GATE Syllabus 2026:IIT Guwahati will conduct GATE Exam 2026 for admission to M.E./M.Tech or PhD courses in most reputed institutes of India. GATE Scorecard 2026 can be used for PSUs jobs for Engineering trainees, management trainees, and other positions in different sectors.
Organising body IIT Guwahati has released GATE syllabus 2026 on official website of gate2026.iitg.ac.in with detailed topics. Candidates can download GATE syllabus 2026 in PDF here on this page.
A proper knowledge of GATE syllabus 2026 is compulsory for candidates to build understanding and a strong strategy towards preparation.
Also read GATE Exam
GATE Exam Syllabus 2026
GATE Exam syllabus 2026 covers a broad range of subjects across various engineering disciplines, including:
- General Aptitude (GA): This section includes verbal ability, numerical ability, and logical reasoning, consisting of topics like English grammar, comprehension, quantitative aptitude, and reasoning.
- Core Subject (Engineering Discipline): Syllabus varies depending on branch chosen by candidate. Each discipline (e.g., Civil, Mechanical, Electrical, Computer Science, etc.) includes:
-
-
- Engineering Mathematics (mathematical concepts related to specific field).
- Subject-specific topics like Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics, Circuits, Structural Analysis, Algorithms, etc.
-
- Engineering Mathematics (common to most branches): Covers topics like linear algebra, calculus, probability, differential equations, and complex variables.
GATE Exam 2026 assesses knowledge, understanding, and problem-solving abilities in these subjects. It comprises multiple-choice and numerical answer-type questions.
In GATE Exam 2026, candidates can choose either one or two papers for entrance exam by filling a single application form. Important to note that candidates can only select paper combinations that are allowed on official website. Each GATE paper will be worth 100 marks, with General Aptitude (GA) section contributing 15 marks. The remaining 85 marks will be dedicated to core subject of chosen paper.
GATE Exam Full Guide 2026 🎯 | Eligibility, Jobs, Scope, Benefits & More | VedPrep Chem Academy
GATE Syllabus 2026 Overview
GATE Syllabus 2026 related information, such as full form, organising authority, gate syllabus release date, official website, papers sectional part, exam dates, are given in table below
| GATE Syllabus 2026 Overview | |
| Particulars | Details |
| Exam Name | GATE 2026 |
| GATE Full Form | Graduate Aptitude Test In Engineering |
| Organizing Authority | IIT Guwahati |
| GATE Syllabus 2026 Release Date | 5 August 2025 |
| GATE Syllabus 2026 Official Website | https://gate2026.iitg.ac.in/ |
| Sections in GATE Syllabus 2026 |
|
| Total No. of Papers | 30 |
| GATE Exam Date 2026 | February 7, 8, 14, 15, 2026 |
| GATE 2026 Official Website | gate2026.iitg.ac.ac.in |
IIT Guwahati GATE Syllabus 2026
Candidates who preparing for GATE Exam 2026 must be familiar with IIT Guwahati GATE Syllabus 2026 released on Official website. IIT Guwahati has released official GATE Syllabus 2026 along with GATE Notification 2026 on 5 August 2025.
| IIT Guwahati GATE Syllabus 2026 official link |
GATE Syllabus 2026 Subject List
GATE syllabus 2026 subject list with paper code is given in table below
| GATE Syllabus 2026 Subjects List | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aerospace Engineering | AE |
| 2 | Agricultural Engineering | AG |
| 3 | Architecture and Planning | AR |
| 4 | Biotechnology | BT |
| 5 | Civil Engineering | CE |
| 6 | Chemical Engineering | CH |
| 7 | Computer Science and Information Technology | CS |
| 8 | Chemistry | CY |
| 9 | Electronics and Communication Engineering | EC |
| 10 | Electrical Engineering | EE |
| 11 | Ecology and Evolution | EY |
| 12 | Geology and Geophysics | GG |
| 13 | Instrumentation Engineering | IN |
| 14 | Mathematics | MA |
| 15 | Mechanical Engineering | ME |
| 16 | Mining Engineering | MN |
| 17 | Metallurgical Engineering | MT |
| 18 | Petroleum Engineering | PE |
| 19 | Physics | PH |
| 20 | Production and Industrial Engineering | PI |
| 21 | Textile Engineering and Fiber Science | TF |
| 22 | Statistics | ST |
| 23 | Biomedical Engineering | BM |
| 24 | Engineering Sciences | XE |
| 25 | Life Sciences | XL |
| 26 | Humanities and Social Sciences | XH |
| 27 | Environmental Science and Engineering | ES |
| 28 | Geomatics Engineering | GE |
| 29 | Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering | NM |
| 30 | Data Science and Artificial Intelligence (NEW) | DA |
Also read GATE Participating Institutes
Will there be any change in GATE Syllabus 2026?
