHO
Every contribution is equal for kinetic energy operator and potential energy operator.

 energy contribution is equal for K and V.
energy contribution is equal for K and V.
Correct option is (a)
118. The energy of a hydrogen atom in a state is  (RH=Ryberg constant). The degeneracy of the state will be.
(RH=Ryberg constant). The degeneracy of the state will be.
(a) 5
(b) 10
(c) 25
(d) 50
Ans. c
Sol. Energy of a hydrogen in a state is 
Degeneracy gn = n2. (for hydrogen atom)
If spin include 
Compare with equation (1), n2 = 25 Degeneracy = 25
Correct option is (c)
119. The trial wave function of a system is expanded as  The matrix elements of the Hamiltonian are
The matrix elements of the Hamiltonian are  The approximate ground-state energy of the system from the linear variational principle is
The approximate ground-state energy of the system from the linear variational principle is
(a) –1.0
(b) –2.0
(c) +4.0
(d) +5.0
Ans. c
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
120. One molecular orbital of a polar molecule AB has the form  where
where  are normalized atomic orbitals centred on A and B, respectively. The electron in this orbitalis found on atom B with a probability of 90%. Neglecting the overlap between
are normalized atomic orbitals centred on A and B, respectively. The electron in this orbitalis found on atom B with a probability of 90%. Neglecting the overlap between  a possible set of cA and cB is:
a possible set of cA and cB is:
(a) cA = 0.95, cB = 0.32
(b) cA = 0.10, cB = 0.90
(c) cA = –0.95, cB = 0.32
(d) cA = 0.32, cB = 0.95
Ans. d
Sol. 
Correct option is (d)
121. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid exhibited signals at  171, 162, 133, 122 and 116 ppm in its broadband decoupoled 13C NMR spectrum. The correct assignment of the signals is
171, 162, 133, 122 and 116 ppm in its broadband decoupoled 13C NMR spectrum. The correct assignment of the signals is
(a)  171 (C – 4), 162 (COOH), 133 (C – 3 & 5), 122 (C – 1) and 116 (C – 2 & 6)
171 (C – 4), 162 (COOH), 133 (C – 3 & 5), 122 (C – 1) and 116 (C – 2 & 6)
(b)  171 (COOH), 162 (C – 4), 133 (C – 2 & 6), 122 (C – 1) and 116 (C – 3 & 5)
171 (COOH), 162 (C – 4), 133 (C – 2 & 6), 122 (C – 1) and 116 (C – 3 & 5)
(c)  171 (C – 4), 162 (COOH), 133 (C – 2 & 6), 122 (C – 1) and 116 (C – 3 & 5)
171 (C – 4), 162 (COOH), 133 (C – 2 & 6), 122 (C – 1) and 116 (C – 3 & 5)
(d)  171 (COOH), 162 (C – 4), 133 (C – 3 & 5), 122 (C – 1) and 116 (C – 2 & 6)
171 (COOH), 162 (C – 4), 133 (C – 3 & 5), 122 (C – 1) and 116 (C – 2 & 6)
Ans. b
Sol. 
Positions – 3 is most shielded because of ortho – to OH and meta to COOH. So, it will appear at 116 ppm.
Position–1 is shielded because it is para – to OH. It will upper 122 ppm.
If we compare position 2 and 4 position 4 is deshielded due to directly attached OH and it will appear at 162 ppm.
Position is normal and appear at 133 ppm.
Correct option is (b)
122. An organic compound (C9H10O3) exhibited the following spectral data:
IR: 3400, 1680 cm–1;
1H NMR:  7.8 (1H, d, J = 8 Hz), 7.0 (1 H, d, J = 8Hz), 6.5 (1 H, s), 5.8 (1 H, s, D2O exchangeable), 3.9 (3H, s), 2.3 (3 H, s).
7.8 (1H, d, J = 8 Hz), 7.0 (1 H, d, J = 8Hz), 6.5 (1 H, s), 5.8 (1 H, s, D2O exchangeable), 3.9 (3H, s), 2.3 (3 H, s).
The compounds is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. d
Sol. All of the compounds given 1 – 4 will give same number of signals and their multiplicity in their NMR spectrum.
The key parameter to assign the correct structure will be chemical shift of aromatic protons.
The most shielded singlet 1H signal in aromatic region is at 6.5 ppm is possible.
In structure 4 only. Because Ortho to OH, Ortho to OMe Meta to COMe

Correct option is (d)
123. The  of a 90% optically pure 2–arylpropanoic acid solution is +1350. On treatment with a base at RT for one hour,
of a 90% optically pure 2–arylpropanoic acid solution is +1350. On treatment with a base at RT for one hour,  changed to + 1200. The optical purity is reduced to 40% after 3 hours. If so, the optical purity of the solution after 1 hour, and its
changed to + 1200. The optical purity is reduced to 40% after 3 hours. If so, the optical purity of the solution after 1 hour, and its  after 3 hours, respectively, would be
after 3 hours, respectively, would be
(a) 80% and 600
(b) 70% and 400
(c) 80% and 900
(d) 70% and 600
Ans. a
Sol. Optically purity also known as enantiomeric excess a compound of 90% B.E. shows 1350 specific rotation.
So, its 100% optically pure isomer will show  specific rot.
specific rot.
At one hour the specific rotation reduced to 1200. So, E.E, or optical purity 
At three hours optical purity is 40%. So, specific rotation 
The over all relation of optical purity, composition and specific rotation can be summarized in the table.

