GATE Chemistry 2009
Previous Year Question Paper with Solution.
1. The 31P NMR spectrum of P4S3 consists of
(a) a singlet
(b) a doublet and a triplet
(c) a doublet and a quartet
(d) two doublets.
Ans. (c)
Sol. P4S3



Correct option is (c)
2. The geometry around the centrla atom in CIF4+ is
(a) square planar
(b) square pyramidal
(c) octahedral
(d) trigonal bipyramidal
Ans. (d)
Sol.

3. The correct statement about the Cu-N bond distances in [Cu(NH3)6]2+ is
(a) all the bond distances are equal
(b) the axial bonds are longer than the equatorial ones
(c) the equatorial bonds are longer than the axial ones
(d) all the bond distances are unequal
Ans. (b)
Sol. In [Cu(NH3)6]2+, the geometry is distorted octahedral due to Jahn-Teller distortion and axial bond distances are larger than equatorial bond distances.
Correct answer is (b)
4. The reaction of phosgene with an excess of NH3 produces
(a) HN = C = O
(b) H2N – C (Cl) = O
(c) (H2N)2 C = O
(d) (H2N)2 CCl2
Ans. (c)
Sol. COCl2 + 4NH3
 CO (NH2)2 + 4NH4Cl
CO (NH2)2 + 4NH4Cl
Phosgene
Correct option is (c)
5. The number of metal–metal bonds in [(C5H5) Fe (CO)2]2 is
(a) zero
(b) one
(c) two
(d) three
Ans. (b)
Sol. [(C5H5) Fe (CO)2]2
TVE = 2Fe = 8 × 2 = 16 electron
2Cp = 5 × 2 = 10 electron
4CO = 4 × 2 = 8 electron
Toral = 34 electron
B = 18 × n – TVE
n = number of metal = 18 × 2 – 34 = 2
 = Number of M – M bond =
= Number of M – M bond =  = 1
= 1
Correct option is (b)
6. The coordination number of the Ba2+ ions in barium fluoride is 8. The coordination number of the fluorie ion is:
(a) 8
(b) 4
(c) 1
(d) 2
Ans. (b)
Sol. In BaF2 molecule, the coordination number Ba2+ is 8 and coordination number fluoride is 4.
Correct option is (b)
7. In the transformation of oxyhemoglobin to deoxyhemoglobin
(a) Fe2+ in the low spin state changes to Fe2+ in the high spin state
(b) Fe2+ in the low spin state changes to Fe3+ in the low spin state.
(c) Fe2+ in the high spin state changes to Fe2+ in the low spin state
(d) Fe2+ in the high spin state changes to Fe3+ in the high spin state.
Ans. (a)
Sol. The transformation of oxydemoglobin to deoxyhemoglobin Fe2+ involves change in low spin state to high spin state.
In deoxyhemoglobin, Fe2+ is in high spin state.
In oxyhemoglobin, iron of heme group bind with oxygen molecule, and become low spin
Correct option is (a)
8. For the compound

the stereochemical notations are
(a) 2Z, 4R
(b) 2Z, 4S
(c) 2E, 4R
(d) 2E, 4S
Ans. (d)
Sol.

9. The compound  is
is
(a) aromatic and has high dipole moment
(b) aromatic and has no dipole moment
(c) non-aromatic and has high dipole moment
(d) anti-aromatic and has no dipole moment.
Ans. (a)
Sol.

10. In the reaction,

the major product X is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol.

11. In the reaction

the major product X and Y are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) None of these
Ans. (b)
Sol.

12. In the reaction 
the major product X is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol.

Note : stablised phosphorous ylide form trans alkene.
Correct option is (c)
13. The most suitable reagent combination to bring out the following transformation
is

(a) PhCOCl and pyridine
(b) DCC and PhCOOH
(c) PhBr, CO and Pd(PPh3)4
(d) EtOOC–N=N–COOEt, PPh3 and PhCOOH
Ans. (d)
Sol.