Usually, GATE syllabus remains same every year, so GATE 2027 aspirants can also follow this syllabus for their preparation. If minor changes are made, conducting authority will inform.
In recent years, some papers were added, but as of 2025, no additional papers have been introduced. It is likely that this decision will depend on GATE Exam 2026 Conducting Authority, which may or may not choose to add other papers.
GATE Syllabus 2026 For General Aptitude
GATE Syllabus 2026 for General aptitude covers 15% of total marks. The detailed topics of GATE Syllabus 2026 for General aptitude are given in table below
| GATE Syllabus 2026 for General Aptitude | |
|---|---|
| SN. No. | Syllabus |
| 1. | Verbal Ability |
| 2. | Quantitative Aptitude |
| 3. | Analytical Aptitude |
| 4. | Spatial Aptitude |
Also read GATE Cut off
Key Papers GATE Syllabus 2026
GATE Syllabus 2026 outlines subjects and topics for Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering, covering General Aptitude, Engineering Mathematics, and core discipline specific subjects. Each branch, such as Mechanical, Civil, Electrical, and Computer Science, has a specific syllabus, encompassing both fundamental concepts and advanced problem-solving skills.
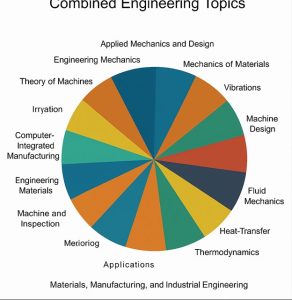
GATE Chemistry Syllabus 2026
GATE Chemistry Syllabus 2026 covers major topics from Inorganic Chemistry, Organic Chemistry, and Physical Chemistry. Detailed GATE Syllabus 2026 for Chemistry with topics and subtopics branch wise is provided in table below
| GATE Chemistry Syllabus 2026 | |
|---|---|
| Topics | Subtopics / Key Concepts |
| Section 1: Physical Chemistry | |
| Quantum Mechanics | Postulates of quantum mechanics; Operators; Time-dependent & time-independent Schrödinger equations; Born interpretation; Dirac bra-ket notation; Particle in box (1D, 2D, 3D), tunnelling; Harmonic oscillator (Hermite polynomials); Rigid rotor; Hydrogen & hydrogen-like atoms; Radial distribution function; Multi-electron atoms; Pauli principle; Slater determinants; Approximation methods (Variation, Perturbation); Atomic units. |
| Molecular Structure & Bonding | Born-Oppenheimer approximation; Valence bond theory; LCAO-MO theory; Hybrid orbitals; LCAO-MO applications to H₂⁺, H₂; MO theory of homo-/heteronuclear diatomics; Hückel approximation (π systems). |
| Group Theory | Symmetry elements & operations; Point groups; Character tables; Internal coordinates & vibrational modes; SALCs; Construction of hybrid orbitals via symmetry. |
| Spectroscopy | Atomic spectroscopy; Russell–Saunders coupling; Term symbols; Selection rules; Rotational, vibrational, electronic & Raman spectra; Line broadening; Einstein coefficients; Transition moment integrals; Molar extinction coefficient; Oscillator strength; NMR basics (gyromagnetic ratio, chemical shift, coupling). |
| Equilibrium & Thermodynamics | Laws of thermodynamics; Standard states; Thermochemical functions; Gibbs–Helmholtz, Maxwell & Gibbs–Duhem relations; van’t Hoff equation; Spontaneity & equilibrium; Partial molar quantities; Mixing thermodynamics; Fugacity & activity; Raoult’s & Henry’s Laws; Ionic mobility & conductivity; Debye–Hückel laws; Electrochemical cells, Nernst equation; Phase rule; Phase diagrams (CO₂, H₂O, S); Fractional distillation, azeotropes, eutectics; Statistical thermodynamics (ensembles, partition function, Boltzmann distribution). |
| Chemical Kinetics | Elementary, parallel, opposing & consecutive reactions; Steady-state approximation; Complex reaction mechanisms; Unimolecular reactions; Transition state theory (Eyring equation); Polymerisation kinetics; Catalysis (homogeneous, enzyme); Kinetic isotope effect; Fast reaction kinetics; Diffusion-controlled & photochemical reactions. |
| Surfaces & Interfaces | Physisorption vs chemisorption; Langmuir, Freundlich & BET isotherms; Surface catalysis (Langmuir–Hinshelwood); Surface tension & viscosity; Self-assembly; Physical chemistry of colloids, micelles, and macromolecules. |
| Section 2: Inorganic Chemistry | |
| Main Group Elements | Hydrides, halides, oxides, oxoacids, nitrides, sulfides; Boranes, carboranes, silicates, borazines, phosphazenes; Allotropes of C, P, S; Noble gases, pseudohalogens, interhalogens; Industrial synthesis; Acid-base theories (Lewis, Brønsted, HSAB). |