Correct option is (a)
124. In the following pericyclic reaction, the structure of the allene formed and its configuration are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. 
3,3 sigmatropic belong to 4n + 2 system and 4n + 2 system undergo photochemical reaction under thermal condition with retention in configuration takes place. So, the stereochemistry of –Me and –Ph group maintain
Correct option is (a)
125. In the following sequence of pericyclic reactions X and Y are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (c)
126. The major product formed in the following reaction is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. This reaction is believed to proceed through deprotonation, 3,3, sigmatropic rearrangement and ketoenol tautomerism.
Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

127. The following conversion involves.

(a) a 1, 3–dipolar species as reactive intermediate, and a cycloaddition.
(b) a carbneium ion as reactive intermediate, and a cycloaddition.
(c) a 1, 3–dipolar species as reactive intermediate, and an aza Witting reaction.
(d) a carbanion as reactive intermediate, and an aza Cope rearrangement.
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as



Now, the 1, 3 dipolar species will Undergo cycloaddition reaction as shown below.
Correct option is (a)
128. The following transformation involves

(a) an iminium ion, [3, 3] – sigmatropic shift and Mannich reaction.
(b) a nitrenium ion, [3, 3] – sigmatropic shift and Michael reaction.
(c) an iminium ion, [1, 3] – sigmatropic shift and Mannich reaction.
(d) a nitrenium ion, [1, 3] – sigmatropic shift and Michael reaction.
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (a)
129. With respect to the following biogenetic conversion of chrismic acid (A) to 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid (C), the correct statement is

(a) X is Claisen rearrangement; Y is oxidative decarboxylation.
(b) X is Fries rearrangement; Y is oxidative decarboxylation.
(c) X is Fries rearrangement; Y is dehydration.
(d) X is Claisen rearrangement; Y is dehydration.
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

So, this reaction is Claisen rearrangement and oxidative decarboxylaton.
Correct option is (a)
130. Math the following

(a) (i) - (C), (ii) - (D), (iii) - (B), (iv) - (A)
(b) (i) - (B), (ii) - (A), (iii) - (C), (iv) - (D)
(c) (i) - (C), (ii) - (B), (iii) - (D), (iv) - (A)
(d) (i) - (A), (ii) - (D), (iii) - (B), (iv) - (C)
Ans. a
Sol. 


Correct option is (a)
131. In the following reaction, the structure of B, and the mode of addition are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. 
The above case belong to aldol condensation. In aldol condensation two types enolate are formed as intermediate
(i) Z enolate (ii) E enolate
The formation of a particular enolate depends upon the carbonyl compound. For example.


Z enolate give syn product. E enolate give anti product.
In the product the stereochemistry of – OH and CH3 is syn. So, Z enolate participate in reaction.




The enolate is Z. So, syn product will be form and Re face of carbonyl compound and Si face of enolate.
132. In the following reaction A and B are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

The Grignard reagent give monosubstitution with Wein – Reb amide.

Correct option is (a)
133. Match the following biochemical transformations with coenzymes involved

(a) (i)-(D), (ii)-(A), (iii)-(C)
(b) (i)-(A), (ii)-(B), (iii)-(D)
(c) (i)-(B), (ii)-(A), (iii)-(C)
(d) (i)-(D), (ii)-(B), (iii)-(C)
Ans. a
Sol. Correct option is (a).
134. The structure of major product B formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (a)
135. Given the energy of each gauch butane interaction is 0.9 kcal/mol,  value of the following reaction is
value of the following reaction is

(a) 0.9 kcal/mol
(b) 1.8 kcal/mol
(c) 2.7 kcal/mol
(d) 3.6 kcal/mol
Ans. b
Sol. 
one 1, 3 interaction energy is 0.9 kcal/mol. So, Total energy 2 × 0.9 = 1.8 kcal / mol
Correct option is (b)
136. In the following reaction, the reagent A and the major product B are

(a) A =  ; B =
; B = 
(b) A =  ; B =
; B = 
(c) A =  ; B =
; B = 
(d) A =  ; B =
; B = 
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

The formation of product B takes place via hydrogenolysis by H2, 10%, Pd/C. Hydrogenolysis of cyclopropane takes place via H2, 10% pd/C and least hindered bond will break.
Correct option is (a)
137. The major product formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. c
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as

Correct option is (c)
138. 12.0 g of acetophenone on reaction with 76.2 g of iodine in the presence of aq. NaOH gave solid A in 75% yield. Approximate amount of A obtained in the reaction and its structure are
(a) 80 g, Cl4
(b) 40 g, Cl4
(c) 60 g, CHI3
(d) 30 g, CHI3
Ans. d
Sol. lodoform reaction, 


Correct option is (d)
139. 
The steps A, B and C, respectively, are
(a) Oxidative addition; transmetallation; reductive elimination.
(b) Oxidative addition; carbopalladation;  elemination.
elemination.
(c) Carbopalladation; transmetallation; reductive elimination.
(d) Metal halogen exchange; transmetallation; metal extrusion.
Ans. a
Sol. Step (A) is O.a. because the oxidation state of the metal is increased by two units.

Step (B) is transmetallation because the ligand is transferring from one metal to another metal.
Step (C) is reductive elimination because the oxidation state of the metal is increased by two units.

Correct option is (a)
140. The major product formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as



Second step is an example of Dakin reaction.
Correct option is (b)
141. The major product B formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as


Correct option is (a)
142. The major product B formed in the following reaction sequence is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as





Correct option is (a)
143. The osazone A could be obtained from

(a) glucose and mannose
(b) mannose and galactose
(c) glucose and fructose
(d) galactose and fructose
Ans. a
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as


So, the osazone (A) could be obtained from D – glucose and D – mannose.
Correct option is (a)
144. The major product formed in the following reaction is:

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. b
Sol. Chemical reaction involved in the above transformation can be illustrated as



Correct option is (b)
145. In the following enantioselective reaction, the major product formed is

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. a
Sol. Correct option is (a)