14. In the two steps reaction sequence:

the major product Y is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 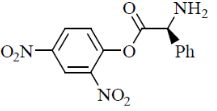
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol.

15. Among the following the system that would require the least amount of thermal energy to bring its temperature to 80ºC.
(a) 200 gm of water at 40°
(b) 100 gm of water at 20°C
(c) 150 gm of water at 50°C
(d) 300 gm of water at 30°C.
Ans.
Sol. q = 
(a) q = 200 CS (80 – 40)
q = 8000 CS
(b) q = 100 CS (80 – 20)
q = 6000 CS
(c) q = 150 CS (80 – 50)
q = 4500 CS
(d) q = 300 CS (80 – 30)
= 15000 CS
Correct option is (c)
16. Among the following, the reaction that is accompanied by a decrease in the entropy is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. If  decrease in entropy.
decrease in entropy.
In option (a) 
Correct option is (a)
17. The number of degrees of freedom of a system consisting of solid sucrose in equilibrium with an aqueous solution of sucrose is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Ans. (c)
Sol. Sucrose(s)  Sucrose (aq)
Sucrose (aq)
It is a non-reactive system.
Therefore, C = number of chemical constitute which is 2 here C = 2.
Correct option is (c)
18. The lowest allowed energy is eual to zero for
(a) the hydrogen atom
(b) a rigid rotor
(c) a harmonic oscillator
(d) a particle in a 3-dimensional box
Ans. (b)
Sol. Lowest energy equal to zero for a rigid rotor
E = BJ (J + 1) J = 0,1,23 ....
J = 0
E = B × 0 (0 + 1)
E = 0
Correct option is (b)
19. According to the Debye-Hückel limiting law, if the concentration of a dilute aqueous solution of KCl is increased 4-fold, the value of in  (
(  is the molal mean ionic activity coefficient) will
is the molal mean ionic activity coefficient) will
(a) decease by a factor of 2
(b) increase by a factor of 2
(c) decease by a factor of 4
(d) increase by a factor of 4.
Ans. (a)
Sol. 

Decrease by factor 2
Correct option is (a)
20. For the parallel first order reaction shown below

the value of k1 is 1×10–4 s–1. If the reaction starts from X, the ratio of the concentrations of Y and Z at any given time during the course of the reaction is found to be  The value of k2 is:
The value of k2 is:
(a) 1×10–4s–1
(b) 2.5×10–5s–1
(c) 4×10–4s–1
(d) 4×104s–1
Ans. (c)
Sol.

K1 = 10–4 s–1
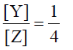

21. The correct order of  for the compounds
for the compounds 
 in the IR spectrum is:
in the IR spectrum is:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
electron density on metal decreases then M–C bond strength decreases
C–O bond strength increases
NMe3 is stronger  -donar
-donar
PX3 are  – donar as well as
– donar as well as  – acceptor
– acceptor
The  – donating ability NMe3 > PMe3 > P(OPh)3 > PCl3
– donating ability NMe3 > PMe3 > P(OPh)3 > PCl3
Hence,  – Mo (CO)3 PCl3 > Mo(CO)3 P(OPh3) > Mo(CO)3 (PMe3)3 > Mo(CO)3 (NMe3)3
– Mo (CO)3 PCl3 > Mo(CO)3 P(OPh3) > Mo(CO)3 (PMe3)3 > Mo(CO)3 (NMe3)3
Correct option is (c)
22. 2.5 g of an iron compound upon suitable treatment yielded 0.391 g of iron (III) oxide. The percentage of iron in the compound is
(a) 10.94
(b) 12.15
(c) 11.31
(d) 9.11
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
2 × 56 2 × 56 + 16 × 3
112 160
112 gm iron yield Fe2O3 = 160 gm
2.5 gm ion yield Fe2O3 =  = 3.571
= 3.571
% of iron  = 10.94
= 10.94
Correct option is (a)
23. In the reaction,  , the compounds X and Y, respectively are
, the compounds X and Y, respectively are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
24. The 1H NMR spectrum of HD consists of a
(a) singlet
(b) 1:1 doublet
(c) 1:1:1 triplet
(d) 1:2:1 triplet.
Ans. (c)
Sol. HD  1H NMR
1H NMR
Multiplicity = (2NI + 1) = (2 × 1 × 1 + 1) = 3 triplet
1 : 1 : 1
Correct option is (c)
25. The X-ray powder pattern of NaCl shows an intense cone at  using X-rays of wave length 1.54×10–8 cm. The spacing between the planes (in Å) of NaCl crystal is
using X-rays of wave length 1.54×10–8 cm. The spacing between the planes (in Å) of NaCl crystal is
(a) 1.41
(b) 2.82
(c) 4.23
(d) 5.63
Ans. (b)
Sol. 