| Transition Elements | Coordination compounds: structure, isomerism; Bonding theories (VBT, CFT, MOT); CFSE, Jahn-Teller effect; Electronic spectra (term symbols, Orgel & Tanabe-Sugano diagrams, Racah parameters); Magnetic properties; Reaction mechanisms (substitution, redox); Metal-metal bonds. |
| Lanthanides & Actinides | Recovery, periodic properties, spectra, and magnetism of f-block elements. |
| Organometallic Chemistry | 18-electron rule; Complexes (metal-alkyl, carbonyl, carbene, olefin, metallocenes); Fluxionality; Organometallic reactions; Homogeneous catalysis (hydrogenation, hydroformylation, metathesis, oxidation); Heterogeneous catalysis (Fischer–Tropsch, Ziegler–Natta). |
| Radioactivity | Detection, decay types, half-life, fission and fusion processes. |
| Bioinorganic Chemistry | Ion transport (Na⁺/K⁺), oxygen transport, electron transfer, nitrogen fixation; Metalloenzymes with Mg, Mo, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn. |
| Solid State Chemistry | Crystal systems, lattices, Miller indices, packing, defects; Bragg’s law; Structures (AX, AX₂, ABX₃, spinels); Band theory; Metals & semiconductors. |
| Instrumental Methods | UV–Vis, fluorescence, FTIR, NMR, ESR, mass spectrometry, AAS, Mössbauer, XRD; Chromatography (GC, HPLC); Electroanalytical (polarography, cyclic voltammetry, ion-selective electrodes); Thermoanalytical techniques. |
| Section 3: Organic Chemistry | |
| Stereochemistry | Chirality with/without chiral centres; Absolute & relative configuration; Homotopic/enantiotopic/diastereotopic groups; Stereoselective/specific synthesis; Conformational analysis (acyclic/cyclic); Geometrical & optical isomerism; Atropisomerism; Neighbouring group participation. |
| Reaction Mechanisms | Thermodynamic vs kinetic control; Hammond postulate; Curtin–Hammett principle; Determining mechanisms (kinetics, intermediates, isotopes); Hammett & Taft equations; Nucleophilic/electrophilic substitution (aliphatic & aromatic); Additions to C=C and C=O; Eliminations; Reactive intermediates (carbocations, carbanions, carbenes, nitrenes, arynes, radicals); Molecular rearrangements. |
| Organic Synthesis | Reactions and mechanisms of alkenes, alkynes, arenes, alcohols, phenols, carbonyls, acids, esters, nitriles, halides, amines, amides; Organometallic reagents (Mg, Li, Cu, Zn, B, P, S, Sn, Si); Coupling reactions (Heck, Suzuki, Stille, Sonogashira, Negishi, Kumada, Hiyama, Tsuji-Trost, metathesis, McMurry); Retrosynthetic analysis; Green chemistry & atom economy; Protection/deprotection; Asymmetric synthesis (resolution, chiral auxiliaries, organocatalysis); Enolate, enamine & silyl enol ether chemistry; Cram, Prelog & Felkin–Anh models. |
| Pericyclic & Photochemical Reactions | Electrocyclic, cycloaddition, sigmatropic reactions; FMO, PMO, Woodward–Hoffmann rules; Photochemistry of alkenes, arenes & carbonyls; Photooxidation/reduction; Di-π-methane rearrangement; Barton–McCombie, Norrish type I & II reactions. |
| Heterocyclic Chemistry | Structure, preparation, properties & reactions of furan, pyrrole, thiophene, pyridine, indole, quinoline, and isoquinoline. |
| Biomolecules | Structure, reactions of carbohydrates, amino acids, peptides, proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, steroids, terpenoids, carotenoids, alkaloids. |
| Experimental Techniques | Optical rotation; Chromatography (TLC, column, HPLC, GC); UV–Vis, IR, NMR, Mass spectroscopy for structure elucidation. |
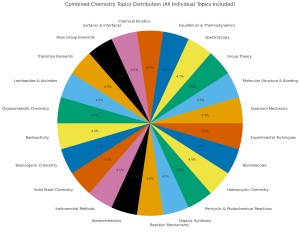
GATE Civil Syllabus 2026
GATE Civil syllabus 2026 covers topics in structural, geotechnical, environmental, and transportation engineering, along with a foundational understanding of mathematics and general aptitude. Detailed GATE syllabus 2026for Civil with topics and subtopics is given in table below
| GATE Civil Syllabus 2026 | |
| Topics | Sub-Topics |
| Structural Engineering | |
| Engineering Mechanics | System of forces, free-body diagrams, equilibrium equations; Internal forces in structures; Frictions and their applications; Centre of mass; Free Vibrations of undamped SDOF system |
| Solid Mechanics | Bending moment and shear force in statically determinate beams; Simple stress and strain relationships; Simple bending theory, flexural and shear stresses, shear centre; Uniform torsion, Transformation of stress; Buckling of column, combined and direct bending stresses |
| Structural Analysis | Statically determinate and indeterminate structures by force/ energy methods; Method of superposition; Analysis of trusses, arches, beams, cables, and frames; Displacement methods: Slope deflection and moment distribution methods; Influence lines; Stiffness and flexibility methods of structural analysis |
| Construction Materials and Management | Construction Materials: Structural Steel – Composition, material properties and behavior; Concrete – Constituents, mix design, short-term and long-term properties. Construction Management: Types of construction projects; Project planning and network analysis – PERT and CPM; Cost estimation |
| Concrete Structures | Working stress and Limit state design concepts; Design of beams, slabs, columns; Bond and development length; Prestressed concrete beams |
| Steel Structures | Working stress and Limit state design concepts; Design of tension and compression members, beams and beam-columns, column bases; Connections – simple and eccentric, beam-column connections, plate girders and trusses; Concept of plastic analysis -beams and frames |
| Geotechnical Engineering | |
| Soil Mechanics | Three-phase system and phase relationships, index properties; Unified and Indian standard soil classification system; Permeability – one-dimensional flow, Seepage through soils – two – dimensional flow, flow nets, uplift pressure, piping, capillarity, seepage force; Principle of effective stress and quicksand condition; Compaction of soils; One- dimensional consolidation, time rate of consolidation; Shear Strength, Mohr’s circle, effective and total shear strength parameters, Stress-Strain characteristics of clays and sand; Stress paths |
| Foundation Engineering | Sub-surface investigations – Drilling boreholes, sampling, plate load test, standard penetration and cone penetration tests; Earth pressure theories – Rankine and Coulomb; Stability of slopes – Finite and infinite slopes, Bishop’s method; Stress distribution in soils – Boussinesq’s theory; Pressure bulbs, Shallow foundations – Terzaghi’s and Meyerhoff’s bearing capacity theories, effect of water table; Combined footing and raft foundation; Contact pressure; Settlement analysis in sands and clays; Deep foundations – dynamic and static formulae, Axial load capacity of piles in sands and clays, pile load test, pile under lateral loading, pile group efficiency, negative skin friction |
| Water Resources Engineering | |
| Fluid Mechanics | Properties of fluids, fluid statics; Continuity, momentum, and energy equations and their applications; Potential flow, Laminar and turbulent flow; Flow in pipes, pipe networks; Concept of boundary layer and its growth; Concept of lift and drag |
| Hydraulics | Forces on immersed bodies; Flow measurement in channels and pipes; Dimensional analysis and hydraulic similitude; Channel Hydraulics – Energy-depth relationships, specific energy, critical flow, hydraulic jump, uniform flow, gradually varied flow, and water surface profiles |
| Hydrology | Hydrologic cycle, precipitation, evaporation, evapotranspiration, watershed, infiltration, unit hydrographs, hydrograph analysis, reservoir capacity, flood estimation and routing, surface runoff models, groundwater hydrology – steady state well hydraulics and aquifers; Application of Darcy’s Law |
| Irrigation | Types of irrigation systems and methods; Crop water requirements – Duty, delta, evapotranspiration; Gravity Dams and Spillways; Lined and unlined canals, Design of weirs on permeable foundation; cross drainage structures |
| Environmental Engineering | |
| Water and Wastewater Quality and Treatment | Basics of water quality standards – Physical, chemical, and biological parameters; Water quality index; Unit processes and operations; Water requirement; Water distribution system; Drinking water treatment; Sewerage system design, quantity of domestic wastewater, primary and secondary treatment. Effluent discharge standards; Sludge disposal; Reuse of treated sewage for different applications |