26. Among the following, the isoelectronic and isostructural pair is
(a) CO2 and SO2
(b) SO3 and SeO3
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol.

27. Two samples have been given to you:  A physical method that can be used to identify these compounds unambiguously is
A physical method that can be used to identify these compounds unambiguously is
(a) HPLC
(b) magnetic susceptibility
(c) 13C NMR spectroscopy
(d) Mössbauer spectroscopy
Ans. (b)
Sol. Here, [NiCl2 (PPh3)2] will be paramagnetic, whereas [PdCl2 (PPh3)2] will be diamagnetic. Thus, magnetic susceptibility can be used to identify these compounds unambigously.
Correct option is (b)
28. In the reaction  , the conjugate acid-base pairs are
, the conjugate acid-base pairs are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
29. Designate the following complexes X, Y and Z as inert or labile
X = [Al(C2O4)3]3– Y = [V(H2O)6]2+ Z = [Cr(C2O4)3]3–
(a) X and Y are inert; Z is labile
(b) X and Z are labile; Y is inert
(c) X is inert; Y and Z are labile
(d) X is labile; Y and Z are inert
Ans. (d)
Sol. The complexes having d3 electronic configuration is most inert complexes.

Both are inner orbital complex, there is no low lying vacant d orbital. Hence only Y and Z are inert.
Correct option is (d)
30. In the reaction sequence:

X and Y, respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
31. The major product X (based on the preferred conformation) in the reaction

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol.

32. In the reactions,

The major products X and Y, respectively are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol.

33. In the reaction

the major product X is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
34. Reaction of m-menthylanisole with lithium in liquid ammonia and t-butyl alcohol at –33°C generates compound X as the major product. Treatment of the compound X with dilute sulphuric acid produces compound Y as the major product. The compounds X and Y, respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. 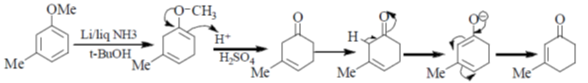
35. The number of signals that appear in the broad-band decoupled 13C NMR spectrum of ortho-, meta-and para-dichlorobenzenes, respectively, are
(a) 3, 4 and 2
(b) 3, 3 and 2
(c) 4, 4 and 2
(d) 3, 4 and 4
Ans. (a)
Sol. 

36. In the reaction sequence,

the structure of the major product Z and the overall yield for its formation from the ketone X, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol.


Correct option is (b)
37. In the reaction sequence

the major product respectively, are:
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol.


38. In the reaction sequence the major products X and Y, respectively are

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 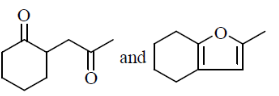
Ans. (c)
Sol.