| Air Pollution | Types of pollutants, their sources and impacts, air pollution quality, air quality standards, Air quality Index and limits |
| Municipal Solid Wastes | Characteristics, generation, collection, and transportation of solid wastes, engineered systems for solid waste management (reuse/ recycle, energy recovery, treatment, and disposal) |
| Transportation Engineering | |
| Transportation Infrastructure | Geometric design of highways – cross-sectional elements, sight distances, horizontal and vertical alignments. Geometric design of railway Track – Speed and Cant. Concept of airport runway length, calculations, and corrections; taxiway and exit taxiway design |
| Highway Pavements | Highway materials – desirable properties and tests; Desirable properties of bituminous paving mixes; Design factors for flexible and rigid pavements; Design of flexible and rigid pavement using IRC codes |
| Traffic Engineering | Traffic studies on flow and speed, peak hour factor, accident study, statistical analysis of traffic data; Microscopic and macroscopic parameters of traffic flow, fundamental relationships; Traffic signs; Signal design by Webster’s method; Types of intersections; Highway capacity |
| Geomatics Engineering | |
| Geomatics Engineering | Principles of surveying; Errors and their adjustment; Maps – scale, coordinate system; Distance and angle measurement – Levelling and trigonometric levelling; Traversing and triangulation survey; Total station; Horizontal and vertical curves. Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing – Scale, flying height; Basics of remote sensing and GIS |
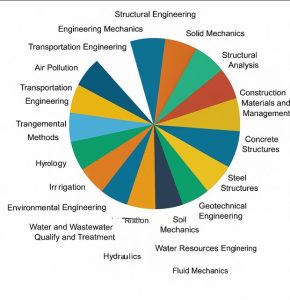
GATE Mechanical Engineering Syllabus 2026
GATE Mechanical Engineering Syllabus 2026 focuses on core topics like thermodynamics, mechanics of solids, fluid mechanics, and manufacturing processes, combined with fundamental mathematical skills. Important topics GATE Syllabus 2026 for Mechanical Engineering include:
| GATE Mechanical Engineering Syllabus 2026 | |
| Topics | Sub-Topics |
| Applied Mechanics and Design | |
| Engineering Mechanics | Free-body diagrams and equilibrium; friction and its applications including rolling friction, belt-pulley, brakes, clutches, screw jack, wedge, vehicles, etc.; trusses and frames; virtual work; kinematics and dynamics of rigid bodies in plane motion; impulse and momentum (linear and angular) and energy formulations; Lagrange’s equation |
| Mechanics of Materials | Stress and strain, elastic constants, Poisson’s ratio; Mohr’s circle for plane stress and plane strain; thin cylinders; shear force and bending moment diagrams; bending and shear stresses; concept of shear center; deflection of beams; torsion of circular shafts; Euler’s theory of columns; energy methods; thermal stresses; strain gauges and rosettes; testing of materials with universal testing machine; testing of hardness and impact strength |
| Theory of Machines | Displacement, velocity, and acceleration analysis of plane mechanisms; dynamic analysis of linkages, cams, gears, and gear trains; flywheels and governors; balancing of reciprocating and rotating masses; gyroscope |
| Vibrations | Free and forced vibration of single-degree-of-freedom systems, effect of damping, vibration isolation, resonance, and critical speeds of shafts |
| Machine Design | Design for static and dynamic loading; failure theories; fatigue strength and SN diagram; principles of design of machine elements such as bolted, riveted, and welded joints; shafts, gears, rolling and sliding contact bearings, brakes, and clutches, springs |
| Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Sciences | |
| Fluid Mechanics | Fluid properties; fluid statics, forces on submerged bodies, stability of floating bodies; control-volume analysis of mass, momentum, and energy; fluid acceleration; differential equations of continuity and momentum; Bernoulli’s equation; dimensional analysis; viscous flow of incompressible fluids, boundary layer, elementary turbulent flow, flow through pipes, head losses in pipes, bends and fittings; basics of compressible fluid flow |