39.
39. In the reaction sequence

The major products X and Y, respectively are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
40. In the photochemical reaction

formation of the compound X can be inferred by the disappearance of the 1H NMR signal at 1H NMR spectrum of the starting material:

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
The signal of –CHO proton disappear at 9.7 ppm
Correct option is (a)
41. The half-life (t1/2) for the hydrolysis of an ester varies with the initial concentration of the reactant ([E]0) as follows:
[E]0 /10–2 mol L–1 5.0 4.0 3.0
T1/2 /s 240 300 400
The order of the reaction is:
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Ans. (c)
Sol. 

n = 2 Order of reaction is 2
Correct option is (c)
42. The fluorescene lifetime of a molecule in solution is 10 ns. If the flurosence quantum yield is 0.1, the rate constant of fluroscene decay is:
(a) 1×109 s–1 .
(b) 1×108s–1
(c) 1×107 s–1
(d) 9×107 s–1
Ans. (c)
Sol. 

Correct option is (c)
43. The fundamental vibrational wavenumbers for H2 and I2 are 4403.2 cm–1 and 214.5 cm–1, respectively. The relative population of the first excited vibrational states of these two molecules compared to their respective ground states at 300 K are respectively.
(a) 6.75 ×10–1 and 3.57 × 10–1
(b) 6.75 × 10–1 and 3.57 and 3.57×10–1
(c) 3.57 × 10–6 and 6.75 × 10–1
(d) 3.57×10–1 and 6.75 × 10–1
Ans. (b)
Sol. 



44. The degeneracy of a quantum particle in a cubic box having energy four times that of the lowest energy is
(a) 3
(b) 6
(c) 1
(d) 4
Ans. (c)
Sol. 12h2/8ml2 ——————————— (222)
11h2/8ml2 ——————————— n = (311) (131) (113)
9h2/8ml2 ——————————— n = (221) (122) (212)
6h2/8ml2 ——————————— n = (211) (121) (112)
3h2/8ml2 ——————————— nx = 1, ny = 1, n2 = 1


45. The rotational Raman spectrum of 19F2 shows a series of Stokes lines at 19230. 769 cm–1 , 19227.238cm–1 and 19223.707 cm–1. The rotational constant for 19F2 in GHz is:
(a) 26.484
(b) 52.968
(c) 105.936
(d) 3.531
Ans. (a)
Sol.

4B = 19230.769 – 19227.238
4B = 3.531
B = 88275 cm–1
B = 0.88275 cm–1 × c = 0.88275 × cm–1 × 3 × 1010 cm/sec
B = 26.484 × 109 Hz = 26.484 GHz
46. The de-Broglie wavelength for a He atom travelling at 1000 ms–1 (typical speed at room temperature) is
(a) 99.7×10–12m
(b) 199.4×10–12m
(c) 199.4×10–18m
(d) 99×10–6m
Ans. (a)
Sol. 

47. Given that the standard molar enthapies of formation of NO(g) and NO2 (g) are, respectively, 90.3 kJ mol–1 and 33.2 kJ mol–1, the enthalpy change for the reaction 2NO(g) + O2 (g) (g)  2NP2 (g) is
2NP2 (g) is
(a) 16.6 kJ
(b) –57.1 kJ
(c) –114.2 kJ
(d) 57.1 kJ
Ans. (c)
Sol. 2NO(g) + O2 (g)  2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)

Correct option is (c)
48. Among the following, the equilibrium which is NOT affected by an increase in pressure is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. When  = 0 then pressure has no effect on equilibrium.
= 0 then pressure has no effect on equilibrium.
In option (d);  = 4 – 4 = 0
= 4 – 4 = 0
Correct option is (d)
49. The free energy change of 1 mole of an ideal gas that is compressed isothermally from 1 atm to 2 atm is:
of 1 mole of an ideal gas that is compressed isothermally from 1 atm to 2 atm is:
(a) RTln2
(b) –2RT
(c) –RTln2
(d) 2RT
Ans. (a)
Sol. 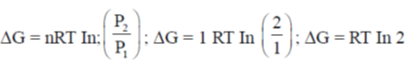
50. Two liquids B and C form an ideal solution. In the figure below, the vapour pressure P of this solution is shown as a function of the mole fraction XB, of component B.

Given a state of this vapour-liquid mixture whose overall composition corresponds to point E in the figure, the mole fractino of B in the vapour phase is approximately.
(a) 0.25
(b) 0.53.
(c) 0.65
(d) 0.80
Ans. (a)
Sol. 
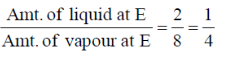
Common data for Q. 51 and Q. 52:
Treatment of W(CO)6 with 1 equivalent of Na(C5H5) in THF solution gives the ionic compound M. Reaction of M with glacial acetic acid results in product N. The 1H NMR spectrum of N displays two singlets of relative intensity 5:1. When N is heated, hydrogen gas is evolved and O is produced; O may also be prepared by refulxing W(CO)6 with cyclopentadiene and H2 is also produced. Treatment of O with an equivalent of Br2 produces P. (Use the 18 electron rule as your guide).
51. The compounds M and N, respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
52. The compounds O and P, respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Sol. 

Correct option is (a)
Common data for Q. 53 and Q. 54.
An organic compound X(C9H10O) exhibited the following spectral data.
IR : 1680 cm–1
1H NMR :  (2H, d, J 7.5 Hz), 7.2 (2H, d, J = 7.5 Hz), 2.7 (3H, s) and 2.4 (3H, s) compound X on treatment with m-chloroperbenzoic acid produced two isomeric compounds Y (major) and Z (minor)
(2H, d, J 7.5 Hz), 7.2 (2H, d, J = 7.5 Hz), 2.7 (3H, s) and 2.4 (3H, s) compound X on treatment with m-chloroperbenzoic acid produced two isomeric compounds Y (major) and Z (minor)
53. Compounds Y and Z, respectively, are
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
5(one ring + 4 double bond)


Correct option is (b)
54. Compound Y and Z can be differentiated by carrying out basic hydrolysis, because
(a) Y produces 4-methylphenol and Z is unaffected.
(b) Y produces 4-methylpheno and Z produces 4-methylbenzoic acid.
(c) Y is unaffected and Z produces 4-methylbenzoic acid.
(d) Y is unaffected and Z produces 4-methylphenol.
Ans. (b)
Sol. 

Correct option is (b)
Common data for Q. 55 and Q. 56
Charater table for the point group C2v is given below:

55. The reducible representation corresponding to the three translational degrees of freedom,  is:
is:
(a) 3, 1, 1, 1
(b) 3, –1, 1, 1
(c) 3, –1, –1, –1
(d) 3, 1, –1, –1
Ans. (d)
Sol. 


Correct option is (d)
56. The asymmertric stretching mode of the H2O is shown below. The molecular plane is yz and the symmetry axis of H2O is z.

This vibration transforms as the irreducible representation
(a) A1
(b) B1
(c) A2
(d) B2
Ans. (b)
Sol. 
In asymmtric stretching C2 is absent only molecular plane is present. So, irreducible representation corresponding to B1.
Correct option is (b)
Linked Answer type Q. 57 and Q. 58.
Triphosphazene is prepared by reacting X and Y in equimolar ratio at 120–150°C using appropriate solvents
57. The reaction X and Y, respectively, are
(a) PCl3 ; NH3
(b) PCl5 ; NH3
(c) PCl5 ; NH4 Cl
(d) PCl3 ; NH4 Cl
Ans. (c)
Sol. 
Correct option is (c)
58. The structure of triphosphazene is
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (d)
Sol. Correct option is (d)
Statement for Linked Q. 59 and Q. 60:
In the reaction mechanism given, 
'k' s represent rate constants, 'EA's represent activation energies, and k2>>k3
59. The overall rate constant (koverall) for the formation of P can be expressed as
(a) k1k3/k2
(b) k1
(c) k1/(k2+k3)
(d) k1|(k2–k3)
Ans. (a)
Sol. 


Correct option is (a)
60. The overall activation energy (EA,overall) for the formation of P can expressed as
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans. (c)
Sol. 


Eoverall = Ea1 + Ea3 – Ea2
Correct option is (c)