| Heat-Transfer | Modes of heat transfer; one-dimensional heat conduction, resistance concept and electrical analogy, heat transfer through fins; unsteady heat conduction, lumped parameter system, Heisler’s charts; thermal boundary layer, dimensionless parameters in free and forced convective heat transfer, heat transfer correlations for flow over flat plates and through pipes, effect of turbulence; heat exchanger performance, LMTD and NTU methods; radiative heat transfer, Stefan-Boltzmann law, Wien’s displacement law, black and grey surfaces, view factors, radiation network analysis |
| Thermodynamics | Thermodynamic systems and processes; properties of pure substances, behavior of ideal and real gases; zeroth and first laws of thermodynamics, calculation of work and heat in various processes; second law of thermodynamics; thermodynamic property charts and tables, availability and irreversibility; thermodynamic relations |
| Applications | Power Engineering: Air and gas compressors; vapour and gas power cycles, concepts of regeneration and reheat. I.C. Engines: Air-standard Otto, Diesel, and dual cycles. Refrigeration and air-conditioning: Vapour and gas refrigeration and heat pump cycles; properties of moist air, psychrometric chart, basic psychrometric processes. Turbomachinery: Impulse and reaction principles, velocity diagrams, Pelton-wheel, Francis and Kaplan turbines; steam and gas turbines |
| Materials, Manufacturing, and Industrial Engineering | |
| Engineering Materials | Structure and properties of engineering materials, phase diagrams, heat treatment, stress-strain diagrams for engineering materials |
| Casting, Forming and Joining Processes | Different types of castings, design of patterns, molds, and cores; solidification and cooling; riser and gating design. Plastic deformation and yield criteria; fundamentals of hot and cold working processes; load estimation for bulk (forging, rolling, extrusion, drawing) and sheet (shearing, deep drawing, bending) metal forming processes; principles of powder metallurgy. Principles of welding, brazing, soldering, and adhesive bonding |
| Machining and Machine Tool Operations | Mechanics of machining; basic machine tools; single and multi-point cutting tools, tool geometry and materials, tool life and wear; economics of machining; principles of non-traditional machining processes; principles of work holding, jigs and fixtures; abrasive machining processes; NC/CNC machines and CNC programming |
| Metrology and Inspection | Limits, fits, and tolerances; linear and angular measurements; comparators; interferometry; form and finish measurement; alignment and testing methods; tolerance analysis in manufacturing and assembly; concepts of coordinate-measuring machine (CMM) |
| Computer-Integrated Manufacturing | Basic concepts of CAD/CAM and their integration tools; additive manufacturing |
| Production Planning and Control | Forecasting models, aggregate production planning, scheduling, materials requirement planning, and lean manufacturing |
| Inventory Control | Deterministic models, safety stock inventory control systems |
| Operations Research | Linear programming, simplex method, transportation, assignment, network flow models, simple queuing models, PERT and CPM |
GATE Electrical Syllabus 2026
GATE Electrical Syllabus 2026 covers areas such as electrical circuits, power systems, control systems, electrical machines, and analog & digital electronics. GATE Syllabus 2026 for Electrical includes:
| GATE Electrical Syllabus 2026 | |
| Topics | Sub-Topics |
| Electric Circuits: Network elements | ideal voltage and current sources, dependent sources, R, L, C, M elements; Network solution methods: KCL, KVL, Node and Mesh analysis; Network Theorems: Thevenin’s, Norton’s, Superposition and Maximum Power Transfer theorem; Transient response of dc and ac networks, sinusoidal steady-state analysis, resonance, two port networks, balanced three phase circuits, star-delta transformation, complex power and power factor in ac circuits |
| Electromagnetic Fields | Coulomb’s Law, Electric Field Intensity, Electric Flux Density, Gauss’s Law, Divergence, Electric field and potential due to point, line, plane and spherical charge distributions, Effect of dielectric medium, Capacitance of simple configurations, Biot‐Savart’s law, Ampere’s law, Curl, Faraday’s law, Lorentz force, Inductance, Magnetomotive force, Reluctance, Magnetic circuits, Self and Mutual inductance of simple configurations |
| Signals and Systems | Representation of continuous and discrete-time signals, shifting and scaling properties, linear time-invariant and causal systems, Fourier series representation of continuous and discrete-time periodic signals, sampling theorem, Applications of Fourier Transform for continuous and discrete-time signals, Laplace Transform and Z transform. R.M.S. value, average value calculation for any general periodic waveform |
| Electrical Machines | Single-phase transformer: equivalent circuit, phasor diagram, open circuit and short circuit tests, regulation and efficiency; Three-phase transformers: connections, vector groups, parallel operation; Auto-transformer, Electromechanical energy conversion principles; DC machines: separately excited, series and shunt, motoring and generating mode of operation and their characteristics, speed control of dc motors; Three-phase induction machines: principle of operation, types, performance, torque-speed characteristics, no-load and blocked-rotor tests, equivalent circuit, starting and speed control; Operating principle of single-phase induction motors; Synchronous machines: cylindrical and salient pole machines, performance and characteristics, regulation and parallel operation of generators, starting of synchronous motors; Types of losses and efficiency calculations of electric machines |
| Power Systems | Basic concepts of electrical power generation, ac and dc transmission concepts, Models and performance of transmission lines and cables, Economic Load Dispatch (with and without considering transmission losses), Series and shunt compensation, Electric field distribution and insulators, Distribution systems, Per‐unit quantities, Bus admittance matrix, Gauss-Seidel and Newton-Raphson load flow methods, Voltage and Frequency Control, Power factor correction, Symmetrical components, Symmetrical and unsymmetrical fault analysis, Principles of overcurrent, differential, directional and distance protection; Circuit breakers, System stability concepts, Equal area criterion |
| Control Systems | Mathematical modeling and representation of systems, Feedback principle, transfer function, Block diagrams and signal flow graphs, Transient and Steady‐state analysis of linear time-invariant systems, Stability analysis using Routh-Hurwitz and Nyquist criteria, Bode plots, root loci, Lag, Lead and Lead‐Lag compensators; P, PI and PID controllers; State-space model, Solution of state equations of LTI systems |
| Electrical and Electronic Measurements | Bridges and Potentiometers, Measurement of voltage, current, power, energy, and power factor; Instrument transformers, Digital voltmeters and multimeters, Phase, Time, and Frequency measurement; Oscilloscopes, Error analysis |
| Analog and Digital Electronics | Simple diode circuits: clipping, clamping, rectifiers; Amplifiers: biasing, equivalent circuit and frequency response; oscillators and feedback amplifiers; operational amplifiers: characteristics and applications; single-stage active filters, Active Filters: Sallen Key, Butterwoth, VCOs and timers, combinatorial and sequential logic circuits, multiplexers, demultiplexers, Schmitt triggers, sample and hold circuits, A/D and D/A converters |
| Power Electronics | Static V-I characteristics and firing/gating circuits for Thyristor, MOSFET, IGBT; DC to DC conversion: Buck, Boost and Buck-Boost Converters; Single and three-phase configuration of uncontrolled rectifiers; Voltage and Current commutated Thyristor based converters; Bidirectional ac to dc voltage source converters; Magnitude and Phase of line current harmonics for uncontrolled and thyristor-based converters; Power factor and Distortion Factor of ac to dc converters; Single-phase and three-phase voltage and current source inverters, sinusoidal pulse width modulation |
GATE ECE Syllabus 2026
GATE ECE syllabus 2026 primarily covers topics in digital electronics, communications, signal processing, and network theory. Key topics GATE syllabus 2026 for ECEinclude:
| GATE ECE Syllabus 2026 | |
| Sections | Topic-Wise Syllabus |
| Engineering Mathematics |
|
| Networks, Signals, and Systems | Circuit analysis: Node and mesh analysis, superposition, Thevenin’s theorem, Norton’s theorem, reciprocity. Sinusoidal steady state analysis: phasors, complex power, maximum power transfer. Time and frequency domain analysis of linear circuits: RL, RC, and RLC circuits, solution of network equations using Laplace transform, Linear 2-port network parameters, wye-delta transformation. Continuous-time signals: Fourier series and Fourier transform, sampling theorem and applications. Discrete-time signals: DTFT, DFT, z-transform, discrete-time processing of continuous-time signals. LTI systems: definition and properties, causality, stability, impulse response, convolution, poles and zeroes, frequency response, group delay, phase delay |
| Electronic Devices |
|
| Analog Circuits |
|
| Digital Circuits |
|
| Control Systems | Basic control system components; Feedback principle; Transfer function; Block diagram representation; Signal flow graph; Transient and steady-state analysis of LTI systems; Frequency response; Routh-Hurwitz and Nyquist stability criteria; Bode and root-locus plots; Lag, lead, and lag-lead compensation; State variable model and solution of state equation of LTI systems. |
| Communications |
|
| Electromagnetics |
|
GATE Syllabus 2026 Subject Wise PDF Download
Candidates can download GATE Syllabus 2026 Subject wise PDF download from Official website on https://gate2026.iitg.ac.in/. However, candidates can download GATE Syllabus 2026 provided in direct link.
GATE syllabus 2026 subject wise PDF Download is given here in table below
Also read GATE Books
GATE Exam Pattern 2026
GATE Exam Pattern 2026 including mode of Exam, duration, total papers, exam pattern, marking scheme and other details are provided here in table below
| GATE Exam Pattern 2026 | |
| Particulars | Details |
| Examination Mode | Computer-Based Test (Online) |
| Duration | 3 Hours |
| Number of Papers in GATE 2026 | 30 Papers |
| Section |
|
| Type of Questions |
|
| Design of Questions |
|
| Number of Questions | 65 Questions (including 10 questions from General Aptitude) |
| Distribution of Questions in all Papers except AR, CY, EY, GG, MA, PH, and XL |
|
| Distribution of Questions in AR, CY, EY, GG, MA, PH, XH, and XL |
|
| Total Marks | 100 Marks |
| Marking Scheme | Each correct answer in the exam will be awarded either 1 or 2 marks |
| GATE Negative Marking |
|
Also read GATE PYQs
| GATE Application Form 2026 | GATE Eligibility Criteria | GATE Participating Institutes |
| GATE Books | Top GATE Colleges in India | GATE Exam Date 2026 |
GATE Syllabus 2026 FAQs
What is the GATE syllabus for 2026?
GATE 2026 syllabus covers subjects like General Aptitude, Engineering Mathematics, and discipline-specific topics. It includes various branches like Civil, Mechanical, Electrical, Computer Science, and more, each with its own set of topics tailored to the specific field.
Can I choose more than one paper in GATE 2026?
Yes, candidates can appear for one or two papers in GATE 2026, depending on their academic background. However, it’s essential to check the eligibility and combination rules as not all combinations are allowed.
Is there any common subject in the GATE syllabus for all papers?
Yes, Engineering Mathematics is a common subject across most GATE papers, covering topics like linear algebra, calculus, probability, and differential equations.
What is the significance of GATE in terms of career opportunities?
GATE is a gateway for higher studies in reputed institutes like IITs, NITs, and IISc. It also opens doors to employment in top Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) and research organizations.
Where can I find the detailed GATE syllabus for 2026?
The detailed GATE syllabus for each subject is available on the official GATE website or through official notifications and guidelines from IITs conducting the exam.